Dominate search results with your SEO dream team by Edna Chavira
Written on April 19, 2024 at 11:44 am, by admin

Ever wondered how to structure an SEO team for unparalleled success? Join us on Tuesday, April 23rd for this webinar where our panel will guide you through the proven strategies to build a dynamic and scalable SEO program.
You’ll discover how a well-structured team can overcome and outperform unpredictable algorithm updates and dive into the art of determining the ideal SEO team structure (and where SEO should sit) that aligns with your business goals and ensures optimal collaboration between departments.
RSVP today for Beyond the Search Bar: Crafting an Impactful SEO Team Structure and Defining its Place in Your Organization and uncover the secrets to building your dream SEO team.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
7 ways to elevate your responsive search ads
Written on April 19, 2024 at 11:44 am, by admin
While Google’s responsive search ads (RSAs) have come a long way from the simple text ads of the past, there are still plenty of opportunities to optimize and take your PPC performance to new heights.
Let’s dive into seven proven strategies that can help you elevate your Google responsive search ads game.
1. Less is sometimes more
We’re starting with a concept rather than a feature here, but just because you can add 15 headlines and four descriptions doesn’t mean you should also populate all of those slots. A few reasons why:
- You could be diluting the key USPs with filler content, just so the ad strength improves (not a quality indicator).
- So often, you try to scrap the website content in a desperate attempt to reach title double figures.
- However, the more copy added, the less your primary messaging will be shown. Always aim for quality over quantity and resist Google’s pressure to add more.
- The more titles/descriptions used in an RSA, the more ad variations there are for Google’s algorithm to use.
- That’s all well and good for campaigns and ad groups that have big budgets and big volumes.
- Still, for small campaigns with smaller keyword demands, Google and Bing (especially Bing) won’t have enough impressions to run all the possible ad variations enough times for a conclusive result.
- Learning periods will be ongoing and performance insights will be limited. Do you ever check the ad asset report for an RSA and see “pending”? This is why.
- Less titles and descriptions can also give you better scope to do manual testing, as there are fewer variations in play.
- As the above point applies to Google automation testing, it applies to the A/B tests we carry out, which we will go into more detail shortly.
2. Keyword insertion
This is a really useful way of making your ads more relevant and improving your quality score. When applied, Google will populate the RSA with whatever keyword your search term triggered the ad for.
You can also add copy before and after the keyword insertion to tailor the message. For example:
- Your title could read “Buy {keyword insertion: {Nike Running Shoes} Today.”
- The keyword will appear between “Buy” and “Today.”
If the keyword triggered pushes the character limit over, Google will use the fallback copy you included, “Nike running shoes” in the above example.
It should not be used in every circumstance, as it can get messy when overused. And you are in danger of the ad not reading right.
This is especially true in consolidated ad groups with more keywords. Less control with more keywords eligible to appear in the keyword insertion.
Extra word of caution: Never use this for competitor keyword campaigns.
3. Countdown insertion
This is a really cool feature and an absolute essential for your sale or event ads. Including a countdown timer is such an effective way to add urgency to your RSAs.
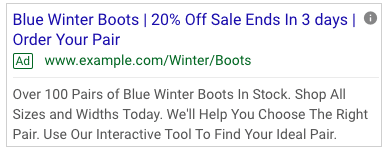
You can customize how many days in advance you’d like the timer to begin. As with the keyword insertion feature, you can include copy before and after insertion. For example:
- “Sale Ends in {countdown yyyy/mm/dd}.”
Even when there is less than a day before the end of the countdown, Google tells you to the second how long you have left. Very eye-catching for users.
4. Ad pinning
Not happy with giving Google the control to put your copy in any order that suits them? Well, then pinning is the answer.
This allows you to tell Google what title and description you want to remain constant in your ad and in which position. You can also pin multiple headlines and descriptions in the same position, which Google will alternate.
Your ad strength will suffer using pins, as Google doesn’t like not being in control. But advertisers sometimes just need the ability to decide what order the copy goes in.
For example, putting your product in the first two titles (long name) and including the price as the final title is not ideal if Google decides to mix that order, even if the algorithm thinks it has a better CTR.
I’d recommend testing two RSAs at once for ad groups with high volume. Use the same copy, but one with pins and one without. Test yourself against the algorithm.
Remember, Google often prioritizes RSA variations based on CTR, but if the objective of the ads is conversion-based, then you should judge the results toward conversion rate, CPA or ROAS instead.
5. Ad experiments
As Google will often prioritize the best CTR performance in ads, if you are testing two RSAs in the same ad group, then they will quickly favor one and show it more often.
Experiments are what you want if you want a fairer, less biased testing framework.
The experiment feature can effectively test different keywords, landing pages, bid strategies, etc. Testing ads is another feather in its cap.
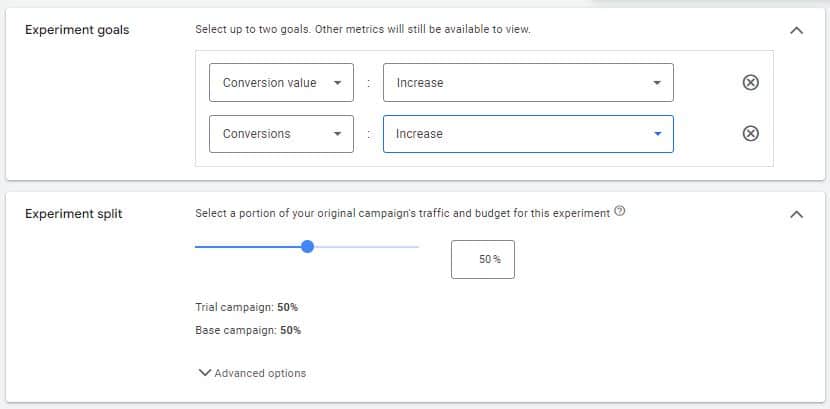
You can set up experiments to show each ad evenly at 50/50 over a selected time period (currently maxed out at 64 days). During setup, Google will duplicate your campaign into a test version. You make whatever changes to the RSA you need to, then just schedule a start date.
Once the test begins, you can access a testing dashboard within the experiment tab that compares control and test campaigns.
When setting up the experiment, you will tell Google your two performance priorities, so the dashboard will focus its reporting on those metrics.
