Archive for the ‘seo news’ Category
Friday, September 6th, 2024
Read it again: there was no leak. The information was shared with industry veterans.
It certainly is a treasure map for SEOs. Solving this puzzle will require our collective insight, critical thinking and analysis – if that’s even possible.
Why the pessimism?
It’s like when a chef tells you the ingredients to the delicious dish you’ve just consumed. You hurry to note it all down as he turns away.
But when you try recreating the same recipe at home, it’s nowhere near what you experienced at the restaurant.
It’s the same with the Google document “leak.” My perspective is our industry was given the types of ingredients used to determine the top search results, but no one knows how it’s all put together.
Not even the brightest two among us who were given access to the documentation.
If you recall…
In May, thousands of internal documents, which appear to have come from Google’s internal Content API Warehouse, claimed to have been leaked (per publication headlines).
In reality, they were shared with prominent industry SEO veterans, including Rand Fishkin, SparkToro co-founder. Fishkin outright acknowledged in his article that the information was shared with him.
In turn, he shared the documentation with Mike King, owner of iPullRank. Together and separately, they both reviewed the documentation and provided their own respective POVs in their write-ups. Hence, my take on all of this is that it’s strategic information sharing.
That fact alone made me question the purpose of sharing the internal documentation.
It seems the goal was to give it to SEO experts so they could analyze it and help the broader industry understand what Google uses as signals for ranking and assessing content quality.
“You don’t pay a plumber to bang on the pipe, you pay them for knowing where to bang.”
There’s no leak. An anonymous source wanted the information to be more broadly available.
Going back to the restaurant metaphor, we can now see all the ingredients, but we don’t know what to use, how much, when and in what sequence (?!), which leaves us to continue speculating.
The reality is we shouldn’t know.
Google Search is a product that’s part of a business owned by its parent company, Alphabet.
Do you really think they would fully disclose documentation about the inner workings of their proprietary algorithms to the world? That’s business suicide.
This is a taste.
For established SEOs, the shared Google documentation that’s now public sheds light on some of the known ranking factors, which largely haven’t changed:
- Ranking features: 2,596 modules are represented in the API documentation with 14,014 attributes.
- Existence of weighting of the factors.
- Links matter.
- Successful clicks matter.
- Brand matters (build, be known).
- Entities matter.
Here’s where things get interesting because the existence of some aspects means Google can boost or demote search results:
- SiteAuthority – Google uses it but also denied having a website authority score
- King’s article has a section called “What are Twiddlers.” While he goes on to say there’s little information about them, they’re essentially re-ranking functions or calculations.
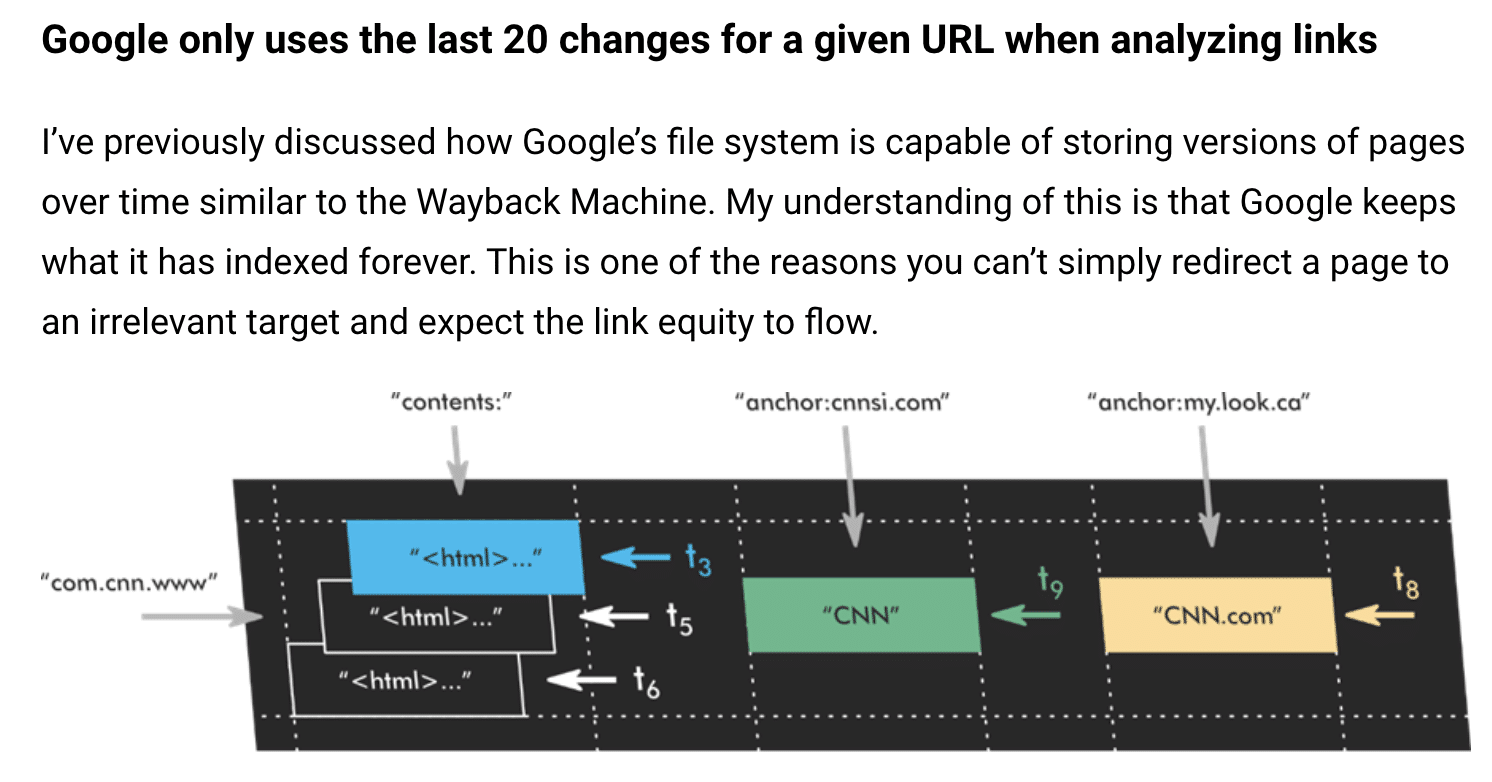
- King’s article “Google only uses the last 20 changes of a URL when analyzing links.” Again, this sheds some light on the idea that Google keeps all the changes they’ve ever seen for a page.
