Archive for the ‘seo news’ Category
Saturday, April 27th, 2024
Google’s March 2024 core update is now done rolling out, it started on March 5, 2024 and completed 45 days later on April 19, 2024. This was a big core update, where Google said that this core update is more complex and involves changes to multiple core systems, while also ending the standalone helpful content update.
Google did not tell us until April 26th, 52 days after the rollout began, that it finished on April 19th.
A Google spokesperson told us, “As the web and spam tactics continue to evolve, we’ll continue to work to reduce low quality, unoriginal content in Search. As always, we appreciate and encourage feedback from users and site owners alike.” Google added:
The March core update ranking improvements, which tackled spam and low quality content on Search, are now finished rolling out. As a reminder, on March 5th we launched a number of meaningful enhancements to our core systems, as well as several updates to our spam policies, to reduce content created for search engines on Search.
45% reduction. Google originally told us there would be a 40% reduction in low quality and unhelpful content. Well, Now Google said it ended up being closer to 45%.
A Google spokesperson said, “The updates led to larger quality improvements than we originally thought – you’ll now see 45% less low quality, unoriginal content in search results, versus the 40% improvement we expected across this work.”
Other changes. Google also updated help center page outlining how site owners can debug drops in Google Search ranking.
Feedback. Google also created a new feedback form for site ranking changes that you’d like the Google Search team to review more closely.
Overlapping updates. Google also rolled out the March 2024 spam update that started on March 5 and was completed on March 20. Google also released a swarm of manual actions related to pure spam issues after these updates started rolling out. Finally, Google changed its core web vitals to use INP instead of FID during this time period.
Because we had so many overlapping changes, it would be hard to pinpoint which Google change may have impacted your site’s performance in Google Search.
More on the March 2024 core update. “The March 2024 core update is a more complex update than our usual core updates, involving changes to multiple core systems. It also marks an evolution in how we identify the helpfulness of content,” Google’s Chris Nelson wrote.
Elizabeth Tucker, Director of Product, Search at Google, told Search Engine Land that the update will help reduce unhelpful content in Google Search by 40%. But Google has updated that number to say 45%.
- “We expect that the combination of this update and our previous efforts will collectively reduce low-quality, unoriginal content in search results by 40%,” Tucker wrote.
This update, unlike some previous core updates, includes enhancements to several components of the overall core system. This March core update will have multiple updates within it, since this update touched on several systems within the core update, Google decided to push out updates to those core systems over the past few weeks.
Google said this update has refined how it understands which webpages are “unhelpful, have a poor user experience or feel like they were created for search engines instead of people.” This “could include sites created primarily to match very specific search queries,” Google added.
With this March 2024 core update, Google will stop announcing new helpful content updates, since the helpful content system has been incorporated into the core update system.
The last helpful content update, the September 2023 helpful content update was a large update that impacted several sites. Hopefully, some sites impacted will see relief from this March 2024 core update, but it is hard to say at this point. The classifier for the helpful content system was overhauled and is now baked into the March 2024 core update.
Mordy Oberstein wrote about the wrath of this March core update, calling it not linear.
What to do if you are hit. Google has given advice on what to consider if you are negatively impacted by a core update in the past. Google has not really given much new advice here.
- There aren’t specific actions to take to recover. A negative rankings impact may not signal anything is wrong with your pages.
- Google has offered a list of questions to consider if your site is hit by a core update.
- Google said you can see a bit of a recovery between core updates but the biggest change would be after another core update.
In short, write helpful content for people and not to rank in search engines.
- “There’s nothing new or special that creators need to do for this update as long as they’ve been making satisfying content meant for people. For those that might not be ranking as well, we strongly encourage reading our creating helpful, reliable, people-first content help page,” Nelson explained.
Previous core updates. Here’s a timeline and our coverage of recent core updates:
Why we care. Google algorithm updates are critical for all brands, businesses, and organizations to be aware of because they can impact how your site performs in search results. Any change in rankings from a core update – positive or negative – can impact your organic traffic, conversions and revenue.
Knowing when Google makes these updates enables site owners to know if traffic fluctuations resulted from a change to the site or something Google changed with its ranking algorithm.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Saturday, April 27th, 2024
The March 2024 core update has been a volatile, mammoth update. It’s been a long and turbulent road for some.
It can be overwhelming when you hear that an update has finished rolling out.
With so many moving parts, pinpointing results and actions for your website can seem like an impossible task after a Google algorithm update finishes rolling out.