6. Campaign-level headline and description assets
This is the newest feature in the list and, as of this writing, is still in beta. It’s a great addition designed for use during a specific period (e.g., a sale or an event).
At the campaign level, you can schedule up to three headlines and two descriptions to appear in all of the campaign’s RSAs rather than updating all of your ads individually.
If messaging is a priority, you can also pin these extra assets and schedule a start and end date.

They are ideal for large Search accounts with a high volume of RSAs that require frequent copy changes to highlight promotional periods.
What could’ve taken hours to regularly update, schedule and revert back to the original copy now takes only a few minutes. Preparing for Black Friday might not seem as daunting this year.
7. Ad variations
This is probably the most underutilized feature for RSA ads. Experiments are the most common A/B testing framework. Still, if you want to test specific titles or descriptions against other variants (as opposed to RSA vs. RSA), this is the ideal solution.
This is very cool for creating tests at a forensic level. If you have a legacy USP scattered across multiple RSAs (e.g., “Free Shipping Available”) but are thinking of replacing it with a similar but refreshed take (e.g., “Free shipping when you spend over $50”), then you simply select the “Find & Replace” variation type, input the original copy and replace with the new.
Just like setting up experiments, you select the start and end date, how much the experiment split is (which for me is always 50%) and then create. There are other types of ad variations that can update whole headlines and descriptions, as well as URLs, but I would use find and replace more commonly.
What about AI content?
I couldn’t go through the whole article without mentioning the hottest industry topic: AI. So, I thought it deserved its own bonus section.
Now, the truth is that the practical application of AI for RSAs lies outside of the advertising platform (Performance Max asset group copy is a different story with the new generative AI feature).
One of the first PPC use cases of ChatGPT, when it came on the scene, was generating additional and alternative creative for RSAs based on expanding the existing copy.
The danger is being too reliant on AI for content. Yes, ChatGPT, Gemini and the rest are great tools for carrying the creative burden. However, using AI to create the majority of the copy can lead to generic output or even a separation away from the brand identity if your prompt engineering isn’t up to scratch.
To strive toward compelling ad copy, simplicity is often the best method, so try not to overcomplicate the process. I’ve found the best use is identifying the best-performing titles and descriptions (hopefully, most of the ad asset report data isn’t pending, so you can see these insights) and using AI to expand and enhance the poor performers with alternative variations.
Lean on AI and use it to generate fresh ideas, but don’t rely on it. Remember, you will know the brand and the USPs better than AI. Humans still have a use, after all.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
How to set and manage PPC expectations for teams and stakeholders
Written on April 19, 2024 at 11:44 am, by admin

Have you ever been in a situation where not everyone was on the same page?
It happens often in the workplace and usually is caused by different expectations among stakeholders.
Here are some ways to set and manage expectations for PPC clients and agency teams.
Outline expectations during the sales process
Setting expectations at the beginning of a client engagement or project is crucial for success.
For advertising agencies, the time to set expectations is before the advertiser even becomes a client – during the sales process.
Giving the client an idea of how your team operates will help you both decide if the relationship is a good fit.
For example, does your agency have an account or media lead who oversees the client relationship, or do individual practice leads handle the relationship? Or is it a hybrid? Who is the main point of contact?
Be clear about how your team operates generally while you’re still negotiating.
Dig deeper: How to build and maintain client trust in your agency
Agree on parameters in the statement of work
It’s critical to lay out the engagement parameters in the statement of work.
The clearer you can be about the parameters of the relationship and how it will operate, the better you can manage expectations once you’re actually doing the work.
Agree on what work will be performed
What services will you be providing to the client? Here are some common agency services:
- Paid search
- Paid social
- SEO
- Programmatic and display advertising
- Traditional media (print, out-of-home, etc.)
- Website or landing page development
- Analytics
- Strategy development
- Revenue operations/CRM work
- Organic social management
- Creative design
This is only a partial list!
Agencies can offer a wide variety of advertising and marketing services.
Some agencies provide strategy and execution of the services listed above and some only provide consulting, with the client responsible for implementation. Spell out what work you intend to perform.
If you’re not clear in the statement of work about what work you’re performing, clients will ask you to do work that you’re not staffed for.
Make it obvious what’s in scope and what isn’t. Be detailed.
It’s impossible to list every possible scenario in a statement of work – and that’s why it’s crucial to be clear about the services the agency will handle.
Tell the client what work is in scope and be clear that anything else is out of scope.
For example, how many search engines will you manage for paid or organic search? How many social engines will you advertise on? Which ones? Are analytics services included? If not, who handles that troubleshooting? What about CRM?
For B2B advertisers, closing the loop between the initial website lead and down-funnel CRM actions is an important piece of the puzzle. Are you prepared to provide these services, or will the client be responsible for this work?
The same thing goes for landing page optimization and development.
Not being able to create optimized landing pages can be a performance blocker that can ultimately doom your relationship with the client. Be clear about who owns this responsibility.
By outlining who is responsible for CRO and landing page optimization, you can help stave off disappointment down the road.
Meeting and reporting cadences
Another aspect of client service to deal with during the sales process is deliverables and cadences.
How often will you meet with the client? Will the meetings be held online, or in person? Who from the agency will attend?
Meetings can become a giant time suck, yet they’re also necessary. Be thoughtful about how to make them efficient for both the agency and the client.
Reporting is another deliverable to address in the statement of work.
What types of reporting will be provided and on what cadence? Will you use Looker dashboards, PowerPoint reports, QBRs, or all three? How will you handle ad-hoc reporting?
Dig deeper: 3 steps for effective PPC reporting and analysis
Response times and client communications
You’ll also want to agree on client communications.
How will day-to-day communication be handled? Will you use email, instant messaging (IM) platforms like Slack or Teams, project management boards like Asana or Trello, or a combination of all of these?
What response times should be expected?
One pitfall of using IM for client communications is that everyone starts to expect instant replies. That’s neither feasible nor productive for anyone.
Agree with your clients that regular communications will be responded to within 24 hours.
For urgent messages, perhaps a 6-hour response time is reasonable. Agree to this ahead of time – that way, no one is disappointed.
Think too about how easy it will be to search for relevant communications later.
I find it much more difficult to find messages and topics in Slack than email, although Slack is easier to organize into channels. Each has pros and cons! Think this through before you engage with the client.
Account staffing
Every statement of work should include a staffing plan. You don’t need to name names, but list the roles and percentage of time each role will be allocated to the engagement.