Both Fishkin and King’s articles are lengthy, as one might expect.
If you’re going to spend time reading through either articles or – tip of the cap to you – the documents themselves, may you be guided by this quote by Bruce Lee that inspired me:
“Absorb what is useful, discard what is not, add what is uniquely your own.”
Which is what I’ve done below.
My advice is to bookmark these articles because you’ll want to keep coming back to read through them.
Rand Fishkin’s insights
I found this part very interesting:
“After walking me through a handful of these API modules, the source explained their motivations (around transparency, holding Google to account, etc.) and their hope: that I would publish an article sharing this leak, revealing some of the many interesting pieces of data it contained and refuting some “lies” Googlers “had been spreading for years.”
The Google API Content Warehouse exists in GitHub as a repository and directory explaining various “API attributes and modules to help familiarize those working on a project with the data elements available.”
It’s a map of what exists, what was once used and is potentially currently being used.
Which ones and when is what remains open to speculation and interpretation.
Smoking gun
We should care about something like this that’s legitimate yet speculative because, as Fishkin puts it, it’s as close to a smoking gun as anything since Google’s execs testified in the DOJ trial last year.
Speaking of that testimony, much of it is corroborated and expanded on in the document leak, as King details in his post.  But who has time to read through and dissect all that?
But who has time to read through and dissect all that?
Fishkin and King, along with the rest of the SEO industry, will be mining this set of files for years to come. (Including local SEO expert Andrew Shotland.)
To start out, Fishkin focuses on five useful takeaways:
- NavBoost and the use of clicks, CTR, long vs. short clicks and user data.
- Use of Chrome browser clickstreams to power Google Search.
- Whitelists in travel, COVID-19 and politics.
- Employing quality rater feedback.
- Google uses click data to determine how to weight links in rankings.
Here’s what I found most interesting:
NavBoost is one of Google’s strongest ranking signals
Fishkin cites “Click Signals In NavBoost” in his article, which is where sharing proprietary information is helpful, a lot more of us now know we should be doing our homework on the NavBoost system. Thank you, Rand!
In case you weren’t aware, that’s coming from Google engineer Paul Haahr. One time, we were in the same conference room together. I feel like I got a tad smarter listening to him.
QRG feedback may be directly involved in Google’s search system
Seasoned SEOs know the QRG is a great source of tangible information for evaluating one’s own site against what Google is asking paid human beings to evaluate quality web results against. (It’s the OG SEO treasure map.)
What’s important about what we learned from this documentation is that quality raters’ feedback might play a direct role in Google’s search system, not just serve as surface-level training data.
This is another reason to carefully read and understand the documentation.
But seriously, high level it for me, Rand
Now, for the non-technical folks, Fishkin also provides an overview to marketers in a section titled “Big Picture Takeaways for Marketers who Care About Organic Search Traffic.” It’s great. It covers things that resonate, like:
- The importance of “building a notable, popular, well-recognized brand in your space, outside of Google search.”
Large, established and trusted brands are what Google likes to send traffic to, subsequently, in favor of smaller publishers. Who knows, maybe that landscape will shift with the latest August 2024 core update.
- He mentions that E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authority, trust) exists, but there are no direct correlations in the documentation.
I don’t think that makes those aspects any less important because there are a fair bit of actionable steps a marketer can take to better reflect these quality/quantity signals.
Fishkin also points to his research on organic traffic distribution and his hypothesis that for most SMBs and small website publishers, SEO yields poor returns. “SEO is a big brand, popular domain’s game.”
The data doesn’t lie, but the broader context is in line with what former in-house enterprise SEO turned consultant Eli Schwartz says: SEO needs to have a product-market fit because, in my experience, it’s an awareness and acquisition channel, not one for demand creation.
Read Fishkin’s article if you’re a marketer looking to get a basic understanding of the shared documentation. King’s article is a lot lengthier and more nuanced for the more seasoned SEOs.
Mike King’s insights
For starters, I completely agree with King here:
“My advice to future Googlers speaking on these topics: Sometimes it’s better to simply say ‘we can’t talk about that.’ Your credibility matters and when leaks like this and testimony like the DOJ trial come out, it becomes impossible to trust your future statements.”
I realize Googlers don’t want to tip their hand by not saying something, but when leaks strategic sharing of information like this surface, people still draw their own conclusions.
It’s no secret that Google uses multiple ranking factors. This documentation pointed to 14,000 ranking features and more, to be exact. King notes this in his article:
King also cites a shared environment where “all the code is stored in one place, and any machine on the network can be a part of any of Google’s systems.”
Talk Matrix to me, Neo.
Truthfully, though, King’s thorough post is probably one of those forever-open Chrome tabs I’ll always have.
I did appreciate this high-level section titled “Key revelations that may impact how you do SEO.” This is what those of us skim readers came for.
King helps SEOs boil the ocean in this section by giving his main takeaways. My personal top takeaways from this section were this:
“The bottom line here is that you need to drive more successful clicks using a broader set of queries and earn more link diversity if you want to continue to rank. Conceptually, it makes sense because a very strong piece of content will do that. A focus on driving more qualified traffic to a better user experience will send signals to Google that your page deserves to rank.”
Then this:
“Google does explicitly store the author associated with a document as text.”
