Reddit eyes potential in search ads following Google traffic gains
Written on May 8, 2024 at 3:15 pm, by admin

Reddit is exploring monetizing its search results pages, teasing a significant untapped opportunity for the popular online forum.
Logical next step. With over 1 billion monthly searches on the platform, Reddit sees advertising against user searches as a logical next step to improve monetization after enhancing the core search experience.
- Reddit has also long benefited from Google search traffic, with indexed Reddit content attracting new users actively seeking information and communities.
Why we care. Reddit venturing into search ads could present a lucrative opportunity to target users with high intent. Advertisers will get the diversity in available platforms they crave as signs of decreasing Google trust levels prevail.
What they’re saying. Steve Huffman, CEO of Reddit, said on the company’s latest earnings call:
- “There are no ads today on search result pages. But that’s a very high-performing product elsewhere on the internet. And I think there’s no reason to believe that it wouldn’t be for Reddit because the intention is so explicit when users are searching.”
State of play. Reddit is first focused on upgrading its search functionality with improved back-end performance, autocomplete, and a revamped user interface slated for this year.
- The company believes nailing the search user experience is crucial before exploring monetization options like search ads.
- As it improves discovery and leverages explicit search intent signals, the platform sees advertising as a natural complement.
What’s next? While no firm timeline was provided, Reddit appears committed to extracting more value from its massive search volume by opening up ad inventory once its revamped search product takes shape.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
ChatGPT search feature rumors heating up
Written on May 8, 2024 at 3:15 pm, by admin

All signs point to ChatGPT launching a search feature soon. When? That remains the big question.
Rumor has it. OpenAI is developing a ChatGPT feature that searches the web and cites sources in its results, Bloomberg reported (subscription required):
- “The feature would allow users to ask ChatGPT a question and receive answers that use details from the web with citations to sources such as Wikipedia entries and blog posts … One version of the product also uses images alongside written responses to questions, when they’re relevant. If a user asked ChatGPT how to change a doorknob, for instance, the results might include a diagram to illustrate the task…”
And. “OpenAI has been aggressively trying to poach Google employees for a team that is working hard to ship the product soon,” according to the Verge.
Why we care. Search has quickly evolving in a new direction since the emergence of generative AI – with OpenAI seemingly perceived to be ahead of Google in many ways (not yet including Search), even though ChatGPT’s user base is still much smaller than Google. However, there is clearly growing frustration with all aspects of Google – from the quality of Search results to its abundance of advertising. Not to mention Google’s alleged monopolistic practices that have hurt advertisers, users and competitors.
X things we know about ChatGPT search. ChatGPT doesn’t want to copy Google’s model or layout (he hates ads). OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said as much earlier this year:
- “I don’t think the world needs another copy of Google,” Altman said.
ChatGPT’s version of Search wouldn’t be traditional, or classic, general web search. Altman’s vision is integrating ChatGPT with Search:
- “…We are interested in how to do that well. That would be an example of a cool thing. I don’t think anyone has cracked the code on yet. I would love to go do that. I think that would be cool,” Altman said.
Dig deeper. Is ChatGPT the Google Search killer we’ve been expecting?
Other ChatGPT search developments. We first heard rumors about OpenAI’s search product in February. Other stories Search Engine Land has covered:
- ChatGPT recently made links more prominent for ChatGPT Plus subscribers.
- OpenAI launched its web crawler, GPTBot, in August.
More evidence. search.chatgpt.com appeared in the log files for some servers, as reported In Report: OpenAI To Launch Search Engine on Search Engine Roundtable by Barry Schwartz. There were rumors that ChatGPT’s search product would launch as early as tomorrow (May 9), but that seems unlikely at this point.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Surviving and thriving in the new Google by Edna Chavira
Written on May 8, 2024 at 3:15 pm, by admin

March 2024 disrupted the SEO industry. Websites were deindexed, and manual penalties were delivered—all to produce more helpful, more trustworthy search results. How did your website fare?
Join us for an insightful webinar as we delve into the seismic shifts brought about by Google’s March 2024 updates and explore strategies to not just survive but thrive in this dynamic digital landscape. In this session, we’ll dissect the implications of the latest algorithm changes on content creation, link building, and SEO practices.
Register now for Surviving and Thriving in the New Google: Navigating March 2024 Updates for Content Creation, Link Building, and SEO Success to secure your spot and unlock the secrets to thriving in the new Google era.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Report: 64% of technical SEOs believe AI isn’t a job security threat
Written on May 7, 2024 at 12:11 pm, by admin
Technical SEOs aren’t concerned that the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) will negatively impact their job security. That’s one insight from the State of Technical SEO Report 2024, released by digital marketing agency Aira and the Women in Tech SEO community.
- 64% said they were “not at all” worried.
- 36% said they were either “a little worried” (30% in-house; 33% agency) or “very worried” (6% in-house; 3% agencies).
- “While such worries are not without merit, it’s crucial for business leaders to recognize that AI is not an all-encompassing substitute for human employees. Particularly in the realm of SEO, the nuanced application of common sense is key—a quality AI has yet to master,” said Roxanna Stingu, head of Search & SEO, Alamy, in the report.
Why we care. All the overwhelming developments in generative AI over the past 18 months have caused concern and stress among SEOs. While AI will undoubtedly eliminate some jobs, it will also create new jobs. AI is a great assistant, but it can’t replace the work done by technical SEOs – a.k.a., humans.
Google SGE fears. While the majority weren’t worried about job security, 70% of respondents were worried about the impact of Google Search Generative Experience (SGE) on regular organic search results.
- “Exactly how worried I am keeps changing. There’s still so much uncertainty about exactly how this will roll out, and I want to see how everyday users react to it as well. So much of the commentary has been from early adopters in the tech and SEO community and we’re not exactly representative of how the rest of the world will use this,” said Natasha Burtenshaw-deVries, director of organic growth, Flywheel Digital, in the report.
In-house and agency. Only 20% of in-house, agency and freelancer respondents haven’t changed their SEO planning and roadmaps due to AI developments. Of the remaining 80% of respondents:
- 59% said “a little.”
- 21% said “a lot.”
AI and machine learning (ML) tools. Fifty-two percent of survey respondents used AI and ML tools to generate metadata (e.g., titles, descriptions) daily, weekly or monthly. Other ways SEOs used the tools:
- 46% for content generation.
- 35% for keyword research.
- 23% for auditing pages.
Other findings. Google seems safe:
- 85% don’t believe ChatGPT as a standalone tool is a threat to Google.
- 70% don’t believe Bing can take away search market share from Google.
About the data. The survey was conducted between Jan. 15 and March 5. It received 382 responses – 56% of respondents were from the U.S. and UK.
The report. The report also digs into the impact of SEO, tools and more. You can read the full report here: The State of Technical SEO Report 2024
Dig deeper. Technical SEO report reveals what matters in 2023
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
What is ad hijacking and how do you protect your brand from it? by Adthena
Written on May 7, 2024 at 12:11 pm, by admin


Have you ever clicked on a brand’s ad and ended up on a website you weren’t expecting? That’s ad hijacking. And it hurts advertisers and users.
Keep reading to learn how ad hijacking works, the risks it poses and how to protect your brand.
What is ad hijacking?
Ad hijacking is when an affiliate mimics a brand’s ads to steal clicks and revenue on their trademarked keywords. Affiliates do this to trick you into clicking on their ad instead of a real one from the brand.
How does ad hijacking work?
Imagine you search for [your favorite clothing brand]. Normally, the first ad you see should be the brand’s official one, taking you straight to its website. Here’s how ad hijacking disrupts that:

- The rightful owner: The first ad above belongs to the brand. It leads directly to its own website via the correct tracking link..
- The obvious culprit: The second ad is from an affiliate. It redirects you to the brand’s website, but adds the affiliate’s tracking link in the process. This lets them steal a commission for any sale you might make, even though you intended to visit the brand directly.
- The masked marauder: The third ad shows a more sophisticated hijacker using a series of redirects to hide their involvement. They might even send you through several websites before finally landing you at the brand’s site. This makes it difficult to identify them and hurts the brand’s affiliate program because it’s hard to track where the stolen commission came from.
What does ad hijacking look like?

In this example, a brand violation instance has been captured using Adthena’s Ad Hijacking Detection for a hotel brand (the brand name has been changed for anonymity). A search for “brandhotels.com” has returned the ad shown, which features the brand name in the display URL and site links.
However, the ad has not been placed by the hotel brand. It was placed by an affiliate bidding on “brandhotels.com.”
Why is ad hijacking harmful to your brand?
Ad hijacking can harm both advertisers and users. Here’s a breakdown of the main challenges it can cause:
For advertisers:
- Lost sales and revenue: Imagine paying for clicks that don’t reach your website! Hijacked ads steal clicks meant for your official ads, diverting potential customers and reducing sales.
- Increased costs: Advertisers compete with hijackers bidding on their brand terms (i.e., your brand name). This drives up the CPC, meaning you pay more for each person who sees your genuine ad.
- Channel conflict and data skewing: If you and a hijacker use affiliate programs, things get messy. Metrics like impression share and revenue attribution become inaccurate, making it difficult to track campaign performance effectively.
- Brand reputation damage: If users click on a hijacked ad and end up on a low-quality website or experience something negative, it reflects poorly on your brand. They might associate the bad experience with your company.
For users:
- Deception: The whole point of ad hijacking is to trick users. They click on an ad believing it leads to a brand’s website, only to find themselves somewhere else. This can feel misleading and like a waste of time.
- Exposure to malware: In some cases, hijacked ads might lead to malicious websites containing malware. This software can steal personal information or harm your device.
- Wasted time: Users expecting to visit a brand’s website after clicking on an ad will be disappointed if they land on an irrelevant page. They’ll waste valuable time navigating away from the wrong website.
Spot and stop ad hijacking attempts
Catching ad hijacking can be tricky, but there are tools to help.
Adthena’s Ad Hijacking Detection catches instances of ad hijacking instances from 50+ affiliate networks and sub-networks, by:
- Constantly monitoring your brand: Ad Hijacking Detection continuously scans search results for ads containing your brand terms, trademarks and even variations of them. It acts like a tireless lookout for imposters!
- Identifying suspicious activity: Sophisticated algorithms analyze ad copy, landing pages and affiliate links. If anything doesn’t seem genuine, it will be flagged for further investigation.
- Alerts and reports: Get notified right away if potential hijacking attempts are detected. These reports will include details like the infringing ad copy, landing page URLs, and even the suspected affiliates involved.
- Gathering evidence for takedown: Having all the evidence in one place makes it easier to report the infringing ad to Google. You’ll have the affiliate ID and other details needed for a swift takedown.