For example, staffing on a large paid search account might look like this:
- Director – 5%
- Manager – 50%
- Analyst – 25%
Being clear about roles and percentage allocation helps clients understand who their key contacts are and how much time they will spend working on the account.
Dig deeper: Client onboarding and offboarding: The PPC agency’s guide
Dealing with unexpected issues
Unforeseen challenges can arise on an account. Perhaps the client’s conversion tracking breaks, or they need help spinning up a landing page when that’s normally something they would handle themselves.
Outline in the SOW how you’ll handle issues that would normally be out of scope.
Will you charge an hourly rate? Will a change order or new SOW be required?
Good agencies will often pitch in and help without compensation. That’s part of being a good business partner.
Still, it’s important to set expectations on out-of-scope work to ensure the engagement remains profitable.
Managing expectations during the engagement
Once the contract is signed, the work begins!
Now is the time to manage expectations.
It’s important on kickoff calls or meetings to establish your rules of engagement.
Reinforce how you will communicate, meeting cadences, turnaround times and other key service-level agreements (SLAs). Getting agreement from the client and buy-in on both sides is critical.
An effective way to get everyone’s buy-in is to whiteboard the rules during the kickoff, either virtually or in person. Then, take time to discuss the rules and hear all perspectives.
Be willing to add items you may not have thought of initially, or to adjust to meet everyone’s needs. Just make sure you can still deliver in the time frame you agree to.
Once you’ve aligned on the rules, distribute them to all stakeholders.
One agency I worked at printed and laminated the rules of engagement for each client. They shared a copy with everyone working on the account, both internally and client-side.
While this may sound quaint in 2024, it’s effective – a physical reminder stakeholders can keep at their desk and easily review at any time.
The rules of engagement could also be in an online document that’s pinned to a Slack or Teams channel.
It’s important to reiterate that getting everyone’s buy-in is key here.
One of Dale Carnegie’s principles in “How to Win Friends and Influence People” is to “Let the other person feel that the idea is his or hers.”
It’s important to remember this principle when establishing the rules of engagement with clients. If clients have a hand in developing the rules, they’ll be more likely to follow them.
Dig deeper: How to retain clients in PPC
How to deal with issues during the engagement
Inevitably, issues will crop up during the engagement that require a review of the SOW.
The client might ask for more meetings than you’ve contracted for.
Or they start to expect faster turn times on the work you’re delivering.
It’s tricky because, on the one hand, you want to do everything you can to keep your client happy.
On the other hand, your agency needs to be profitable.
Think carefully about whether you should accommodate the client’s request or push back.
There are pros and cons to each approach.
If you’ve established ground rules and SLAs in the contract process, it’s not wrong to gently remind the client of what you agreed to.
In this case, I’ll usually say something like, “We understand how important this launch is for your business. Our contract stipulates a 5-day lead time for new campaign launches. Given the urgent timing of this campaign, we can aim to deliver it in 2 days. We’ll have to reprioritize some of your other work to accommodate this and we’re happy to do so to help you meet your goals.”
A statement like that does several things.
- It acknowledges the importance of the ask to the client’s business.
- It reminds them of the lead times you’ve laid out in the contract.
- It accommodates their ask, while also pointing out the ramifications of compressing the timeline.
- It reinforces the client-agency partnership in the last statement: “we’re happy to do so to help you meet your goals.”
Making exceptions for clients is part of being a good partner. But if the exceptions start to become a regular thing, you’ll want to give a more forceful reminder of the rules of engagement and you may want push back.
Renegotiating the contract is another option.
For example, you could add staff to the account that would enable faster turn times – at an additional cost.
Or you could charge the client the hourly rates you provided for in the contract.
If you’ve set expectations clearly in the beginning, you have a good chance of avoiding a big mismatch between your reality and the client’s.
Clear expectations make for profitable relationships for everyone!
Dig deeper: 6 tips to build PPC client relationships
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Brave Search unveils AI answer engine
Written on April 18, 2024 at 8:44 am, by admin
Brave Search introduced a new AI answer engine called Answer with AI. It will produce AI-generated answers “synthesized” from multiple sources for any query.
What is Answer with AI. Answer with AI, as the name suggests, uses AI to generate answers to queries directly in the search results. This new Brave Search feature appears above the organic search results.
The format varies slightly, depending on the query type. At the bottom, Brave includes a section called Context, underneath which Brave links to the sources it used to generate its answer. Based on a small number of searches I conducted, Brave tends to pull most of its answers from the top-ranking pages.
It follows on from Brave’s AI Summarizer feature, introduced last year.
How Answer with AI works. When a user enters a query, Brave is using large language models (LLMs), primarily Mixtral 8×7B and Mistral 7B, data from its search results and RAG (retrieval augmented generation) to generate answers nearly instantly.
When will users see Answer with AI. For informational, question-like queries, Answer with AI will be the default experience. For other query types (navigational, commercial, transactional), Answer with AI will be optional – you will click on an Answer with AI button.
What it looks like. Here’s an example search for [what is after gen z]:
And here’s what it looks like for a vanity search:
But it’s not perfect. It thought I was the same person/entity as the former Major League Baseball player who shares my name.
Brave Search size. Brave Search has an index of 20 billion webpages, has more than 1 billion location-based schemas and serves:
- 27 million queries per day.
- 10 billion queries per year.
Answer with AI availability. It is available on all platforms (desktop and mobile) for all searches in English, French, German, Italian and Spanish. Searching in any other languages may return answers in English language.
What Brave is saying about AI answers. The big concern among SEOs and content creators is how AI answers in the search results could potentially impact the amount of traffic search engines send to websites. Brave addressed this concern, telling Search Engine Land:
- “Brave, as both a browser and search engine, is aware of these challenges. Consequently, we will be monitoring and quantifying the impact of AI-generated content on site visits, and eventually will address the disruptions that could be caused by the drop in traffic.”
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Tracking in 2024: Where we are and how to prep
Written on April 18, 2024 at 8:44 am, by admin
Remember how painful iOS 14 was for performance marketers? An even more seismic change is looming, and way too many marketers are still unprepared.
Yes, I’m talking about the impending death of third-party cookies. If you’re reading this article, this is probably the 1,000th time you’ve heard it mentioned.
And that might be part of the problem: “the death of cookies” could now be one of those familiar phrases you skim over without understanding the depth of its ramifications.