So, while E-E-A-T may be nebulous aspects of expertise and authority to score, they are still accounted for. That’s enough proof for me to continue advising for it and investing in it.
Lastly, this: (within the Demotions section)
“Anchor Mismatch – When the link does not match the target site it’s linking to, the link is demoted on the calculations. As I’ve said before, Google is looking for relevance on both sides of a link.”
Lightbulb moment. In the back of my head, I know the importance of anchor text. But it was good to be reminded of the specific way in which relevance is communicated.
Internal and external linking can seem like an innocuous technical SEO aspect, but they serve as a reminder of the care required when using links.
See, it is valuable to read other SEO veterans’ evaluations because you just might learn something new.
My top 5 takeaways for SEOs from the sharing of internal Google documents
You’ve heard from the best, now here are my recommendations to websites that want to benefit from sustainable, organic growth and revenue opportunities.
Always remember, online, your two primary “customers” of your website are:
- Search engine bots (i.e., Googlebot).
- Humans searching for solutions to their problems, challenges and needs.
Your website needs to be cognizant of both and focus on maintaining and improving these factors:
1. Discovery
Ensuring your site is crawlable by search engine bots so that it is in the online index.
2. Decipher
Make sure search engines and humans easily understand what each page on your site is about. Use appropriate headings and structure, relevant internal links etc.
Yes, I said each page because people can land on any page of your website from an online search. They don’t automatically start at the homepage.
3. User experience
UX matters, again, for bots and people.
This is a double-edged sword, meaning that the page needs to load quickly (think CWV) to be browsed and the overall user interface is designed to serve the human user’s needs, “What is their intent on that page?”
A good UX for a bot typically means the site is technically sound and receives clear signals.
4. Content
What are you known for? These are your keywords, the information you provide, the videos and the demonstrated experience and expertise (E-E-A-T) in your vertical.
5. Mobile-friendly
Let’s face it, Googlebot looks for the mobile version of your site first to crawl. “Mobilegeddon” has been a thing since 2015.
Why you should always test and learn
For example, the rankings of exact match domains continue to fluctuate constantly.
As someone with a background in local SEO search directories, I continue to evaluate whether exact-match domains improve or lose rankings because Google’s advancements in this area interest me.
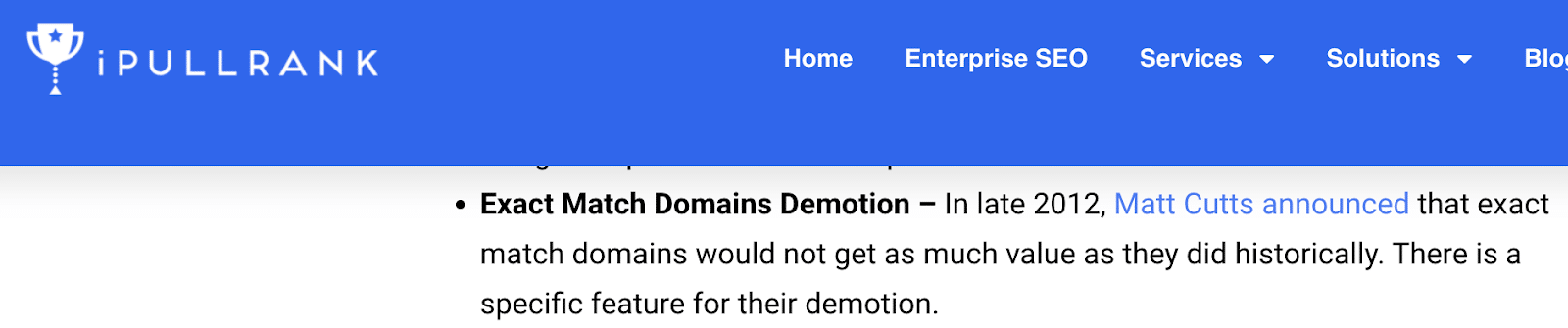
“Exact Match Domains Demotion – In late 2012, Matt Cutts announced that exact match domains would not get as much value as they did historically. There is a specific feature for their demotion.”
Personally, in my research and observation working with small businesses for keywords with very, very specific and low (10 or less) search volume, I haven’t found this to be an absolute. I may have found an outlier. Ha, or an actual leak.
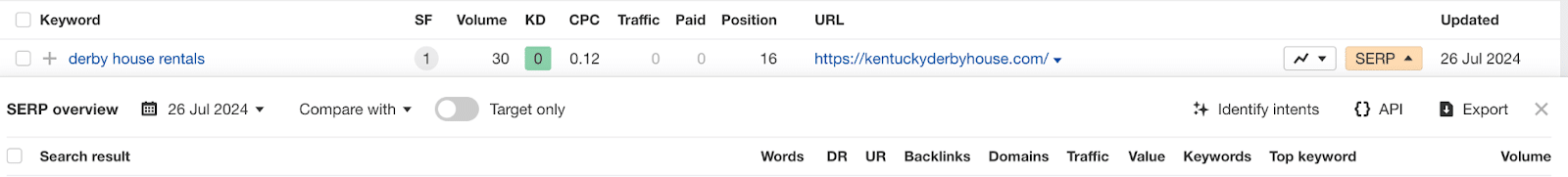
Here’s what I mean: every Saturday in May, a lot of people will want to be in Kentucky at Churchill Downs for the fastest two minutes in sports, the Kentucky Derby.
The rental homes and properties SERP is dominated by marketplace sites, from Airbnb to Kayak to VRBO and Realtor.com. But there’s one hanging on in this pack. In opposition 8, it’s an exact match domain.
 Source: Ahrefs organic keywords report
Source: Ahrefs organic keywords report
Has it been demoted? Maybe.
It’s also, in its own way, an aggregator site, listing a handful of local rental properties.
So while it’s not a name brand aggregator site, it has hyper-local content and, therefore, may continue to weather the storm.