See Ad Hijacking Detection in action in a self-guided platform tour. Get started.
How to spot ad hijacking in your campaigns
Being proactive is key to fighting ad hijacking. Here are some red flags to watch out for in your branded ad campaigns:
- Performance slump: A sudden drop in clicks and conversions for your branded ads could be a sign that hijacked ads are stealing your clicks.
- Suspicious spikes in affiliates: A surge in referral traffic or conversions from an unknown affiliate is a cause for concern.
- Copycat conversions: If an affiliate’s conversion rates suspiciously mirror your branded ad campaigns, it might be because they’re benefiting from hijacked clicks.
- URL mismatches: Always check the landing page URLs linked to your affiliates. If they don’t match your brand’s domain or contain strange redirects, it could be a hijacking attempt.
These warning signs can help you catch ad hijacking early and take action to protect your brand.
Prevent ad hijacking before it strikes
Why wait for trouble? By being vigilant and monitoring your campaigns closely, you can take steps to identify and address ad hijacking attempts by affiliates.
1. Secure your brand identity:
- Trademark protection: Register your trademarks and brand terms. This strengthens your legal stance if you need to confront hijackers.
- Brand watch: Use brand monitoring tools to track online mentions, including search results. This helps you spot potential hijacking attempts early on.
2. Manage your affiliate program:
- Clear affiliate agreements: Outline acceptable practices in your affiliate agreements. Ban affiliates from bidding on your brand terms or using misleading ad copy.
- Performance monitoring: Regularly monitor your affiliate program performance. Look for unusual spikes in traffic or conversions from specific affiliates.
3. Paid search defense:
- Negative keywords: Use negative keywords to prevent your ads from showing for searches that include hijacked terms or variations of your brand name.
- Trademark bidding: Consider trademark bidding on your branded keywords. This ensures your ads appear prominently in search results, pushing hijacked ads down the page.
4. Advanced protection solutions:
- Brand Protection: Explore advanced brand protection tools like Adthena’s Ad Hijacking Detection, a part of the Brand Protection solution. These tools actively scan for hijacking attempts and provide detailed reports to help you take action.

Learn more about PPC brand protection and how to do it in the complete guide to PPC brand protection.
5. Take action:
- Report infringing ads: Report any instances of ad hijacking to the relevant search engine platform.
- Terminate rogue affiliates: If you identify affiliates engaging in ad hijacking, terminate their agreements immediately.
Fight back against ad hijacking
Ad hijacking can be sneaky, stealing clicks and damaging your brand reputation. By understanding how it works, you can take proactive measures to:
- Protect your brand: Register trademarks and use brand monitoring tools to stay vigilant against hijacking attempts.
- Secure your affiliate program: Define acceptable practices in affiliate agreements. Block affiliates from bidding on your brand terms or using misleading ad copy.
- Put paid search protection in place: Use negative keywords to prevent hijacked terms from triggering your ads. Consider trademark bidding to ensure your ads appear prominently.
- Consider advanced protection: Explore tools like Adthena’s Ad Hijacking Detection for advanced monitoring and defense.
- Take down hijackers: Report infringing ads to search engines and terminate relationships with rogue affiliates.
By staying informed and implementing these strategies, you can reclaim control of your online presence and ensure a positive experience for your customers.
Do you know if your branded keywords are being hijacked by your affiliates? Take a self-guided platform tour of Adthena’s Ad hijacking detection or Book a demo to get started.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Unpacking Google’s 2024 E-E-A-T Knowledge Graph update
Written on May 7, 2024 at 12:11 pm, by admin