If you’re a little unclear on what kind of havoc “the death of cookies” is going to wreak in your campaigns, stay with me for a few minutes as I tackle:
- What’s changing from a technical perspective.
- What’s changing from a marketing perspective.
- 4 real steps you need to take ASAP to start planning.
What’s changing from a technical perspective
First, let’s be clear: we’re talking about the death of third-party cookies, not first-party cookies. You own first-party cookies and the data they collect, which won’t be impacted by the Chrome update.
Third-party cookies, which pass data from your website to external parties (like ad platforms) to your site to paint a picture of the user and user behavior, are what’s disappearing.
If this sounds familiar, it’s because that’s exactly what happened with iOS 14.
In that update, Apple’s “App Tracking Transparency” introduction prevented companies from tracking user behavior across third-party apps. Advertising platforms (particularly Facebook) suddenly couldn’t help advertisers understand what users were doing after engaging with their ads.
Cookies, whether first-party or third-party, are snippets of code saved by the browser or app to the user’s device. They contain user and session identifiers, ad click IDs, timestamps and functions (e.g., whether you’re logged into an app).
In short, they are (or were until recently) the most common way to identify and track users, and they’re about to disappear from Chrome (which is following Firefox and Safari in doing so).
If you’re using pixels, UTM parameters outside of a first-party environment, GTAG (ask your analytics team), or other tracking based on – and stored in – browsers, you’re in for a world of transition.
What’s changing from a marketing perspective
It might be easier to list what isn’t changing, but here’s a quick list of the biggest hits:
- Attribution is changing. Lots of advertisers still rely on click-to-action, last-click attribution, and that data is about to get torpedoed. That could actually have a huge silver lining if it forces advertisers en masse to adopt more holistic measurement strategies that consider the entire user journey.
- Tracking performance is changing. If you’re in love with the ability to see performance at the ad and/or keyword level, maintaining some level of visibility will require some updates to most currently adopted tracking set-ups.
- Targeting is changing. Utilizing pixels for retargeting efforts, and accuracy of in-platform audiences are likely going to shift. We’re going to face steep challenges in understanding how to identify valuable users and to create ads that are relevant to them.
- Data collection is changing. The more first-party data we can collect and own, the more control we’ll have over understanding and engaging our users. If you don’t have a plan for collecting and ingesting more first-party data, you’re going to be at a huge disadvantage.
Dig deeper: 7 paid media reporting tips when tracking is messy
Given all of that, you can hopefully now realize that the time to start planning was about a year ago – and if you’re behind the curve, you’d better keep reading.
4 real preparation steps to take ASAP
I break this down for my clients into four buckets:
- CRM cleanliness
- Data collection
- Platform tracking solutions
- Server-side hosting
1. Focus on CRM cleanliness
At the very least, you should be able to reference your CRM data to understand your users’ point of entry and identify your most valuable users.
Make sure you have a plan to assess your data cleanliness, your reports, and your dashboards and you can get things in good enough shape to trust what your first-party data is telling you. Work to
2. Tune up your data collection
First-party data will become even more important as data from third-party sources erodes.
Make sure your ad campaigns, organic campaigns, owned properties, etc., are fully maximized to collect first-party data and have a plan to use it in your campaigns (email, SMS, retargeting, lookalikes, etc.).
3. Implement platform solutions
Get extremely comfortable with Google’s Enhanced Conversions, Meta and LinkedIn’s conversions APIs, and whatever monikers you’ll see other platforms use. They help ensure that ad algorithms can track valuable actions both online and offline, which is essential for future-proofing your tracking efforts.
(Bonus points if you combine platform solutions with first-party data to teach the platform algorithms to find your best users via offline conversion tracking.)
4. Go server-side
Analytics and data stored in servers you control (as opposed to browsers that can change their rules at any time) are one big hedge against cookie erosion.
Implement initiatives like server-side GTM and start researching CDP (customer data platform) options like Segment and Tealium to take at least partial ownership of your data and analytics.
Winning strategies for a data-driven, privacy-first future
If you need a little good news after reading all of that, I have a couple of tidbits for you.
- Cookie-based tracking had big inherent flaws. This shift is an opportunity for the industry to reevaluate tracking, measurement and attribution methodologies.
- It’s very unlikely that the marketing industry will face anything as transformative in the near future. You might carry some battle scars from this transition, but if you can get through it with your job and brand intact, you’ll be a better marketer for it.
- Lastly, we’re all in the same boat, figuring this out together.
Dig deeper: 3 ways search marketers can prepare for the big cookie crumble
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
How to survive the search results when you’re using AI tools for content
Written on April 18, 2024 at 8:44 am, by admin
The rise of AI content creation has been a game-changer – for better or worse.
On the one hand, you have benefits like:
- Improved efficiency.
- Powerful content ideation.
- Rapid research.
These efficiencies have allowed SEO programs to move faster and produced cost savings, added value and, in some cases, more revenue.
On the other hand, you have issues like:
- Generic content.
- Poorly written text.
- Ineffective content.
These drawbacks can lead to a bad user experience, lost rankings or deindexing from the search results.
As more and more people eagerly adopt AI content tools, it seems two schools of thought are emerging around how to use AI:
- AI enthusiasts believe that with the right tools, AI can crank out content ready to publish faster than you can say, “Google spam update.”
- Traditionalists argue that AI is a tool, and without the insight of a human writer, the content lacks the depth and expertise needed to succeed.
I fall into the second camp. However, AI tools are rapidly evolving, and some tout you don’t even need to edit the content to be ready to publish and rank.
They are more likely to mean “publish and not get caught” because if ranking were that easy, everyone would be No. 1. The risk is on you.
Next, let’s explore these two schools of thought around AI content creation.
The AI-only approach
While it’s true that AI tools are getting more sophisticated by the minute, that doesn’t mean we should act too soon.
Brands that acted hastily have experienced consequences – from embarrassing content that led to PR snafus (like MSN, Sports Illustrated and others) to being removed from the Google index in Google’s March 2024 updates.
While we don’t know which AI tools those sites relied on, we know it went badly for them.
Here’s a fun test: Go to ChatGPT and start the stopwatch timer on your phone. Copy and paste the following prompt:
- “Write an article that discusses “how to repair a broken light switch,” list several types of light switches, add some statistics about the usefulness of multi-way and dimmer light switches and add a one-question FAQ section.”