It could also be a core update away from being bounced onto page 2. Nothing to do but ride it until it bucks you.
Heck, the organic listing above it is ranking for the incorrect location “Derby, NY.”
So, is Google search perfectly ranking all query types? Neigh.
NavBoost highlights
For those who haven’t been paying close enough attention. Meet NavBoost.
The documentation mentioned NavBoost is a system that employs click-driven measures to boost, demote, or otherwise reinforce a ranking in Web Search.
Various sources have indicated that NavBoost is “already one of Google’s strongest ranking signals.”
The leaked shared documentation specifies “Navboost” by name 84 times, with five modules featuring Navboost in the title. That’s promising.
There is also evidence that they contemplate its scoring on the subdomain, root domain and URL level, which inherently indicates they treat different levels of a site differently.
It’s worth continuing to research and process Google’s patent and use of NavBoost.
Conclusion
It’s a gift to continue to have great minds in the SEO space like Fishkin and King, who can distill large amounts of documentation into actionable nuggets for us mortals.
None of us know how the data is used or weighted. But we now know a bit more about what’s collected and that it exists as part of the data set used for evaluation.
In my professional opinion, I’ve always taken statements from Google with a grain of salt because, in a way, I’m also intimately familiar with being a brand ambassador for a publicly traded company.
I don’t think any corporate representative is actively trying to be misleading. Sure, their responses can be cryptic at times, but they fundamentally can’t be explicit about any form of internal operating system because it’s core to the business’s success.
One reason why Google’s DOJ testimony is so compelling. But it can be difficult to comprehend. At the very least, Google’s own Search Central documentation is often more succinct.
The shared internal document is the best we’re going in terms of learning what’s actually included in Google’s “secret sauce.”
Because we’ll never fully know, my practical advice to practicing SEOs is to take this additional information we now have and to keep testing and learning from it.
After all, Google and all of its algorithms are, in parallel, doing the same along the path of being better than they were the day before.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, September 4th, 2024
Google will launch a new consolidated resource on Oct. 3, called “Masthead format requirements.” This new page will streamline all requirements for masthead ads across YouTube and Google TV, providing a centralized reference point for advertisers.
Why we care. While the specific requirements for YouTube masthead ads remain unchanged, this move to consolidate guidelines into one location simplifies the process for advertisers. Ensuring compliance with these requirements is crucial, as non-compliant ads will not be eligible to serve as masthead ads.
What’s happening.
- Launch date: The new help center page will go live on Oct. 3.
- Preview available: A preview of the Masthead format requirements is accessible, so you can familiarize yourself with the consolidated guidelines ahead of the official launch.
- Policy enforcement: The English version of this page will serve as the official language for policy enforcement, although translated versions will be available for reference.
Bottom line: You should review the Masthead format requirements to ensure their ads comply and remain eligible to serve on premium surfaces like YouTube and Google TV. With the official launch just weeks away, taking action now can prevent disruptions in campaign performance.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, September 4th, 2024
Google is testing a new display and user interface for forum content within its search results. “We’re testing a new display for forum content when it appears in search results, allowing people to quickly view top comments and related discussions to help them find useful information and dig deeper,” a Google spokesperson told us.
What is this new display. The new display will highlight the “top comments” on a specific discussion forum thread and then also highlight related discussions on that topic.
Google told us that searchers often want to learn from others’ experiences with a topic, and because of that, Google is trying new ways to highlight those experiences in Google Search. This is in addition to the “Discussions and Forums” feature and the Forums filter, previously named perspectives.
Google has shown “top answers” for years, a decade actually, but this new UI shows more to the searcher. Google told us also that in some cases, Google has agreements from a forum to show these additional details. I assume this is about the Reddit partnership. But Google added that it surfaces content from hundreds of forums and other communities across the web.
What it looks like. Here is a mock up of the interface that a Google representative sent me, showing the “top comments” section” and also the “related content” section – you can click to enlarge the image:
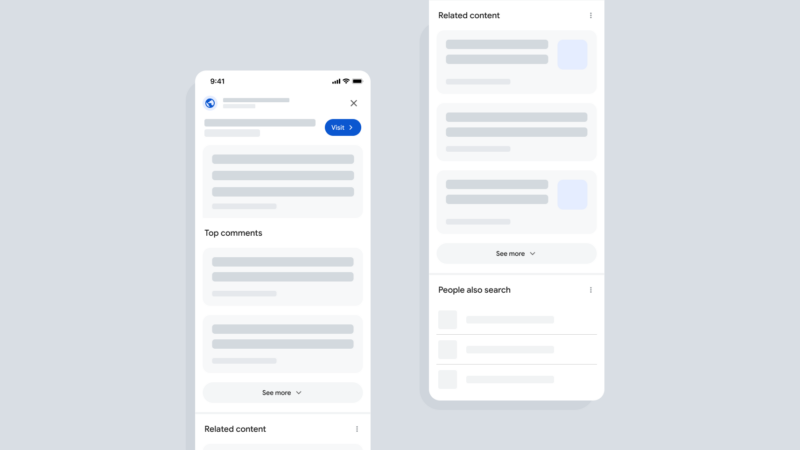
No impact on rankings. Google said this search feature has no impact on rankings. Again, it does not affect how forum pages rank in Google Search for a given query. This is just a new way for people to access this content, and it appears on searches where forum content would have already surfaced in results.
Why we care. Like Google doesn’t show enough forum content, i.e. Reddit, in the search results, Google is now testing showing this content with new features. Google will show the top comments and related comments for these forum results.
We’ve seen Google testing various flavors of this before, but this one seems different.
It is unclear when and if this will fully roll out but Google is testing it now to see how it performs.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, September 4th, 2024
With the emergence of conversational AI models like ChatGPT, there is an increasingly loud debate about how the future of search and information retrieval could evolve.
Traditional search engines like Google have long been the primary method for accessing information on the web. Now, advanced AI models offer a new approach to finding and retrieving information.