The Killer Whale is back.
The latest Knowledge Graph update, released in March, continued the laser focus on person entities. It appears Google is looking for person entities to which it can fully apply E-E-A-T credibility signals and aims to understand who is creating content and whether they are trustworthy.
In March, the number of Person entities in the Knowledge Graph increased by 17%. By far, the biggest growth in new Person entities is people to whom Google is clearly able to apply full E-E-A-T credibility signals (researchers, writers, academics, journalists, etc.).
Reminder: The original Killer Whale update
The “Killer Whale” update started in July 2023 as a huge E-E-A-T update to the Knowledge Graph. The key takeaways from the July 2023 Knowledge Graph are that Google is doing three things:
- Accelerating the growth of the Knowledge Vault (starting with Person entities).
- Restructuring the Knowledge Vault to focus on important subtitles for user trust to improve the algorithms’ application of E-E-A-T signals.
- Rapidly sunsetting its dependence on Wikipedia and other human-curated sources.
We concluded that the March Killer Whale update was all about Person entities, focused on classification and designed to promote E-E-A-T-friendly subtitles.
The Knowledge Graph is Google’s machine-readable encyclopedia, memory or black box. It has six verticals and this article focuses on the Knowledge Vault vertical.
The Knowledge Vault is where Google stores its “facts” about the world. The Killer Whale update increased the facts and entities in the Knowledge Vault to over 1,600 billion facts on 54 billion entities, per Kalicube’s estimate.
What happened in the March 2024 Knowledge Graph update?
- The number of entities in the Knowledge Vault increased by 7.23% in one day to over 54 billion.
- Person entities in the Knowledge Vault increased by 17%.
- The biggest increase (+38 %) was among Person entities with E-E-A-T-friendly subtitles (researchers, writers, academics, journalists, etc.).
- The number of Knowledge Vault entries for Person entities using Wikipedia did not increase. That means all the new Person entities came from other trusted sources.
- Knowledge Panels for person entities increased by 2.55% and appeared in the SERPs immediately. This is a new phenomenon: the July 2023 Killer Whale update did not immediately affect Knowledge Panels in the SERPs.
- We estimate that between 15% and 25% of all Person entities in the Knowledge Vault are duplicates.
- 18% of new person entities tracked by Kalicube Pro that were added in the July 2023 Killer Whale update were deleted from the Knowledge Vault before the Return of the Killer Whale update. When an entity gets a place in the Knowledge Vault, there is a 1 in 5 chance it will be deleted – unless you continue working on your entity and its E-E-A-T credibility signals.
The Killer Whale update is all about Person entities
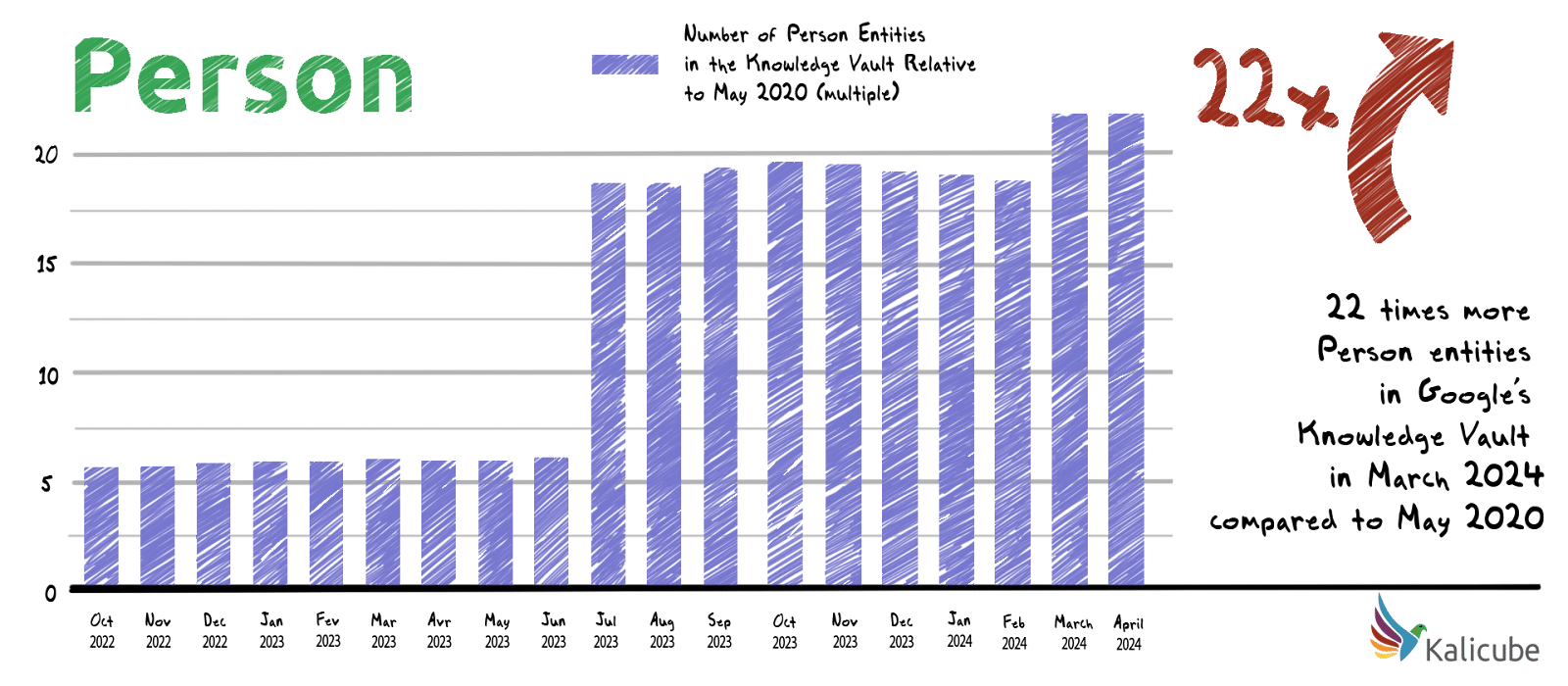
Between May 2020 and June 2023, the number of Person entities in Google’s Knowledge Vault increased steadily, which is in line with the growth of the Knowledge Vault overall.
In July 2023, the number of Person entities tripled in just four days. In March, Google added an additional 17%.
In less than four years, between May 2020 and March 2024, the number of Person entities in Google’s Knowledge Vault has increased over 22-fold.
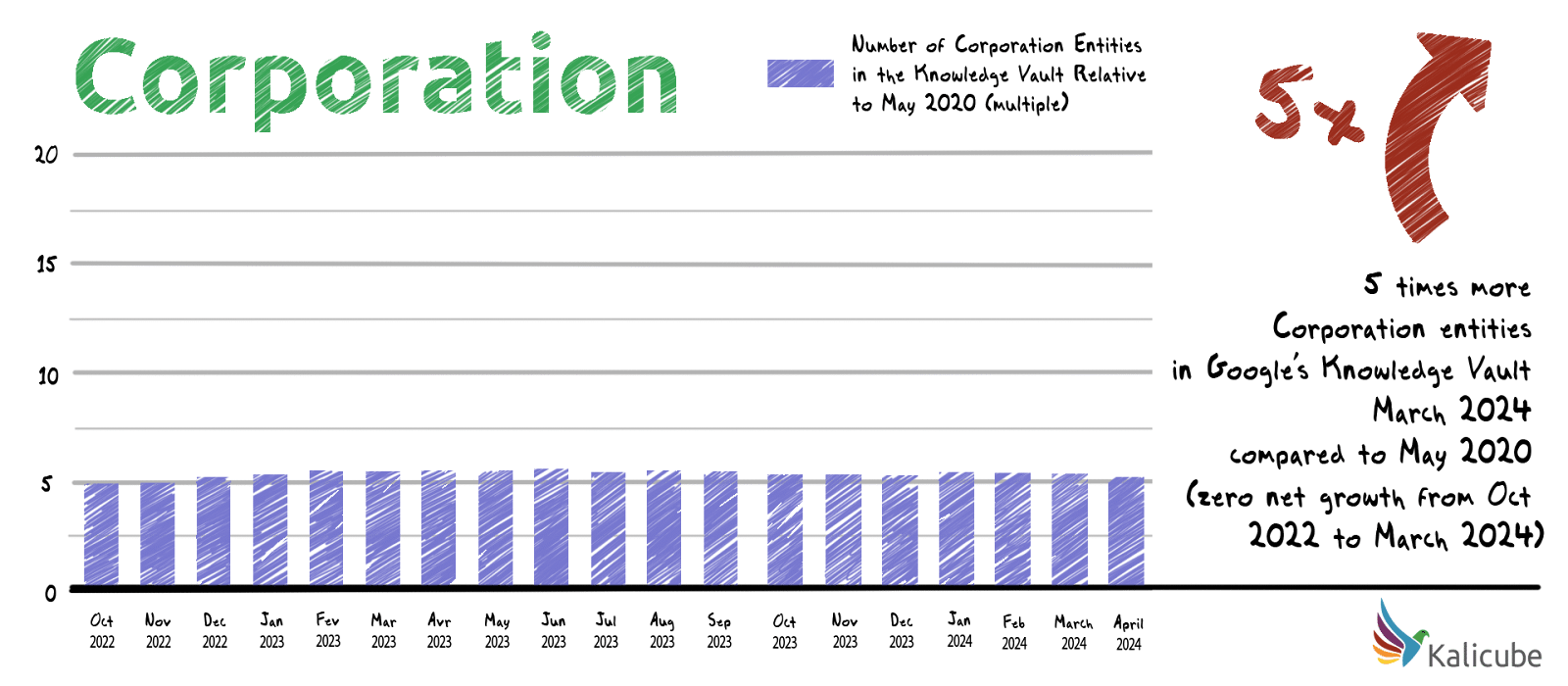
Between May 2020 and March 2024, the number of Corporation entities in Google’s Knowledge Vault has increased 5-fold. In the last year, however, the number of Corporation entities decreased by 1.3%.
Google is focusing on Person entities to a stunning degree, almost exclusively.
Data: Kalicube Pro was tracking a core dataset of 21,872 people in 2020 and our analysis in this article uses that dataset. As of 2023, Kalicube Pro actively tracked over 50,000 corporations and 50,000 people.
Why is Google looking for people to apply E-E-A-T (N-E-E-A-T-T) signals to?
Google is looking for people. However, it specifically focuses on identifying people to whom it can apply E-E-A-T signals because it wants to serve the most credible and trustworthy information to its audience.
We use N-E-E-A-T-T in the context of E-E-A-T because our data shows that transparency and notability are essential in establishing the bonafide of a brand.

The types of people Google is focusing on are writers, authors, researchers, journalists and analysts.
In March, the number of people Google can apply E-E-A-T signals to increased by 38%.
You can safely ignore Wikipedia and other ‘go-to’ sources
Google added over 10 billion entities to the Knowledge Vault in four days in July 2023, then followed that up with another 4 billion entities in a single day in March.
At that scale, it is safe to assume that the Knowledge algorithms have now been “freed” from the shackles of the original human-curated, seed set of trusted sites (Wikipedia only has 6 million English language articles).
That means an entry in traditional trusted sources such as Wikipedia, Wikidata, IMDB, Crunchbase, Google Books, MusicBrainz, etc., is no longer needed.
They are helpful, but the algorithms can now create entities in the Knowledge Vault with none of these sources if the information about the entity is clear, complete and consistent across the web.

Anecdotally, I received this message on LinkedIn the other day

For a Person entity, simply auditing and cleaning up your digital footprint is enough to get a place in Google’s Knowledge Vault and get yourself a Knowledge Panel. Anyone can get a Knowledge Panel.
Everyone with personal E-E-A-T credibility that they want to leverage for their website or the content they create should work to establish a presence in the Knowledge Vault and a Knowledge Panel.
You aren’t safe (until you are)
Almost one in five entities created in the Knowledge Vault is deleted within a year, and the average lifespan is just under a year.
That should make you stop and think. Getting a place in Google’s Knowledge Vault is just the first step in entity optimization. Confidence and understanding are key to maintaining your place in the Knowledge Vault over time and keeping your Knowledge Panel in the SERPs.
The confidence score the Knowledge Vault API provides for entities is a popular KPI. But it only tells part of the story since it is heavily affected by:
- News cycles. (More news, the score goes up, then drops as the news cycle dies.)
- Google’s grasp of the multifacetedness of the entity. (For example, as it understands more about a person’s multiple careers, the score will likely drop.)
- Relationships with other entities. (The score of one entity will distort the score of its closest neighbors.)
In addition, Google is sunsetting this score. Much like PageRank, it will continue to exist, but we will no longer have access to the information.
As such, success can be measured by:
- Retaining a stable KGID in the Knowledge Vault over time.
- Not triggering duplicates of the entity (this splits and dilutes N-E-E-A-T-T credibility equity).
- Creating relationships with a large number of relevant related entities.
- Having an information-rich Knowledge Panel.
- Having an accurate Knowledge Panel.
You aren’t alone (but you want to be)
This update shines a light on entity duplication, which is a particularly thorny problem for Person entities. This is due to Google’s approach to the ambiguity of people’s names.
Almost all of us share our names with other people. I share mine with at least 300 other Jason Barnards. I hate to think how many John Smiths and Marie Duponts are there.
When Google’s algorithms find and analyze a reference to a Person, they assume this person is someone it has never met before unless multiple corroborating facts match and convince it otherwise.
That means a duplicate might be created if there is a factually inaccurate reference to a Person entity or the reference doesn’t have sufficient common traits with an existing Person entity.
If that happens, then any N-E-E-A-T-T credibility equity that references the duplicate is lost. This is the modern equivalent of link building but linking to the wrong site.
When will the next update be?
From our historical data, for the last nine years, the pattern for entity updates is clear: December, February (or March) and July have consistently been the critical months.
In each of the last five years, July has seen by far the most impactful updates.
Get ready. Our experience building and optimizing thousands of entities is that you need to have all your corroboration straight 6 to 8 weeks before the major updates. The next updates might be in July and December.
Google’s growing emphasis on Person entities in its Knowledge Graph
Looking at the data from the Killer Whale updates of July 2023 and March 2024, I am finally seeing the first signs that Google is actually starting to walk the talk of “things, not strings” at scale.
The foundation of modern SEO is educating Google about your entities: the website owner, the content creators, the company, the founder, the CEO, the products, etc.
Without creating a meaningful understanding in Google’s “brain” about who you are, what you offer and why you are the most credible solution, you will no longer be in the “Google game.”
In a world of things, not strings, only if you can successfully feed Google’s Knowledge Graphs with the facts will Google have the basic tools it needs to reliably figure out which problems you are best in the market to solve for the subset of its users who are your audience.
Knowledge is power. In modern SEO, the ability to feed the Knowledge Algorithms is the path to success.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Google hides search results count under tools section
Written on May 7, 2024 at 12:11 pm, by admin