 A portion of a ChatGPT-generated article on how to repair a broken light switch.
A portion of a ChatGPT-generated article on how to repair a broken light switch.Took about a minute or less? Those who think they can earn top rankings out of millions of results with this approach to creating content with little to no human intervention will fail.
There are more sophisticated AI content tools out there. And many of them are intriguing. I question how many are just better at wording and are targets for a future Google trap.
We must be cautious about using these tools, regardless of how good they appear or their promises – until we figure out the best way to engage with them and prove they can withstand Google’s algorithms.
It’s no secret that Google’s March 2024 updates targeted websites abusing AI content.
My thoughts:
- AI tools can help create content but avoid violating Google’s spam policies. The content must include unique elements such as expert perspectives or personal experiences.
- When using AI tools, avoid merely stitching together information from search results without adding extra value.
- It’s acceptable to use AI tools to perform research, create unique outlines, provide content summaries and even give chunks of text to be edited (so long as you can fact-check its validity), but avoid plagiarism and generic content.
You’re playing with fire if you’re going “all in” on an AI content tool without a good process.
Dig deeper: AI for SEO content creation: 5 real-world examples
The collaborative approach
If you want content that can survive Google algorithms and offers something valuable to your readership, and you also want the efficiencies that AI can offer, you need:
- Professional writers and editors.
- The right AI tools.
- A good process.
It sounds simple – because it is!
Don’t completely remove writers and editors from your marketing projects. Instead, hire writers and editors who know how to use the right AI tools the right way (read: with discernment).
For example, AI tools helped with the following in the article you are reading right now:
- Brainstorming article titles (which ultimately weren’t used but helpful in getting the ideas flowing).
- A content outline (about 50% of the suggestions were considered and the rest was scrapped).
- Summarizing some of my previously published content into a list of ideas to edit or expand on.
So repeat this mantra: “Only the quality content survives,” and then follow these rules as you add AI tools to your content creation process:
- Produce user-centric, unique and valuable content that builds trust, authority and credibility in your niche.
- Focus on creating helpful, people-first content that addresses the needs of your audience.
- Ensure your content adds something unique to the conversation, avoiding a “copy/paste/reword” approach.
What does the collaborative process look like? I’ve written about this in my AI content creation beginner’s guide, and here are some tips:
Prework
Develop a solid process for prompting AI tools to generate content, including defining the persona, target audience, tone of voice and format of the content.
Content creation
In the content creation phase, use the AI tool to generate ideas, create outlines, do research, provide summaries, create intros and/or conclusions to be edited and, in some cases, create a first draft.
When I say first draft, I mean it’s a start. Without a doubt: Do not publish any AI content verbatim unless you want to risk a hit from Google’s spam policies.
Put in the work to make it unique to your brand, your perspective and differentiate it from what’s out there in some way.
Editing
Many times, the writing and editing processes happen at the same time. Regardless of when you do it, make sure that when you are creating the content, you do the following:
- If large parts of AI content are baked into the final piece, the editor must use an AI detector and/or plagiarism tool to ensure everything looks good. And then have them look again. When you use AI enough, you will recognize the phrases and wording common to an AI writer.
- Fact-check by making sure the statements, the data and anything else AI generates is factual and what the brand would get behind.
- Review the content for tone of voice synergy, grammar and adherence to brand guidelines.
All these things take time. So, you and your team must know if AI saves you time and money in the long run. If not, then maybe there’s a different way you should be using it.
The balancing act between automation and collaboration
Things will change – Google’s algorithms will change and strategies will change. So, the advice I’m sharing now is what I believe to be true for the foreseeable future.
However, a solid content strategy puts quality first, which will never change.
While AI tools offer efficiency in content creation, they are tools, not solutions. The key is integrating AI tools into the writer’s process, not replacing the writer.
Continue to provide value to your audience and adhere to Google’s guidelines to ensure your content stands the test of time.
Dig deeper: 7 reasons why your AI content sucks (and how to fix it)
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
U.S. search ad revenues hit record $88.8 billion in 2023
Written on April 18, 2024 at 8:44 am, by admin

Paid search advertising revenues reached a new high in 2023 – though annual growth continues to slow, according to a new report.
In total, search accounted for $88.8 billion of a record $225 billion in U.S. digital advertising revenues, according to the IAB Internet Advertising Revenue Report: Full Year 2023, conducted by PwC. That figure represents a $4.4 billion increase over 2022.
Why we care. Paid search becomes more expensive and challenging every year, with less transparency. But advertisers continue to embrace paid search for one simple reason: it drives results for brands and businesses.
Paid search is still king. Search continues to own the largest market share of advertising – 39.5%, but that is down from 40.2% in 2022, 41.4% in 2021 and 42.2% in 2020.
- But YoY growth for search advertising is slower than the digital industry as a whole and the majority of other ad formats, according to the report.