Let’s discuss the potential of ChatGPT and other AI models to disrupt search, drawing comparisons to traditional search engines and exploring their future role in the domain of digital marketing and beyond.
The traditional search engine model
Google has led search for over 20 years and still controls about 90% of the global search market. Traditional search engines work using a web index-based model, crawling vast pages of information on the web and ranking their results according to relevance and authority.
This model is highly effective for users searching for specific information, research or products. It makes vast resources accessible in seconds with just a few keywords.
Some of the key features of traditional search engines are the following:
- Keyword-based searching: Users input keywords and the search engine returns a list of relevant web pages.
- Page ranking: Algorithms rank pages based on relevance, user engagement and other factors.
- Ad integration: Sponsored results and advertisements are integrated into search results, forming a significant revenue stream.
- Wide data access: Search engines index a vast array of websites, providing comprehensive access to information across the web.
The rise of conversational AI: ChatGPT
Conversational AI, such as ChatGPT by OpenAI, has blurred the lines between man and machine, moving toward interactive, even subtle, information retrieval.
While the classical model of a search engine returns a list of results, ChatGPT engages the user in conversation, providing more personalized and context-aware responses.
These AI models, trained with vast amounts of data, can understand and generate text that closely mimics human conversation, making interactions feel natural and conversational.
ChatGPT brings unique benefits to the table, transforming the way we access and engage with information:
- Natural language understanding: ChatGPT excels at understanding and processing natural language queries, allowing users to ask questions in a conversational manner without needing to think in terms of keywords.
- Contextual awareness: The model retains context over multiple interactions, enabling more coherent and relevant responses during extended conversations.
- Personalization: By understanding user preferences and previous interactions, ChatGPT can tailor responses to individual needs.
- Real-time interaction: Users can receive immediate feedback and clarification, enhancing the user experience.
Comparing ChatGPT and traditional search engines
Search precision and depth
Traditional search engines are very good at being precise and wide, returning many different results.
Google’s algorithms grasp the precise meaning of keywords and determine the relevancy of top-ranking results based on many signals.
Contrast this with ChatGPT, which essentially contains richness through interaction.
It won’t provide you with an avalanche of results like a keyword search, but it will give you detailed descriptions, summaries and recommendations on specific queries. It’s a deep tool for a complex query where sense and context come into play.
User experience
The user experience differs significantly between the two models. Traditional search engines provide a straightforward list of links that users can explore.
This approach is efficient for those who know what they are looking for and prefer to browse multiple sources.
Conversational AI offers a more interactive and engaging experience. Users can ask follow-up questions and seek clarifications in real time, making the search process feel more like a dialogue with a knowledgeable assistant.
This can be particularly advantageous for users seeking comprehensive understanding without needing to navigate multiple web pages.
Limitations and challenges
Despite its advantages, ChatGPT has limitations. One significant challenge is the potential for generating inaccurate or misleading information.
While traditional search engines rank results based on credibility and authority, conversational AI might generate responses that sound plausible but are not necessarily accurate.
Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of AI-generated content is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed.
Additionally, traditional search engines benefit from a well-established ecosystem of SEO practices. Businesses and content creators have long adapted their strategies to align with search engine algorithms.
In contrast, optimizing content for conversational AI is still a developing field, requiring new approaches and metrics.
The impact on SEO and search marketers
The rise of conversational AI models is set to change SEO strategies and how search marketers work.
As these AI models become more important, traditional SEO tactics may need to be adjusted to fit this new approach.
Shift in SEO strategies
SEO has traditionally focused on optimizing content to rank highly in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves keyword optimization, backlink building and ensuring high-quality, relevant content.
However, with the introduction of conversational AI, SEO strategies must evolve to meet the demands of these new tools:
- Natural language optimization: Content must be optimized for natural language queries. This means shifting from short, keyword-focused phrases to more conversational language that aligns with how users interact with AI models like ChatGPT.
- Answering specific questions: Instead of simply ranking for keywords, content must be tailored to answer specific questions comprehensively. AI models excel at providing detailed responses to queries, so content should be structured to provide clear, concise answers.
- Enhanced content structure: Content should be organized to make it easy for AI models to extract and present information. This could involve using more headings, bullet points and summaries to improve readability and accessibility.
Dig deeper: What is generative engine optimization (GEO)?
New opportunities for search marketers
The shift towards conversational AI also presents new opportunities for search marketers:
- Personalized marketing campaigns: By leveraging the personalized nature of AI interactions, marketers can create more targeted campaigns that resonate with individual user preferences and behaviors.
- Content for conversational interfaces: Marketers can develop content specifically designed for conversational interfaces, creating a more engaging experience for users interacting with AI-powered search tools.
- Real-time user engagement: Conversational AI allows for real-time interaction, enabling marketers to engage users directly and provide immediate responses to inquiries, potentially increasing conversion rates.
The future of information retrieval
The future of information retrieval is likely to be a hybrid model combining traditional search engines’ strengths and conversational AI. This hybrid approach can offer a more comprehensive, accurate and engaging search experience.
- Hybrid search models: Search engines might evolve to incorporate conversational interfaces such as Google’s Gemini, providing users with both traditional search results and interactive, AI-generated responses.
- Improved AI training: Ongoing advancements in AI training methods will enhance the accuracy and reliability of conversational models, addressing current limitations.
- Regulation and ethical considerations: As AI becomes more integrated into search and information retrieval, ensuring ethical use and preventing the spread of misinformation will be critical. Regulatory frameworks and industry standards will play a vital role in guiding the development and deployment of these technologies.
Redefining search: How ChatGPT is challenging traditional search
Though ChatGPT and other conversational AI models will make a huge impact on the future of search and information retrieval, traditional search engines like Google will still hold dominance – and that won’t change any time soon.
At the same time, in the future, when AI models are strongly implemented inside search engines, so will SEO strategies and the work of search marketers.