Google Search now has made it harder to find the number of search results for a search query. Instead of it being displayed under the search bar, at the top of the search results, now you need to click on the “tools” button to reveal the results count number.
What it looks like. Here is a screenshot of the top of the search results page:

To see the results, you need to click on “Tools” at the top right of the bar and then below that you will see Google show you the estimated results count:
Here is what it looked like before:
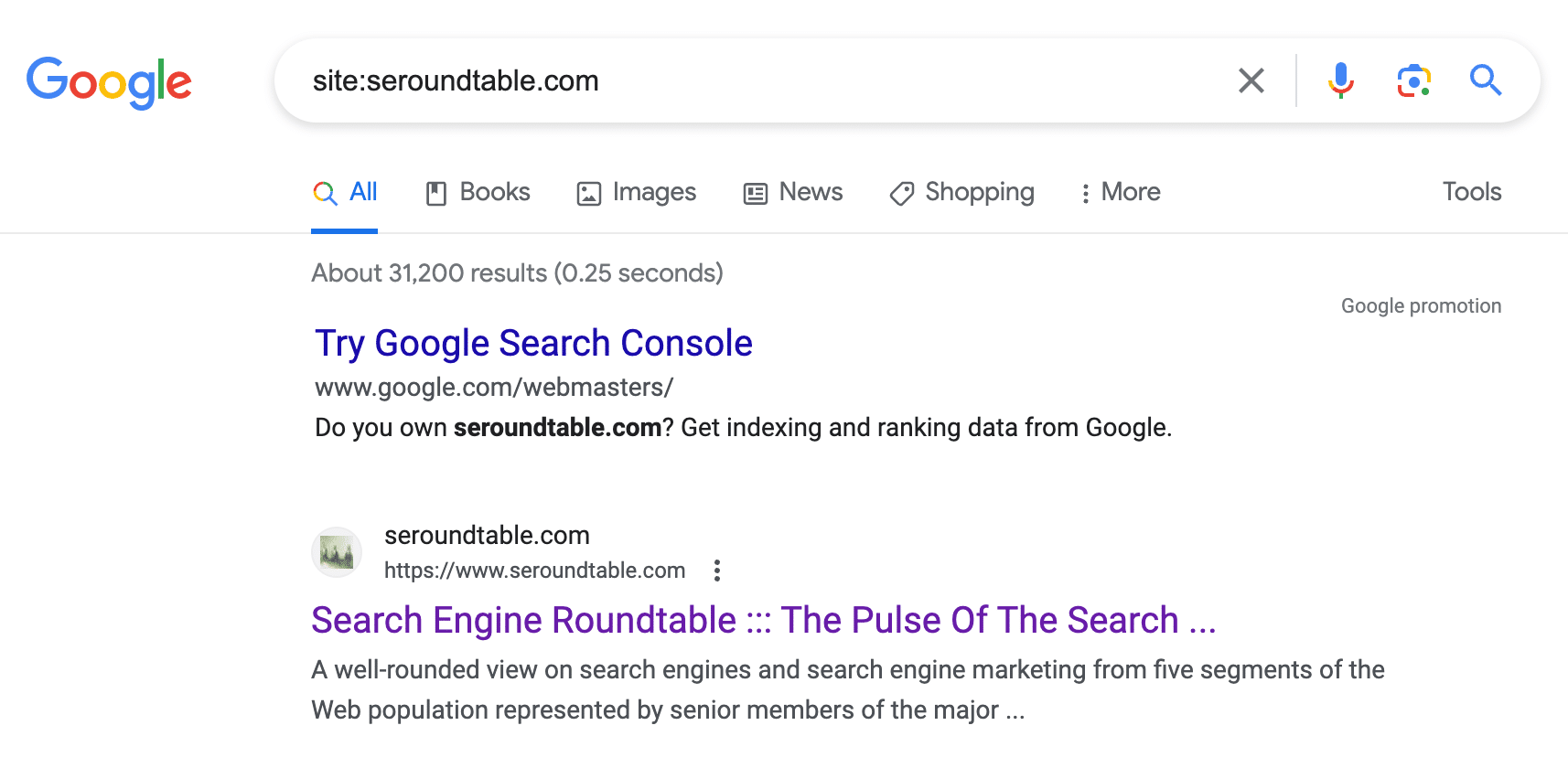
Previous testing. Google has been testing removing the results count for years, as early as 2016 and maybe before. Google also removed them from the SGE results a year ago.
So, this seems to be on Google’s roadmap to remove the feature.
In fact, Google has said numerous times that the results count is just an estimate and not a good figure to base any real research and SEO audits on.
Why we care. Many SEOs still use the results count to estimate keyword competitiveness, audit indexation, and many other purposes. If this fully goes away, many SEOs won’t be happy. Although, I doubt Google cares too much if SEOs are happy.
If the results count is not accurate, Google may decide to do away with it anyway.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
DOJ hammers Google over search ad price manipulation
Written on May 6, 2024 at 9:10 am, by admin