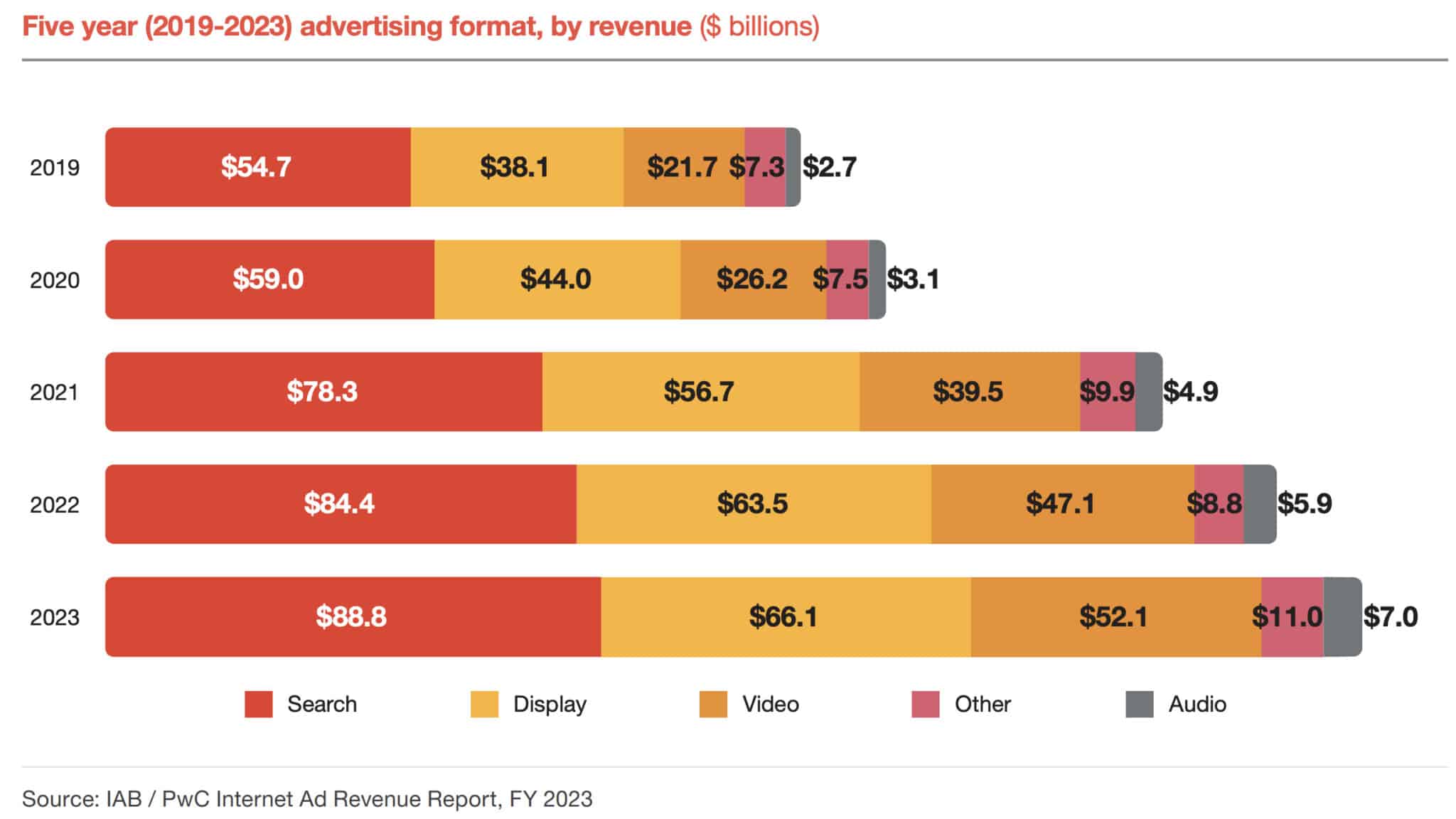
The state of digital advertising. Resilient. Advertising continued to grow in a time of high inflation, rising interest rates and job cuts, according to the report. Of note from the IAB report:
- Q4 had the highest growth rate – 12.3% – with revenues growing to $64.5 billion. In 2022 the growth rate for the quarter was 4.4%.
- Social media ad revenue rose 8.7% YoY to reach $64.9 billion in 2023, with much of that growth coming in the second half of the year.
- Video advertising accounted for $52.1 billion, or 23.2% of all advertising revenue, in 2023.
- Display advertising revenues remained high in 2023 – $66.1 billion – though YoY growth was 4%, down from 12% growth in 2022.
- Retail media networks saw a 16.3% increase in revenue YoY, reaching $43.7 billion.
2024 outlook. It’s “promising,” according to the IAB. Advertisers must, as always, adapt to changing consumer behaviors, consumption channels, privacy regulations and the ongoing generative AI revolution.
The report. You can read the report here (registration required).
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Why the shift from ‘conversions’ to ‘key events’ in GA4 is a game-changer
Written on April 17, 2024 at 5:41 am, by admin

The recent shift from “conversions” to “key events” in (GA4) represents a significant change that digital marketers, especially SEO professionals, need to understand and act on.
This article explores the implications of this change and insights on how to leverage it to elevate your marketing reporting.
Understanding key events in GA4
On March 21, I got an email from a former student who said he’d logged into Google Analytics 4 (GA4) that morning and saw, “Analytics conversions have been renamed key events.”
Google explained:
“To distinguish conversions in Google Analytics from those in Google Ads, Analytics conversions are now called key events. You don’t need to take any action on your existing setup. Key events are created and reported like previous conversions in Google Analytics.”
When he clicked the arrow for more information, he learned:
“Key events in Google Analytics measure the interactions most important to your business. For example, you could mark an important event like a purchase or newsletter subscription as a key event. This will appear as a key event metric in Analytics reports.”
And when he clicked on the next arrow, he saw a summary of the updates:
- “An event measures a specific behavioral interaction on your website or app.
- “A key event is an event that you mark as important to your business. Key events appear in Analytics reports but aren’t directly eligible for reporting or bidding in Google Ads.”
Since he’d taken my online course on GA4, my former student asked me, “How will the change to key events impact my metrics and reporting? And is there anything I need to be doing?”
I started thinking about all the other subtle name changes that Google engineers had made to Universal Analytics (UA), which had signaled significant paradigm shifts in GA4:
- UA used data based on sessions; GA4 uses data based on events.
- UA measured bounce rate; GA4 measures engagement rate.
- UA used cookies; GA4 uses modeling to estimate key events.
- UA let you set up to 20 goals; GA4 lets you mark up to 30 key events.
- UA provided data; GA4 automatically provides anomaly detection.
- UA reported what users did; GA4 generates predictive insights.
- UA used last-click attribution; GA4 uses data-driven attribution.
That’s when I realized that the shift from conversions to key events in GA4 is a game changer.
This is especially true for SEO specialists and managers who currently use website traffic from organic search to measure their results. But it is also the case for other marketing professionals, who could use website traffic from referral, organic social or other default channels to measure their contribution to the success of their company or clients.
What this change means for SEOs
So, let’s start with the impact that measuring key events can have on the career path of SEOs. Many SEOs use Search Console to measure organic search traffic. And who can blame them?
Organic search is responsible for 53% of all website traffic, while paid search is responsible for 15%, per a BrightEdge study. (This study included thousands of domains and tens of billions of sessions, though it excluded direct traffic.)
Unfortunately, providing “53% of all website traffic” doesn’t appear to be highly valued by the executives in the C-suite at more organizations that you can shake a stick at. If it were, then you’d see a lot more VPs of SEO, wouldn’t you?
So, what is highly valued by the C-suite? Well, it differs by organization. But most executives are focused on business objectives like “raise brand awareness,” “generate leads” or “drive online sales.”