Follow the following steps for a methodical and strategic way forward.
1. Assess the impact on your site
The first step is determining how the latest update has affected your site. This isn’t always clear-cut, and it’s important to carry out in-depth analysis and review things critically.
Here are some of the best places to start your investigation.
Get a visibility overview
The best starting point is to look at search visibility often using tools like Semrush, Ahrefs or Sistrix.
You’ll quickly see if there has been an obvious change in visibility around the time of an algorithm update. This will give you an overview, but it’s only part of the picture.
You might see a huge surge or drop, but it’s more likely that you’ll see a smaller fluctuation. While this is a good indication of how a core update has impacted your site’s visibility in the SERPs, you’ll need to dig deeper to really understand the update’s effects.
Your site could have lost or gained in areas that aren’t crucial to your strategy or been picked up for broad terms that don’t convert well.
So, while this is a great place to start to get a feel for what’s been going on, it’s important to go further.
Monitor traffic and rankings
Once you’ve assessed visibility changes, take a more in-depth view of rankings and traffic. This will give you a better view of how any changes are actually affecting your results.
You can monitor any changes using Google Analytics, Search Console and other third-party tools. Look for marked changes in traffic, clicks, impressions, conversions and rankings.
Analyze Google Search Console data
Google Search Console is where you’ll be notified if your site has been issued with a manual action. If you’ve seen a large drop, check for messages.
Examine your performance reports, looking for changes in impressions, clicks or average position compared to the previous period. Use the filter functionality to isolate positive or negative changes.
2. Evaluate the market and gain industry insight
Once you’ve analyzed your site, assess the bigger picture. What else has happened around you and what has been prioritized in the SERPs?
Review changes in SERPs
If you want to improve your understanding, manually check the SERPs for your key terms. Look out for new competitors entering the SERPs, changes in featured snippets or other SERP features.
It’s important to gain this awareness and use it alongside your data. It’s always possible that changes in the wider search landscape have caused the impact you’re seeing. When one site goes up, another is always displaced.
If fluctuations aren’t very pronounced, you may be seeing changes due to these factors more than what you have or haven’t done on your own site.
New or different SERP features could impact user interactions. Even if your rankings haven’t dropped or risen, you could still feel an impact in your results.
Monitor competitors
Assessing what you can about the competition can help you spot what’s working for them that you might not have considered.
While there’s only so much you can dig into, taking stock of how your closest competition has lost or gained after an update can help you to understand the movements in your industry.
Remember, they may not have changed anything drastic. Perhaps something they’ve already been doing now holds more value. So try not to focus only on recent changes, but review any plus points that could be missing from your strategy.
Stay informed
Follow reputable SEO blogs, forums and industry news sources to stay updated on Google algorithm update findings and best practices.
Agencies and experts who work across a whole host of sites can have a better view of common patterns and trends that have emerged after a core update, so keep an eye on their blogs and social media or attend local events to discuss with peers.
Sistrix releases blog posts on winners and losers that can help shed some light on what is working and what’s causing issues for other websites. These are well worth a read to improve your understanding of what’s changed.
“Spend time analyzing the data to understand the changes, while also keeping in the loop with the community on platforms like X to understand any patterns or trends that have developed – this can help to identify areas to evaluate and also give guidance on trends across the industry.”
– Amanda Walls, Director, Cedarwood Digital
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
3. Isolate the bad and the good
If you’ve seen an overall uplift or a downturn, the next step is to determine which areas of your website it has affected.
Segment data
Try to determine any trends in the increases or decreases you’re seeing. You could segment your data by device, location, user behavior, content type and content quality. This will give you a more in-depth understanding of the factors that may or may not be helping your performance.
You can also compare similar content pieces or groups with competitors to assess your performance relative to theirs.