Google manipulated ad auctions and inflated costs to increase revenue, harming advertisers, the Department of Justice argued last week in the U.S. vs. Google antitrust trial.
What follows is a summary and some slides from the DOJ’s closing deck, specific to search advertising, that back up the DOJ’s argument.
Google’s monopoly power
This was defined by the DOJ as “the power to control prices or exclude competition.” Also, monopolists don’t have to consider rivals’ ad prices, which testimony and internal documents showed Google does not.
To make the case, the DOJ showed quotes from various Googlers discussing raising ad prices to increase the company’s revenue.
- Dr. Adam Juda said Google tried to come up with “better prices or more fair prices, where those new prices are higher than the previous ones.”
- Dr. Hal Varian indicated that Google had many levers it could use to change the ad auction design to achieve its desired outcome.
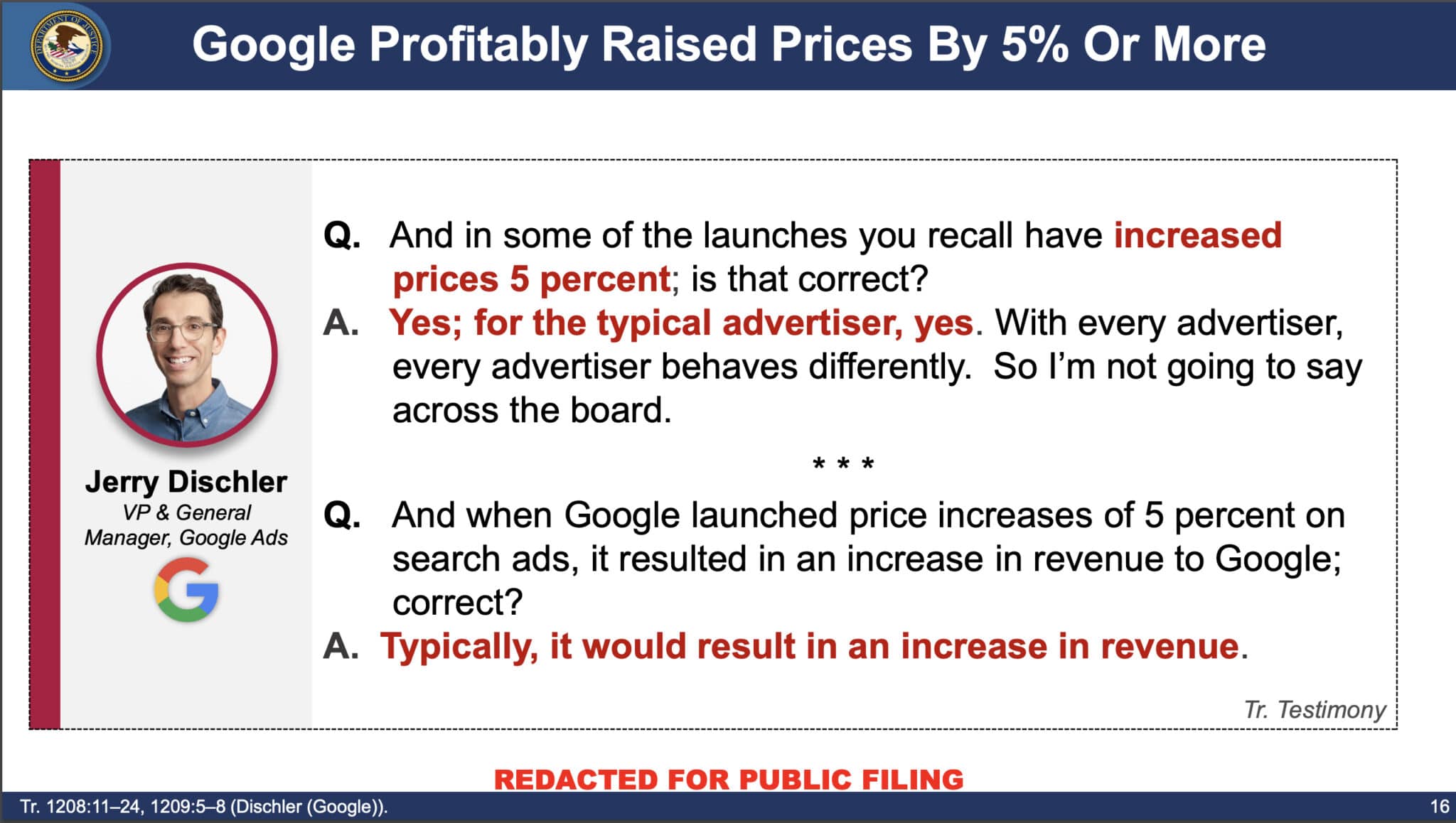
- Juda and Jerry Dischler confirmed this. Dischler was quoted discussing the impact of increasing prices from 5% to 15% in these two slides:
Other slides from the deck the DOJ used to make its case:
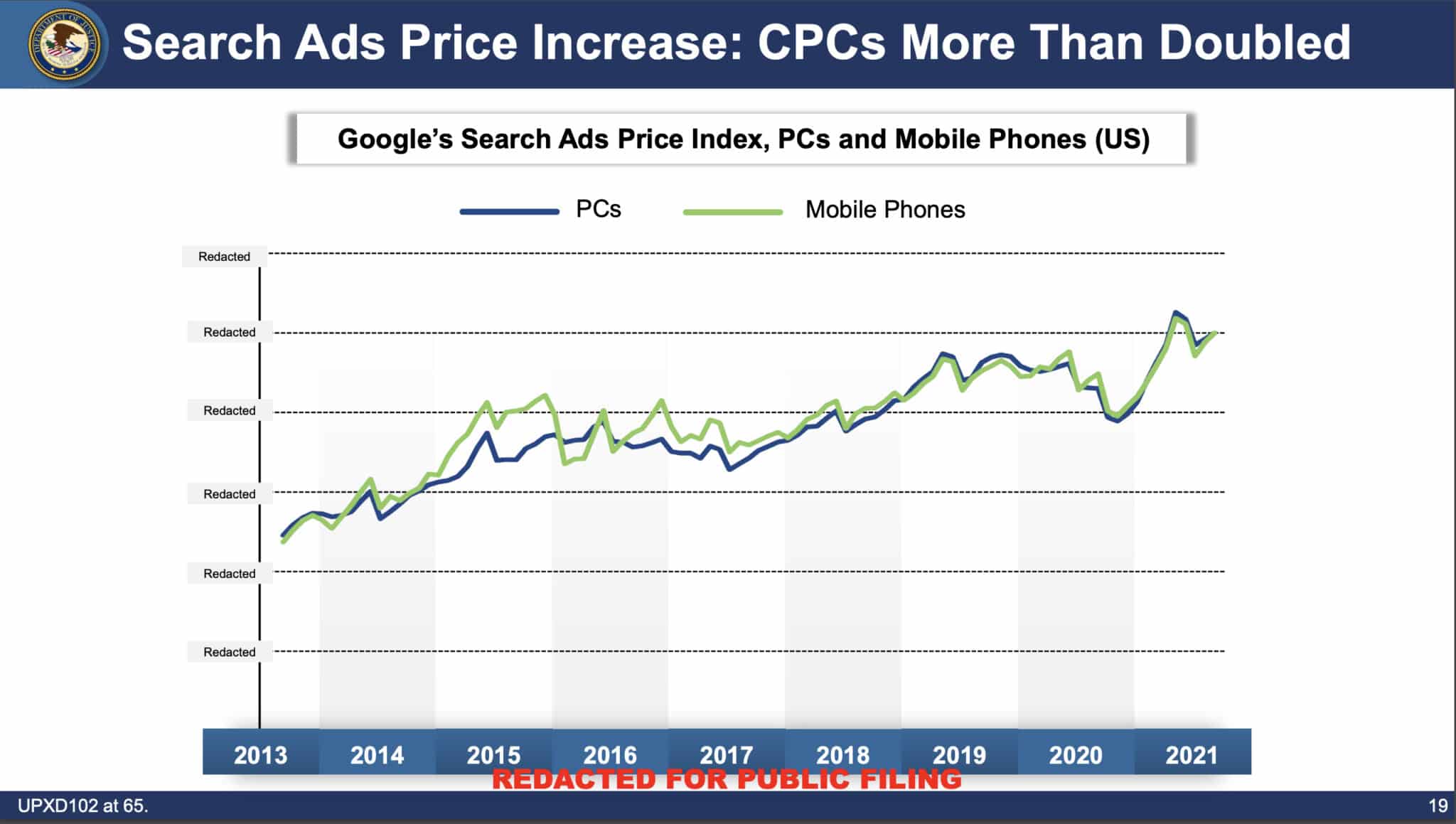
- Google Search ad CPCs more than doubled between 2013 and 2020.
Advertiser harm
Google has the power to raise prices when it desires to do so, according to the DOJ. Google called this “tuning” in internal documents. The DOJ called it “manipulating.”
Format pricing, squashing and RGSP are three things harming advertisers, according to the DOJ:
Format pricing
- “Advertisers never pay more than their maximum bid,” according to Google.
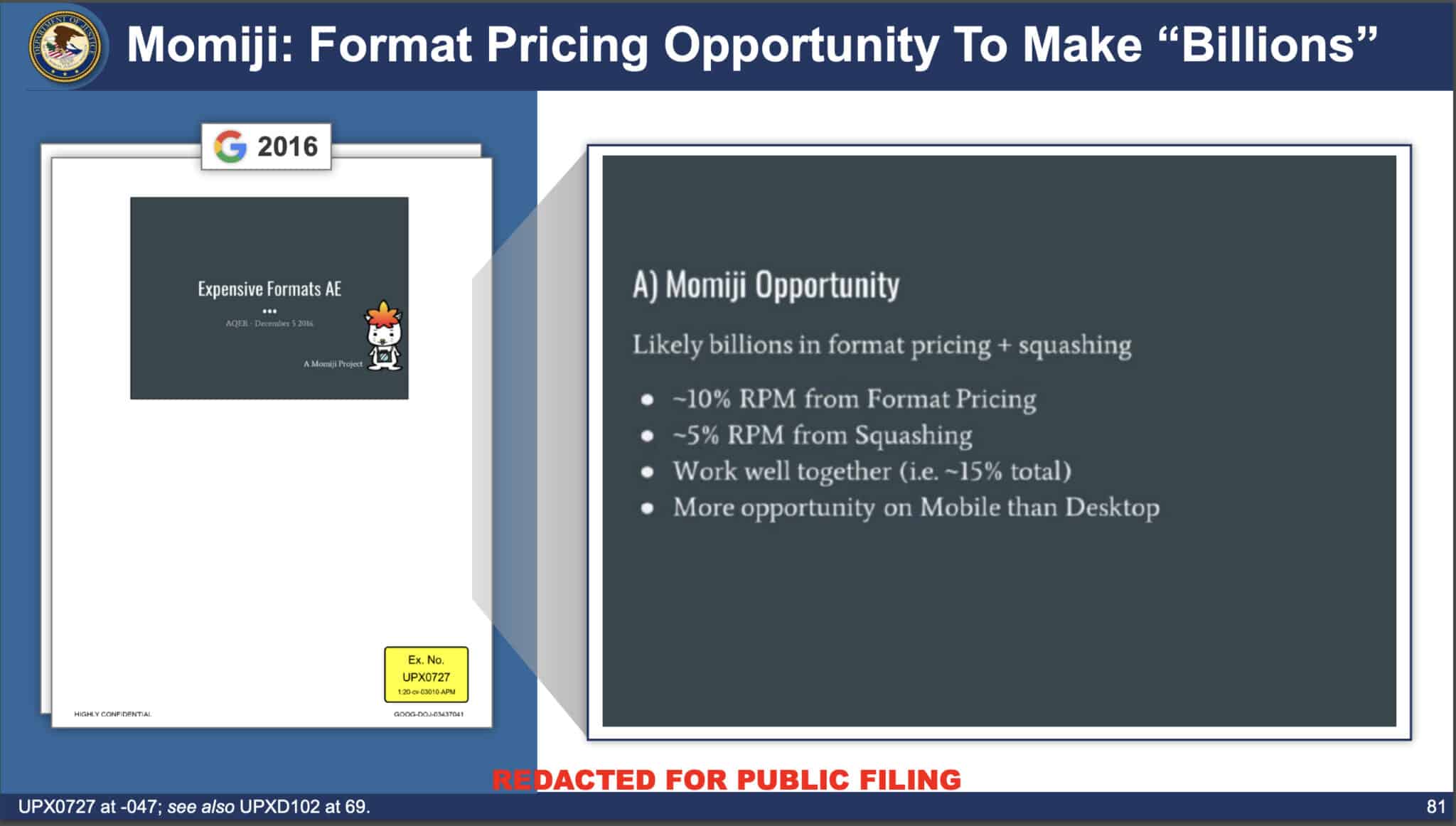
- Yes, but: What Google failed to mention is “Project Momiji,” which very quietly launched in 2017.
- What is Momiji: It artificially inflated the bid made by the runner-up.
- The result: A 15% increase for the “winning” advertiser. More ad revenue for Google.
- Relevant slides: From the DOJ’s deck:
Squashing
- How it worked: Google increased an advertiser’s lifetime value based on how far their predicted click-through rate (pCTR) was from the highest pCTR. According to a 2017 document introducing a new product called “Kumamon,” Google had been doing this using “a simple algorithm consisting of bid, three quality signals, and some (mostly) hand tuned parameters.” (A screenshot of this document seemed to indicate Kumamon would add more machine learning signals in the auction.)
- In other words: Google raised “the price against the highest bidder.”
- Google’s goal: To create a “more broad price increase.”
- The result: The Google ad auction winner paid more than it should have if squashing wasn’t part of the ad auction.
- And: The DOJ indicated this all led to a “negative user experience” as Google ranked ads “sub-optimally in exchange for more revenue.”
- Relevant slides: From the DOJ’s deck:
RGSP
- What is it: The Randomized Generalized Second-Price was introduced in 2019. (Dig deeper. What is RGSP? Google’s Randomized Generalized Second-Price ad auctions explained)
- How it worked: Google referred to it as the ability to “raise prices (shift the curve upwards or make it steeper at the higher end) in small increments over time (AKA ‘inflation’). It did not lead to better quality, according to 2019 Google emails.
- How Google talked about it: “A better pricing knob than format pricing.”
- The result: It incentivized advertisers to bid higher. Google increased revenue by 10%.
- Relevant slides: From the DOJ’s deck:
Search Query Reports
The lack of query visibility also harms advertisers, according to the DOJ. Google makes it nearly impossible for search marketers to “identify poor-matching queries” using negative keywords.
The DOJ’s presentation. You can view all 143 slides from the DOJ: Closing Deck: Search Advertising: U.S. and Plaintiff States v. Google LLC (PDF)
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
Google disavow link tool will go away at some point
Written on May 6, 2024 at 9:10 am, by admin