That’s why Google added the Business Objectives collection to GA4 in June 2023. However, the latest shift from conversions to key events gives SEOs a new opportunity to measure what matters.
Aligning with business objectives
Before this latest shift, it was possible to measure “micro conversions.”
But the term “micro conversions” tended to remind their executives that these small steps fell short of “macro conversions,” which are the important interactions that directly impact the success of their business.
However, “key events” sound much more valuable than “micro conversions.” If you disagree, then ask yourself this question: Would you rather tell your executives that you will be providing “sushi” or “cold, dead, raw fish” at their next meeting?
Words matter.
So, if your chief marketing officer is focused on raising brand awareness at your B2C company, then you should start reporting how many organic search users go on to:
- Scroll to 90% of a blog post or article.
- Play at least 50% of a product video.
- Complete a tutorial.
If your chief revenue officer is focused on generating leads at your B2B company, then you should kick off a new set of reports on the number of organic search users who go on to:
- Download a white paper.
- Subscribe to a newsletter.
- Complete a registration form.
And if your chief executive officer is focused on driving online sales at your ecommerce, then you should begin reporting the percentage of organic search users who go on to:
- Begin the checkout process.
- Add merchandise to the shopping cart.
- Make a purchase.
This is particularly true if you can assign a default monetary value to a key event in GA4.
Assigning monetary value to key events
Now, purchase events already have value and currency parameters. But you can add the same parameters to any other key event. Just calculate the economic value of a key event based on how often the people who take this important action go on to become customers later.
For example, if 10% of the people who sign up for a newsletter go on to become customers and your average transaction is $500, then you can associate $50 (10% of $500) as the monetary value of this key event.
If you want to see this for yourself, then go to the Google Analytics demo account. Just click on the Google Analytics 4 property: Google Merchandise Store (web data) and then ask yourself this question: Would you rather tell your executives that organic search provided “27,657 users,” “42,596 key events” or “$61,370 in revenue” over the last 90 days?
I know the revenue number above looks like “small change,” but the most popular item purchased from the Google Merchandise Store in the last 90 days was a “Google Cloud Sticker,” which cost $1.25. So, you may provide your company or clients with significantly more economic value.
Adopting key events beyond SEO
SEOs aren’t the only ones who can adopt key events and revenue as key performance indicators (KPIs).
For example, if you scroll down the Google Merchandise Store data in GA4, then you’ll see the “referral” channel, which is an innovative way to measure digital PR, delivered 5,987 users, 12,260 key events and $10,210 in revenue over the last 90 days.
The “organic social” channel, which offers a new way to measure social media marketing, delivered 1,920 users, 4,952 key events and $5,797 in total revenue over the same period.
This brings us to direct traffic, also known as “dark traffic.”
Back in 2014, an “experiment” by Groupon found that up to 60% of “direct” traffic was actually organic search traffic.
In 2023, a large portion of traffic marked as “direct” in Google Analytics was likely sent by “dark social” networks like TikTok, Slack, Discord, Mastodon and WhatsApp, according to research by SparkToro. (Disclosure: I was one of about 100 experiment participants recruited to conduct this experiment.)
So, would it be a “career-damaging move” to ask an executive to discuss the probable sources of direct traffic?
Well, you know the “highest paid person’s opinion” in your office better than I do. But I’d bet dollars to donuts that he or she would welcome such a discussion – especially if it takes place before his or her next meeting with other members of the C-suite.
And while you will want to use your own data from GA4, here’s what the Google Analytics demo account will show you:
- The “direct” channel provided 75,788 users, 91,304 key events and $189,918 in revenue over the last 90 days.
- That makes it almost 2.5 times more valuable than the organic search, referral and organic social channels put together.
However, only a very small percentage of these users went to the home page of the Google Merchandise Store.
The overwhelming majority went to a wide variety of landing pages, including ones for stationery, new products, sale (clearance) items, men’s and unisex apparel and drinkware and bags (lifestyle) merchandise.
So, where did all these people discover the relatively long URLs for the plethora of landing pages?
Here’s my scientific, wild-ass guess: It was a two-step process.
- Step 1: A small group of opinion leaders discovered a page about a specific product using organic search, news articles or social media posts.
- Step 2: This small group copied and pasted links to these pages – along with their opinion of the product – in thousands of emails, text messages or Zoom chats to a larger group of their friends, family and colleagues.
And voila! You get a ton of so-called direct traffic to a wide variety of landing pages on the Google Merchandise Store’s website that’s hard to track directly.
Now, I didn’t make up this two-step flow model of communication. According to an article written by Monica Postelnicu and fact-checked by the editors of Encyclopedia Britannica:
“The two-step flow model was formulated in 1948 by Paul Lazarsfeld, Bernard Berelson and Hazel Gaudet in the book The People’s Choice, after research into voters’ decision-making processes during the 1940 U.S. presidential election.”
I think it offers a tested and validated model of what is probably happening today.
Test and prepare for imminent changes in search marketing
Even if you haven’t tested or validated it yet, it’s a fairly smart move to ask an executive to discuss the probable sources of direct traffic – especially if you also recommend conducting some tests using Google’s campaign URL builder tool, which enables you to easily add campaign parameters to URLs so you can measure your custom campaigns in GA4.
You should have this conversation and conduct these tests sooner, rather than later. Why?
Because a seismic change is coming in 2024 and those who can measure the quality as well as the quantity of organic search, referral and organic social traffic will be in a stronger position to survive – and thrive.
In an article entitled, “Google SGE a top threat to brand and product terms, study finds,” Danny Goodwin wrote:
“You should expect to see ‘some erosion of current traffic levels’ from brand-related terms as a result of Google’s Search Generative Experience, according to a new Authoritas analysis.”
So, how much erosion are we talking about?
Well, Authoritas found Google SGE displayed for 91.4% of all search queries. Another study by BrightEdge found 84% of search queries will include Generative AI when SGE is fully deployed by Google.
So, imagine that you’re living on the brink of the verge of the edge of the San Andreas Fault. You’d probably take some prudent precautions to prepare for the upcoming “searchquake.” And you’d almost certainly want to do more than hang your pictures with two nails instead of one.
The sooner you start measuring key events, the better. As Sun-Tzu observed, “In the midst of chaos, there is also opportunity.”