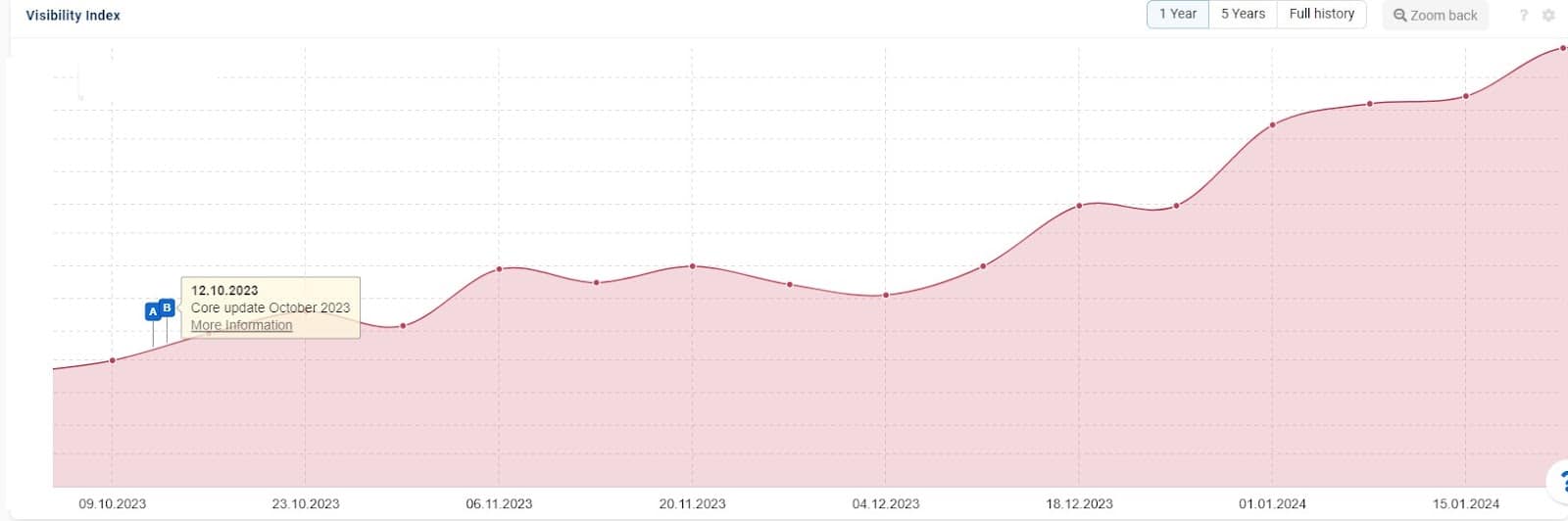
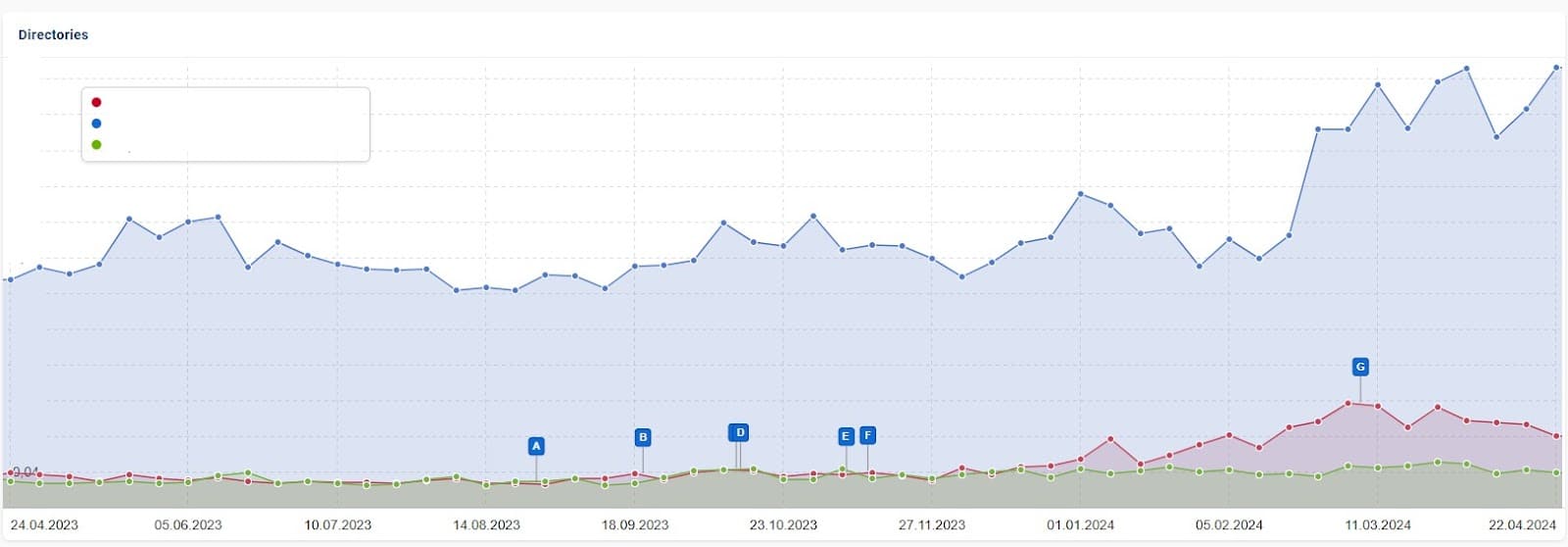
Check URL directories
Assessing visibility trends by URL directory structure can show whether certain areas are gaining, maintaining or losing ground. This provides a useful overview to help you narrow down what’s working for you and what isn’t.