Google may do away with the disavow link tool within Google Search Console in the future. John Mueller, a Senior Search Analyst at Google, said on X, “At some point, I’m sure we’ll remove it,” referring to the disavow link tool.
What Google said. John Mueller responded to questions about the disavow tool, suggesting again that most sites do not need to use the feature. Here are those posts:
At some point, I'm sure we'll remove it.
I'm tempted to add something snarky regarding the conspiracy-posts, but I'll hold my tongue.
— John
…
(@JohnMu) May 4, 2024
Bing removed it. Earlier this year, Bing Webmaster Tools removed their disavow link tool. Back then Fabrice Canel from Microsoft explained that the disavow links tool is no longer needed now that the Bing Search algorithms are great at figuring out which links to count and which ones to ignore. “Times have changed, and so has our technology,” Canel wrote.
More. Google added the disavow link tool back in October 2012, then migrated to the new Google Search Console interface in 2020. Back then we explained why one would want to use this tool:
If you are concerned that you have bad links pointing to your site that may end up hurting your site’s performance in Google Search, you can give Google a list of URLs or domains you would like Google to ignore. This can be done for manual actions but likely is not needed, according to Google, for algorithmic issues since Google primarily just ignores bad links, as opposed penalizes for them algorithmically.
“If you have a manual action against your site for unnatural links, or if you think that you’re about to get one because of paid links or link schemes that violate our quality guidelines, ask the other site to remove those links,” said Google. “If you can’t get these links removed, then disavow those sites using this tool.”
Why we care. There are many SEOs who spend time disavowing links in Google Search Console. If and when Google drops the link disavow tool from Google Search Console, SEOs will no longer need to be busy with that task. Truth is, most SEOs probably should not be spending much time on this task at this point based on the communication Google has been providing over the past few years.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.
How to avoid an SEO disaster during a website redesign
Written on May 6, 2024 at 9:10 am, by admin
If you’ve been investing in SEO for some time and are considering a web redesign or re-platform project, consult with an SEO familiar with site migrations early on in your project.
Just last year my agency partnered with a company in the fertility medicine space that lost an estimated $200,000 in revenue after their organic visibility all but vanished after a website redesign. This could have been avoided with SEO guidance and proper planning
This article tackles a proven process for retaining SEO assets during a redesign. Learn about key failure points, deciding which URLs to keep, prioritizing them and using efficient tools.
Common causes of SEO declines after a website redesign
Here are a handful of items that can wreak havoc on Google’s index and rankings of your website when not handled properly:
- Domain change.
- New URLs and missing 301 redirects.
- Page content (removal/additions).
- Removal of on-site keyword targeting (unintentional retargeting).
- Unintentional website performance changes (Core Web Vitals and page speed).
- Unintentionally blocking crawlers.
These elements are crucial as they impact indexability and keyword relevance. Additionally, I include a thorough audit of internal links, backlinks and keyword rankings, which are more nuanced in how they will affect your performance but are important to consider nonetheless.
Domains, URLs and their role in your rankings
It is common for URLs to change during a website redesign. The key lies in creating proper 301- redirects. A 301 redirect communicates to Google that the destination of your page has changed.
For every URL that ceases to exist, causing a 404 error, you risk losing organic rankings and precious traffic. Google does not like ranking webpages that end in a “dead click.” There’s nothing worse than clicking on a Google result and landing on a 404.
The more you can do to retain your original URL structure and minimize the number of 301 redirects you need, the less likely your pages are to drop from Google’s index.
If you must change a URL, I suggest using Screaming Frog to crawl and catalog all the URLs on your website. This will allow you to individually map old URLs to any receiving changes. Most SEO tools or CMS platforms can import CSV files containing a list of redirects, so you’re stuck adding them one by one.
This is an extremely tedious portion of SEO asset retention, but it is the only surefire way to guarantee that Google will connect the dots between what is old and new.
In some cases, I actually suggest creating 404s to encourage Google to drop low-value pages from its index. A website redesign is a great time to clean house. I prefer websites to be lean and mean. Concentrating the SEO value across fewer URLs on a new website can actually see ranking improvements.
A less common occurrence is a change to your domain name. Say you want to change your website URL from “sitename.com” to “newsitename.com”, though Google has provided a means for communicating the change within Google Search Console via their Change of Address Tool, you still run the risk of losing performance if redirects are not set up properly.
I recommend avoiding a change in domain name at all costs. Even if everything goes off without a hitch, Google may have little to no history with the new domain name, essentially wiping the slate clean (in a bad way).
Webpage content and keyword targeting
Google’s index is primarily composed of content gathered from crawled websites, which is then processed through ranking systems to generate organic search results. Ranking depends heavily on the relevance of a page’s content to specific keyword phrases.
Website redesigns often entail restructuring and rewriting content, potentially leading to shifts in relevance and subsequent changes in rank positions. For example, a page initially optimized for “dog training services” may become more relevant to “pet behavioral assistance,” resulting in a decrease in its rank for the original phrase.
Sometimes, content changes are inevitable and may be much needed to improve a website’s overall effectiveness. However, consider that the more drastic the changes to your content, the more potential there is for volatility in your keyword rankings. You will likely lose some and gain others simply because Google must reevaluate your website’s new content altogether.
Metadata considerations
When website content changes, metadata often changes unintentionally with it. Elements like title tags, meta descriptions and alt text influence Google’s ability to understand the meaning of your page’s content.
I typically refer to this as a page being “untargeted or retargeted.” When new word choices within headers, body or metadata on the new site inadvertently remove on-page SEO elements, keyword relevance changes and rankings fluctuate.
Web performance and Core Web Vitals
Many factors play into website performance, including your CMS or builder of choice and even design elements like image carousels and video embeds.
Today’s website builders offer a massive amount of flexibility and features giving the average marketer the ability to produce an acceptable website, however as the number of available features increases within your chosen platform, typically website performance decreases.
Finding the right platform to suit your needs, while balancing Google’s performance metric standards can be a challenge.
I have had success with Duda, a cloud-hosted drag-and-drop builder, as well as Oxygen Builder, a lightweight WordPress builder.
Unintentionally blocking Google’s crawlers
A common practice among web designers today is to create a staging environment that allows them to design, build and test your new website in a “live environment.”
To keep Googlebot from crawling and indexing the testing environment, you can block crawlers via a disallow protocol in the robots.txt file. Alternatively, you can implement a noindex meta tag that instructs Googlebot not to index the content on the page.