The answer lies in optimizing by natural language, answering questions comprehensively and making the most of the AI-driven personalized marketing opportunities.
Understanding both the strengths and limitations of traditional search engines and conversational AI will help us navigate the evolving digital landscape more effectively.
Balancing accuracy with engaging presentation will shape how we search for and interact with information online.
Dig deeper: How to win with generative engine optimization while keeping SEO top-tier
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, September 4th, 2024
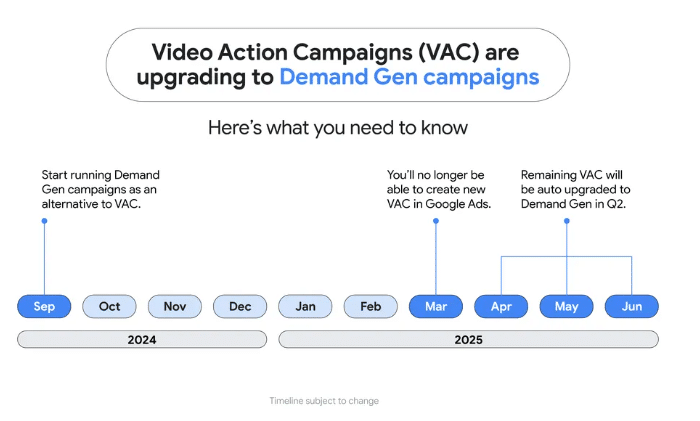
Google Ads is merging its Video Action Campaigns (VAC) into the more versatile Demand Gen campaigns starting Q2 2025. This shift aims to enhance advertisers’ ability to capture emerging demand and drive growth through a multi-format approach.
Why we care: Advertisers using VAC could see significant benefits from adopting Demand Generation campaigns. Combining video and image assets in Demand Generation can increase conversions by 20% at the same cost per action (CPA), compared to those relying solely on video, according to Internal Google data.
The details:
- Expanded reach: Demand Gen campaigns will allow advertisers to engage with up to 3 billion monthly users across YouTube, Discover and Gmail.
- Creative flexibility: Advertisers can use both video and image ads in a single campaign, with granular insights available to optimize creative strategies.
- Enhanced audience targeting: Lookalike segments in Demand Gen help brands reach new audiences similar to their existing customer base.
- Consistent performance: Advertisers using only video assets in Demand Gen have seen performance comparable to VAC, ensuring a smooth transition without compromising results.
What’s next. Here’s the transition timeline:
- Now: Advertisers are advised to start running Demand Gen campaigns and explore its advanced features.
- Early 2025: Google will launch a migration tool for manual upgrades from VAC to Demand Gen.
- March 2025: Google Ads will disable creation of new VACs.
- Q2 2025: Automatic upgrades of all remaining VACs to Demand Gen will occur.
Success stories: Google, as usual, highlighted a well-known brand – DoorDash, a U.S.-based food delivery service – to help make a case for Demand Gen. According to Google:
- DoorDash reported a 15x higher conversion rate and a 50% more efficient CPA using Demand Gen compared to VAC.
Bottom line: This latest update represents a strategic move to meet evolving consumer expectations following ad format preferences updates in Demand Gen earlier this year. Testing Demand Gen and VAC now can give you a head start in leveraging these tools to drive stronger, more efficient results before your competition catches up.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, September 3rd, 2024
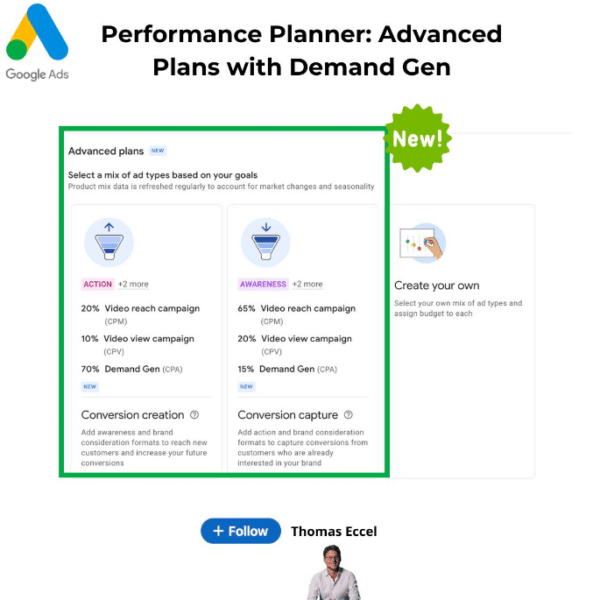
Google Ads launched advanced “Performance Planner” plans, now including tailored strategies for YouTube campaigns, with a focus on Demand Gen for both Action and Awareness goals.
Why we care. These new plans allow advertisers to better align their full marketing strategy with campaign goals, offering customizable options for budget, ad format, buying method, and campaign objectives—whether aiming for conversions or building brand awareness.
Key features:
Action Plans. Prioritize conversions with a mix of Video Reach, Video View, and Demand Gen campaigns.
Awareness Plans. Focus on brand visibility, incorporating Video Reach and Demand Gen campaigns to capture conversions.
Pro tip. Demand Gen estimates assume a mix of image and video creatives, allowing for more versatile campaign execution.
First seen. We were first alerted to this update from Thomas Eccel’s LinkedIn:
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, September 3rd, 2024
Google’s August 2024 core update is now done rolling out, a Google spokesperson told us. It started on August 15, 2024 and completed 19 days later on September 3, 2024. This update caused a lot of ranking movement and changes to the overall Google Search results.
As we said before, this update is not just a normal core update. The August 2024 core update took into account the feedback Google heard since the September 2023 helpful content update that seemed to have a negative impact on many small and independent publishers.