Often, pages in a specific directory (e.g., /blog vs. /product) are structured in a certain way or share many factors in common. This quick analysis might give you immediate insight into what’s working well on your site and what needs work.
Compare and contrast
Perhaps you can’t see a clear trend in specific URL paths on your site. In this case, you can compile a spreadsheet of your biggest winning and losing pages. Review the similarities and differences between these pages to see if you can determine any common factors.
The worst-case scenario is an overall downturn with very few positives in any area of your site. This is likely to indicate a widespread problem with your website or SEO strategy as a whole.
The chances are, you’ll already know if you’ve been taking risks or trying to push the boundaries for quick wins. But if a downturn like this blindsides you, you’ll need to conduct a thorough review.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
4. Review areas for improvement
Most SEO professionals are very close to the websites they work with, so the above analysis will indicate what’s working on your site and in your industry after the algorithm update has finished rolling out.
However, it’s important not to jump to conclusions or make assumptions. The next step is to do a thorough review of the areas that need improvement.
If you work from the agency side, you might have landed new clients who have suffered during an update and need help. You may not be familiar with their websites, content and performance. This makes it easier to review unbiasedly and let your analysis lead.
Evaluate content quality
Review Google’s guidelines for content and quality and use them to assess the quality of your content. You might want to do this specifically on the pages that have lost traffic or rankings.
However, you could also take a more holistic view and conduct a content audit. After all, you may have content that wasn’t performing well before or after a core update that could get missed with the former approach.
You’ll easily spot thin or duplicate content, but keep an eye out for outdated information, too. Focus on factors like E-E-A-T, satisfying user intent and filling any content gaps that can improve your page.
Dig deeper: Writing people-first content: A process and template
Check technical SEO elements
If you’ve experienced a downturn across your site, a technical SEO issue could hold you back. Audit your site, considering site speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability and indexability.
“Look at the crawling and indexing state of pages. If certain pages are removed from the index after an update, it’s a good time to investigate it.”
– Preeti Gupta, Founder and SEO, Packted
Assess user experience (UX)
Check metrics such as engagement rate, average session duration and pages per session in Google Analytics to gauge user engagement. Usability issues could also be prevalent across many pages on your site, so if you’ve seen a widespread downturn, it’s worth assessing.
If you suspect you have usability issues, you could conduct user testing or track visits with a tool like Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity to gain insight into user behavior. Use this information to plan any changes you’ll make to improve usability.
5. Review your strategy and plan
Once you have a clear picture of what’s working and what isn’t, it’s sensible to look at this alongside your strategy and determine whether you need to shift your focus.
After all, we can’t plan ahead for core updates so it’s important to be flexible and work with the changes rather than remaining blinkered.
Target problem areas
If you’ve seen certain key pages or sections of your site suffer after an update, make sure you have a plan in place to improve them. You might schedule a more thorough review, assess user intent, carry out a content gap analysis and detail the work needed to give them a boost.
Perhaps you were already aware that these areas needed work, but this dip in performance is your reminder to prioritize them. Adjust your strategy to reflect the importance of making improvements in these areas. You might need to allocate extra resources or simply re-prioritize.
Embrace the wins
If you’ve noticed one area of your site is gaining while others aren’t, assess what you might be doing differently. Can you apply it to the other sections that have stayed fairly static or declined?
It’s easy to feel that glow when your hard work has paid off and you’ve made some positive gains after a core update. But there’s likely to be even more you can do. Consider how you can work with this to keep momentum going, setting your website up for future success rather than just sitting back and reveling in your win!
Plan for recovery
If you suffer negative effects from a core update, you can feel overwhelmed, paralyzed and panicked. The best thing to do is to try to stay calm and methodical. Create an achievable action plan you can start on as soon as possible.