As silly as it may seem, websites are launched all the time without removing these protocols. Webmasters then wonder why their site immediately disappears from Google’s results.
This task is a must-check before your new site launches. If Google crawls these protocols your website will be removed from organic search.
Dig deeper: How to redesign your site without losing your Google rankings
Tools for SEO asset migration
In my mind, there are three major factors for determining what pages of your website constitute an “SEO asset” – links, traffic and top keyword rankings.
Any page receiving backlinks, regular organic traffic or ranking well for many phrases should be recreated on the new website as close to the original as possible. In certain instances, there will be pages that meet all three criteria.
Treat these like gold bars. Most often, you will have to decide how much traffic you’re OK with losing by removing certain pages. If those pages never contributed traffic to the site, your decision is much easier.
Here’s the short list of tools I use to audit large numbers of pages quickly. (Note that Google Search Console gathers data over time, so if possible, it should be set up and tracked months ahead of your project.)
Links (internal and external)
- Semrush (or another alternative with backlink audit capabilities)
- Google Search Console
- Screaming Frog (great for managing and tracking internal links to key pages)
Website traffic
- Google Analytics 4
- Google Search Console
Keyword rankings
- Semrush (or another alternative with keyword rank tracking)
- Google Search Console
Information architecture
- Octopus.do (lo-fi wireframing and sitemap planning)
How to identify SEO assets on your website
As mentioned above, I consider any webpage that currently receives backlinks, drives organic traffic or ranks well for many keywords an SEO asset – especially pages meeting all three criteria.
These are pages where your SEO equity is concentrated and should be transitioned to the new website with extreme care.
If you’re familiar with VLOOKUP in Excel or Google Sheets, this process should be relatively easy.
1. Find and catalog backlinked pages
Begin by downloading a complete list of URLs and their backlink counts from your SEO tool of choice. In Semrush you can use the Backlink Analytics tool to export a list of your top backlinked pages.
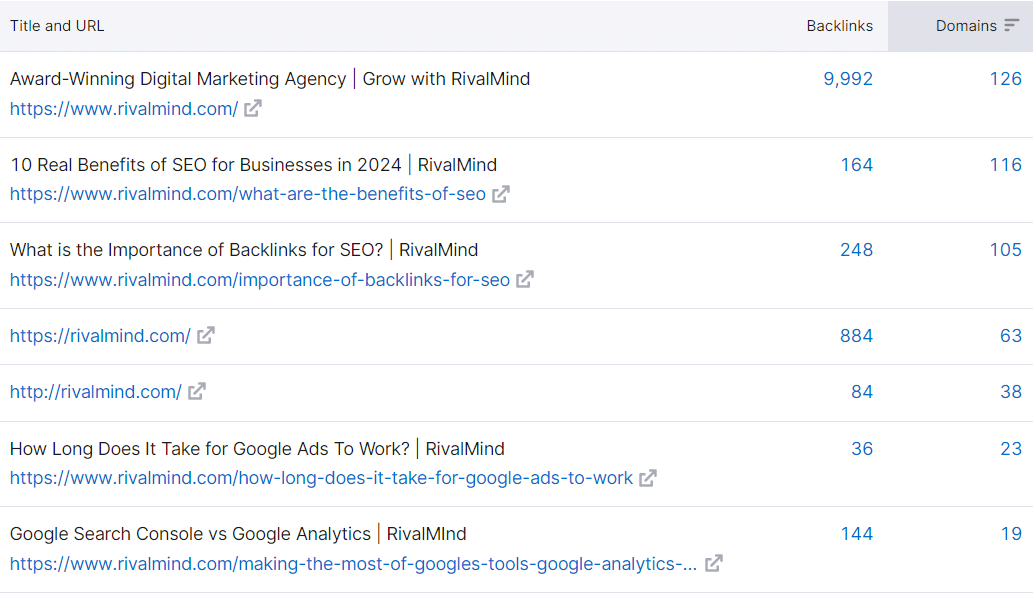
Because your SEO tool has a finite dataset, it’s always a smart idea to gather the same data from a different tool, this is why I set up Google Search Console in advance. We can pull the same data type from Google Search Console, giving us more data to review.
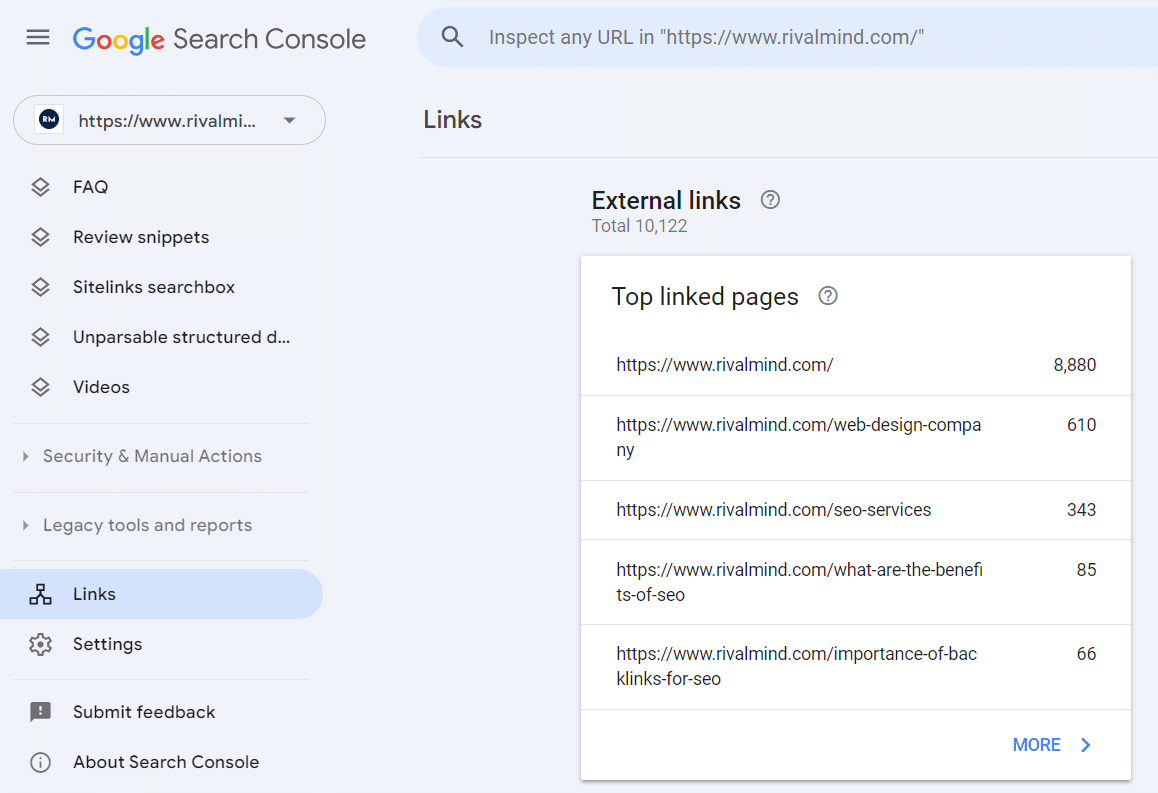
Now cross-reference your data, looking for additional pages missed by either tool, and remove any duplicates.
You can also sum up the number of links between the two datasets to see which pages have the most backlinks overall. This will help you prioritize which URLs have the most link equity across your site.
Internal link value
Now that you know which pages are receiving the most links from external sources, consider cataloging which pages on your website have the highest concentration of internal links from other pages within your site.
Pages with higher internal link counts also carry more equity, which contributes to their ability to rank. This information can be gathered from a Screaming Frog Crawl in the URL Details or Inlinks report.
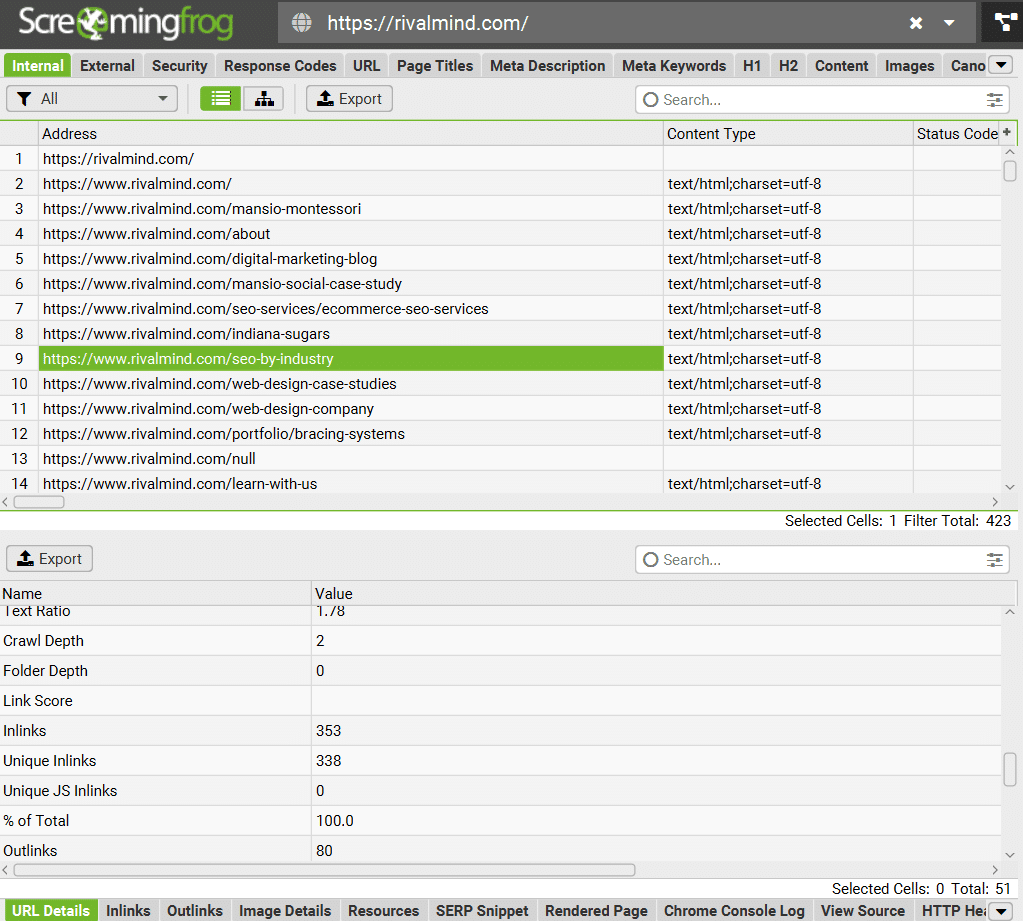