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Google Search Console security update improves management of ownership tokens
Written on April 17, 2024 at 5:41 am, by admin

Google Search Console has released a security update around user permissions and controls management where you can better manage the ownership tokens. Ownership tokens are used for when people verify your site in Search Console, Merchant Center and other Google products and sometimes people who had access in the past to your profiles no longer should.
This update show make it easier to manage such access and remove those tokens and permissions when they are no longer needed.
What Google said. Google wrote:
We’re rolling out further improvements to Search Console’s user and permission management, incorporating capabilities related to unused ownership tokens management. Tokens are the codes used for website ownership verification in Search Console, Merchant Center, and other Google products. We have seen cases where these were accidentally left behind after owners have moved on. In February 2023, we rolled out improvements to the user and permissions management report. The latest changes will improve the accuracy and reflect the actual state of unused ownership tokens.
What it looks like. Int he user and permissions interface, under the “unused ownership tokens” you will see a screen like this where you can click “remove” to remove access to those ownership tokens:
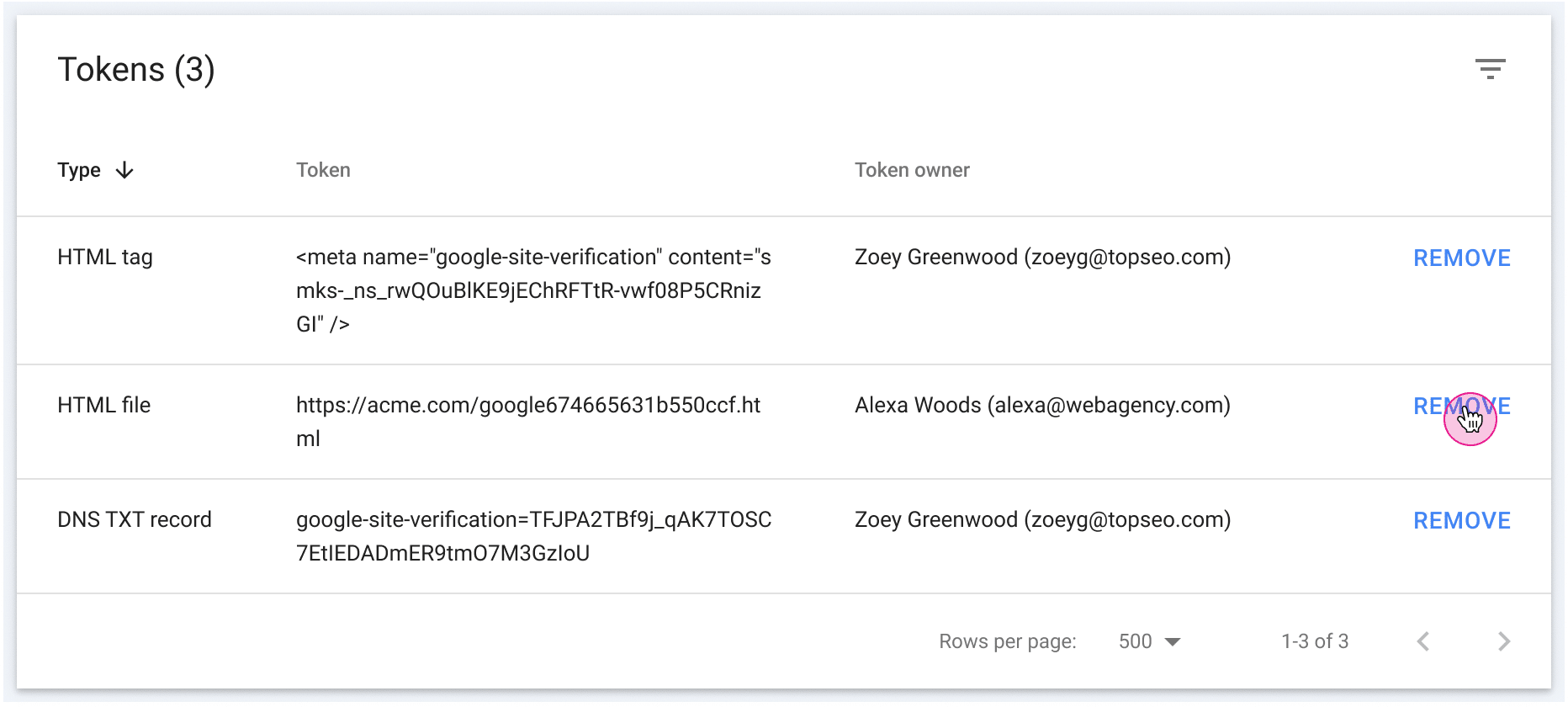
How it works. Here are the steps to take to manage these ownership tokens:
- Visit the Users and permissions interface
- Click “Unused ownership tokens”
- Choose the tokens you’d like to remove and click “Remove” (see screenshot below)
- Click “Verify removal” to get update for the unused ownership token
Why we care. It is always a good idea to ensure the right people have access to your data and Search Console properties and more importantly that the wrong people do not have access to it. As Nir Kalush from Google wrote, “The update rolled out today lets you verify the removal of the unused verification token so that removed owners cannot regain access to the property.”
So check your tokens and remove those who should not have access.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Exclusive keynotes, expert-level sessions, live Q&A and more: Preview the SMX Advanced agenda
Written on April 17, 2024 at 5:41 am, by admin

Some of the world’s most iconic search marketers — including Glenn Gabe, Brad Geddes, Lily Ray, Amy Hebdon, Jessica Bowman, and Bruce Clay — are now confirmed to speak at Search Engine Land’s SMX Advanced, online June 11-12… and you can learn from them, along with the thousands of marketers who have already signed up, for free.
The agenda is coming together beautifully, with tactical AI, SEO, and PPC sessions exploring everything from what you need to know about Google’s Search Generative Experience to a spirited debate about AI and automation in paid search.
Each day kicks off with an exclusive keynote, followed by tactic-rich sessions from search marketing experts…
The entire SMX Advanced program – including keynotes, sessions, Q&As, live demos, and interactive Coffee Talk meetups – will be available live and on-demand starting June 11 so you can train at your own pace.
It’s all free. No plane ticket. No expense report. No kidding.
I hope you’ll join me – and the nearly 200,000 search marketers who have relied on SMX since 2006 – for this once-a-year training experience.
Grab your free SMX Advanced pass now!
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.