What we saw. In fact, we saw some movement for the first time with some (not all) sites hit by that update. I recent poll I ran showed that most who took the poll were negatively impacted by the last core update:
- 44% said My Rankings/Traffic Are Down (total votes 1,583)
- 27% said My Rankings/Traffic Are Up (total votes 993)
- 29% said No Change (total votes 1,038)
Overall, it seems like while we saw some recoveries from the September helpful content in 2023, that was only for a few sites and limited recoveries. Most sites did not see significant or meaningful recoveries, from what we can tell. And even more sites saw even more declines or just stayed the same.
Ranking bug. The first four or so days of the August core update, we also had a big search ranking bug that was fixed 4 days later. So, you should disregard any movement you saw during those first four days or so. You should compare the rankings and traffic you have seen from Google this week, going forward, compare to the weeks prior to the release of the August core update.
What Google said about the August core update. John Mueller, Search Advocate at Google, wrote when the update was originally released.
- “Today, we launched our August 2024 core update to Google Search. This update is designed to continue our work to improve the quality of our search results by showing more content that people find genuinely useful and less content that feels like it was made just to perform well on Search.”
Google said this update aims to promote useful content from small and independent publishers, after Google listened to feedback it received since the release of the March 2024 core update. Mueller added:
- “This latest update takes into account the feedback we’ve heard from some creators and others over the past few months. As always, we aim to connect people with a range of high quality sites, including ‘small’ or ‘“’independent’ sites that are creating useful, original content on relevant searches. This is an area we’ll continue to address in future updates.”
This August 2024 core update “aims to better capture improvements that sites may have made, so we can continue to surface the best of the web,” Mueller added.
Guidance updated. Google posted several updates to its help page about core updates, including more in-depth guidance for those who may see changes after an update.
Previous core updates. The previous core update – the March 2024 core update – was the largest core update, according to Google. It started March 5 and completed 45 days later on April 19.
Here’s a timeline and our coverage of recent core updates:
What to do if you are hit. Google has given advice on what to consider if you are negatively impacted by a core update in the past. Google has not really given much new advice here.
- There aren’t specific actions to take to recover. A negative rankings impact may not signal anything is wrong with your pages.
- Google has offered a list of questions to consider if your site is hit by a core update.
- Google said you can see a bit of a recovery between core updates but the biggest change would be after another core update.
In short, write helpful content for people and not to rank in search engines.
- “There’s nothing new or special that creators need to do for this update as long as they’ve been making satisfying content meant for people. For those that might not be ranking as well, we strongly encourage reading our creating helpful, reliable, people-first content help page,” Google said previously.
Why we care. By now, you should probably see the trend of this update and how it may have affected your website. If you noticed improvements, then great – if not, then maybe you have more work to do so Google will deem your site helpful enough to rank better in the Google search results.
Google releases core update every few to several months, so you should always continue to work on improving your site and the content on your site. Future updates may benefit your site’s ranking and Google traffic – so always be working on improvements – not just for Google Search but also for your website users.
Google did tell us there won’t be a feedback form for this update.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, September 3rd, 2024
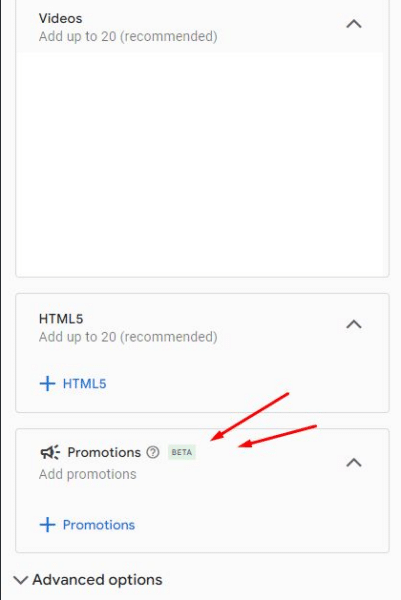
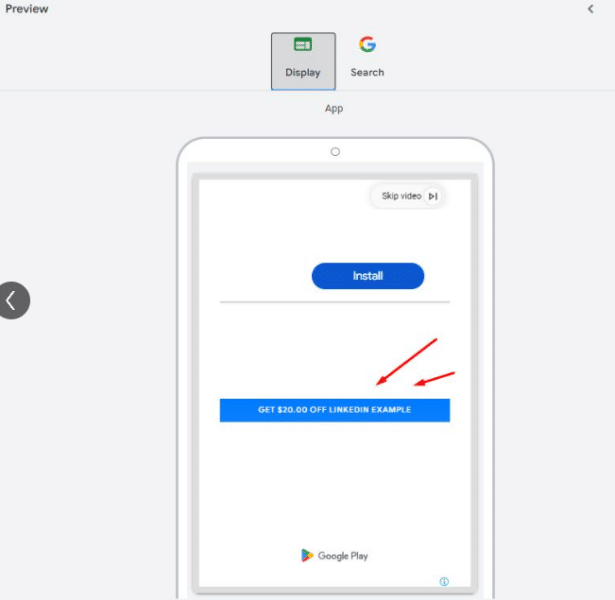
Google Ads is quietly testing a new “Promotions” feature within App Campaigns, offering advertisers a fresh way to drive engagement during key events. This beta feature is currently only available to a limited number of ad accounts, making it a rare find.
Why we care: This new tool allows advertisers to create app-specific promotions, similar to those available in web campaigns, but tailored for mobile users. With options to customize for occasions like Black Friday or Christmas and choose between different promotion types, advertisers can now boost app engagement and conversions more effectively.
How it works: The feature includes fields like occasion selection, promotion type (e.g., percent discount), item name, and a pre-filled final URL for the app. Advanced options allow for tracking URLs and scheduling, ensuring campaigns are timely and trackable. A preview feature helps visualize how ads will appear across Search and Display networks.