Consider what internal links you plan to use. Internal links are Google’s primary way of crawling through your website and carry link equity from page to page.
Removing internal links and changing your site’s crawlability can affect its ability to be indexed as a whole.
2. Catalog top organic traffic contributors
For this portion of the project, I deviate slightly from an “organic only” focus.
It’s important to remember that webpages draw traffic from many different channels and just because something doesn’t drive oodles of organic visitors, doesn’t mean it’s not a valuable destination for referral, social or even email visitors.
The Landing Pages report in Google Analytics 4 is a great way to see how many sessions began on a specific page. Access this by selecting Reports > Engagement > Landing Page.
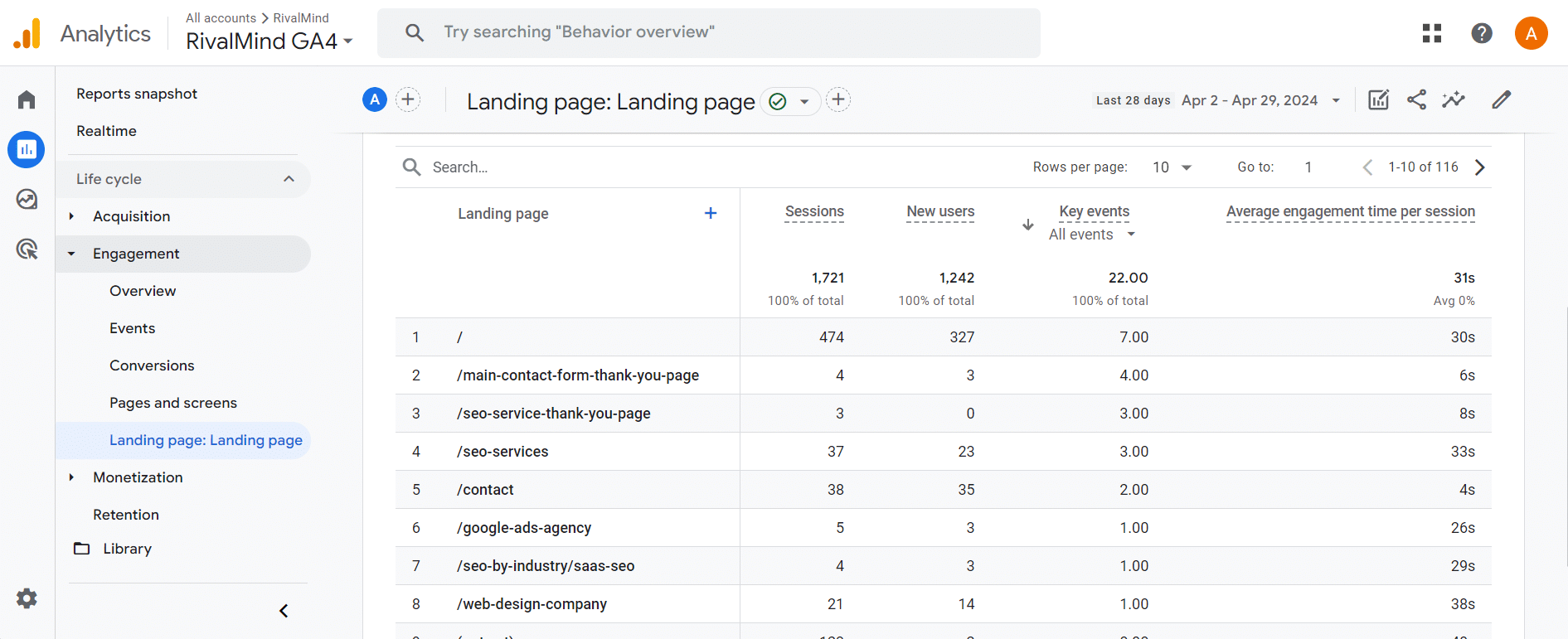
These pages are responsible for drawing people to your website, whether it be organically or through another channel.
Depending on how many monthly visitors your website attracts, consider increasing your date range to have a larger dataset to examine.
I typically review all landing page data from the prior 12 months and exclude any new pages implemented as a result of an ongoing SEO strategy. These should be carried over to your new website regardless.
To granularize your data, feel free to implement a Session Source filter for Organic Search to see only Organic sessions from search engines.
3. Catalog pages with top rankings
This final step is somewhat superfluous, but I am a stickler for seeing the complete picture when it comes to understanding what pages hold SEO value.
Semrush allows you to easily gather a spreadsheet of your webpages that have keyword rankings in the top 20 positions on Google. I consider rankings in position 20 or better very valuable because they usually require less effort to improve than keyword rankings in a worse position.
Use the Organic Research tool and select Pages. From here you can export a list of your URLs with keyword rankings in the top 20.
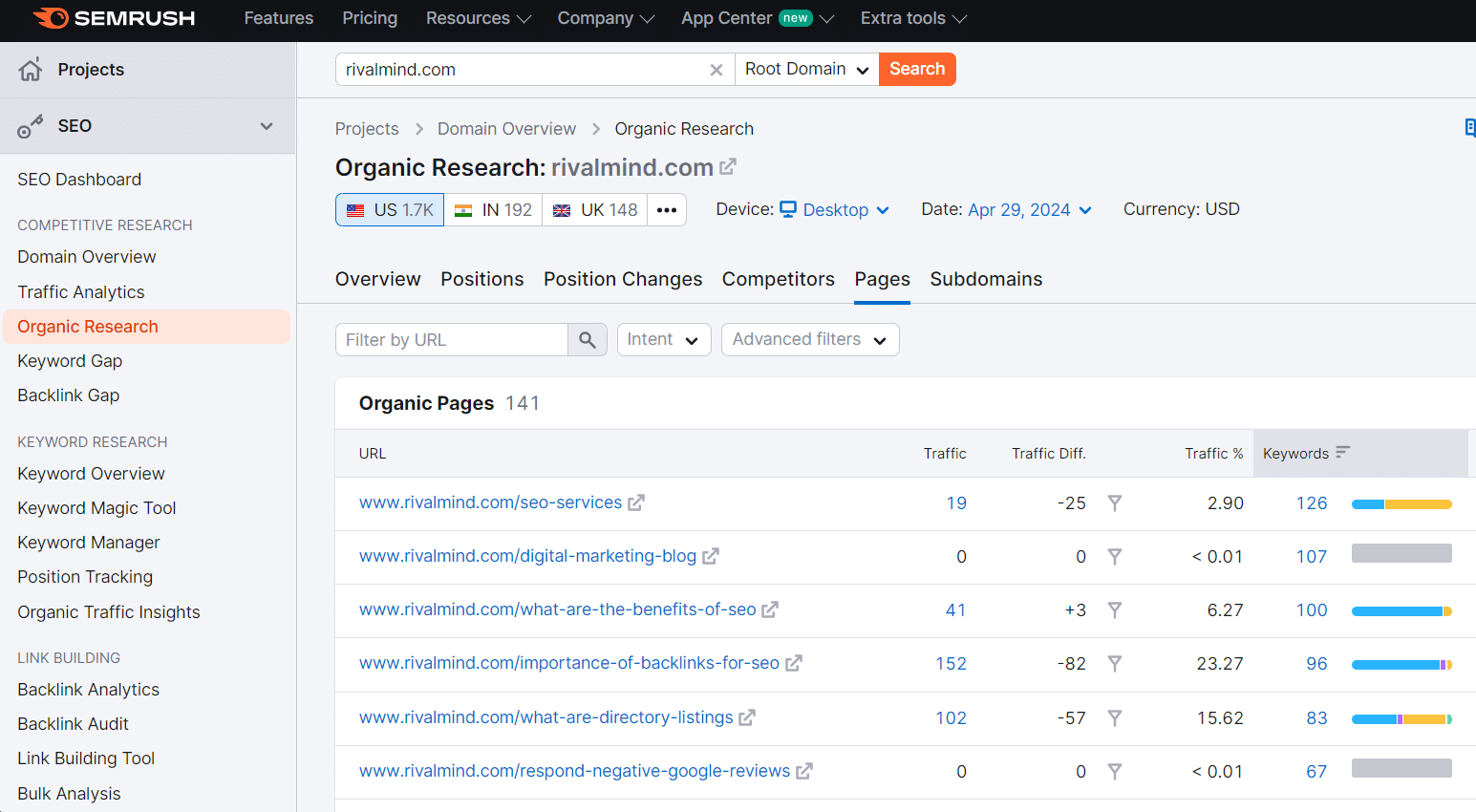
By combining this data with your top backlinks and top traffic drivers, you have a complete list of URLs that meet one or more criteria to be considered an SEO asset.
I then prioritize URLs that meet all three criteria first, followed by URLs that meet two and finally, URLs that meet just one of the criteria.
By adjusting thresholds for the number of backlinks, minimum monthly traffic and keyword rank position, you can change how strict the criteria are for which pages you truly consider to be an SEO asset.
A rule of thumb to follow: Highest priority pages should be modified as little as possible, to preserve as much of the original SEO value you can.
Seamlessly transition your SEO assets during a website redesign
SEO success in a website redesign project boils down to planning. Strategize your new website around the assets you already have, don’t try to shoehorn assets into a new design.
Even with all the boxes checked, there’s no guarantee you’ll mitigate rankings and traffic loss.
Don’t inherently trust your web designer when they say it will all be fine. Create the plan yourself or find someone who can do this for you. The opportunity cost of poor planning is simply too great.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Category seo news | Tags:
Social Networks : Technorati, Stumble it!, Digg, de.licio.us, Yahoo, reddit, Blogmarks, Google, Magnolia.