First seen. We first were made aware of this update from David Vargas’s LinkedIn:
The bottom line: As Google Ads expands its capabilities, this feature presents a valuable opportunity for app marketers to leverage event-driven promotions, potentially driving higher engagement and conversions during peak periods. Keep an eye out for this feature as it rolls out more broadly.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, September 3rd, 2024
Microsoft Advertising rolled out several updates this September, building on recent advancements in AI and retail media. Following August’s highlights on Joint Business Plans and AI-driven insights, these new features are designed to make advertising more efficient, relevant, and accessible.
Key updates:
- Enhanced Display and Video Ads: Starting this month, advertisers can access new bidding strategies, targeting options, and conversion tracking for display and video ads. These tools offer greater flexibility to tailor ads across the funnel.
- Native Ads with Logos and Call to Actions: Advertisers can now add business logos and call-to-action buttons to native ads, increasing engagement. Options include automated calls to action or importing them from Google.
- IAS Verification Across All Ad Formats: Microsoft now supports IAS verification for viewability, brand safety, and invalid traffic on native, display, and video ads, regardless of bid strategy. Advertisers can integrate their IAS tag URL within the platform.
Making Connected TV (CTV) more accessible
Microsoft Advertising is expanding its CTV offerings to make this powerful medium available to businesses of all sizes. Advertisers can now:
- Use longer Video Ads: Support for 45 and 75-second video ads caters to new pharma regulations and provides more creative flexibility for all industries.
- AI-Powered creative recommendations: Integrated AI tools now assist in generating ad content for CTV, using existing assets to create video-ready ads.
Performance Max Updates
Microsoft continues to refine its Performance Max campaign type, with key updates including:
- SA360 Support: Performance Max campaigns imported from Google are now fully supported.
- Search Term Insights: Rolling out to all advertisers, this feature provides deeper insights into campaign performance.
- Search Themes: Now in pilot, these themes help optimize campaigns during the learning phase.
New bid strategy available. For those focusing on high-value conversions, the Max Conversion value bid strategy is now available for portfolio bidding, helping advertisers maximize the total sales value of their campaigns.
Why we care. These updates are worth paying attention to as they are most likely to boost engagement, and provide greater flexibility in campaign customization. With even more AI-driven tools, expanded access to premium channels like Connected TV, and advanced verification features, these updates give more ways to reach the right audience, optimize performance, and protect your brand.
The bottom line: These updates not only expand the capabilities of Microsoft Advertising but also streamline the process for advertisers, making it easier to reach and engage audiences across various platforms and formats.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Saturday, August 31st, 2024
Google rolled out a significant update to Google Analytics 4 (GA4), allowing users to compare their performance with other businesses in their industry.
Why we care: This new feature will provide valuable context for advertisers trying to understand their performance relative to their peers, potentially informing strategic decisions and goal-setting.
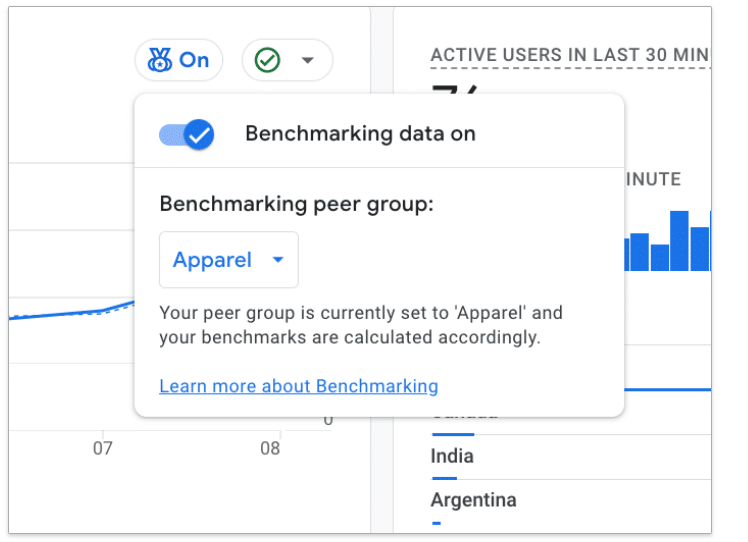
How it works.
- Users can access benchmarking data if their property has the “Modeling contributions & business insights” setting enabled in Admin > Account Settings.
- Benchmarks are refreshed every 24 hours.
- The summary displays:
- Your trendline.
- Median in your peer group.
- Range in your peer group (25th to 75th percentile).
Key features.
- Customizable peer groups: Users can select from various categories to find the most relevant comparison group.
- Data privacy: Google assures that benchmarking data is encrypted, protected and aggregated to maintain privacy.
- Wide range of metrics: Covers acquisition, engagement, retention and monetization.
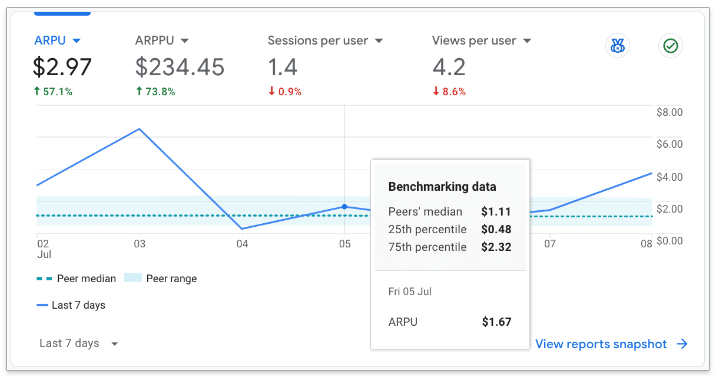
The big picture. This update addresses a long-standing need in the analytics community for comparative data, allowing businesses to gauge their performance more accurately within their industry context.
What’s next. Users are encouraged to check their GA4 accounts for this new feature and explore how it can enhance their analytics insights.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing



 But who has time to read through and dissect all that?
But who has time to read through and dissect all that?

 Source: Ahrefs organic keywords report
Source: Ahrefs organic keywords report