Plenty of useful resources exist, so if you’re at a loss, do some reading to help you on your path. You’re already reading this, so you’re halfway there. Check the Google algorithm updates list with recovery tips from Marie Haynes to set your plan off in the right direction.
Stick with it
If you’ve suffered after a core update, seeing improvements can take some time. But if you’ve done all the above analysis and are genuinely working toward improving your website, content and user experience, don’t get disheartened.
It takes consistent, long-term work to get results.
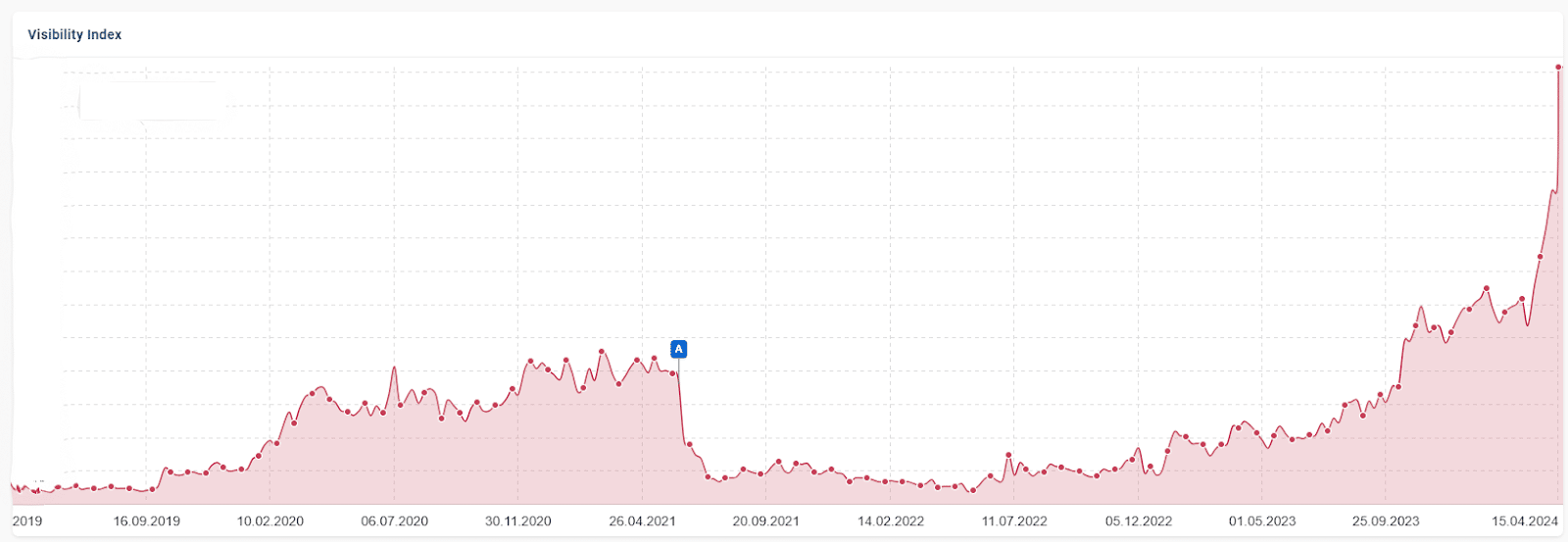
The site below suffered at marker A, the June 2021 core update. While other issues were present following this time, with consistent work since the beginning of 2023, progress is clearly being made as more recent updates take effect.
6. Communicate with stakeholders
The final piece of the puzzle is communication. Ensuring that key stakeholders know about the algorithm update and are well informed about its impact and your actions will help keep everyone working towards the same goals.
“First of all, inform the client if there is a core update coming up that might influence their ranking and tell them not to be afraid, as you check their positioning regularly and will inform them if something happened. It helps to not have the client freak out over something they read regarding the core update. For the communication afterward, always communicate your findings with actions to take. This makes it easier for the client to accept problems as they know you planned how to work on it already.”
– Dani Leitner, Independent SEO consultant
Dig deeper: How to communicate Google core updates to executives
Prepare a summary report
Summarize the key points from the analysis you have carried out and create a concise report.
- Add charts and visualizations where appropriate.
- Keep this high-level and easy to digest so stakeholders can immediately see the core update’s impact on their business.
- Cover both positive and negative changes, keeping the report balanced and informative.
- Provide background and context if necessary, helping those who might not be as familiar with algorithm updates to find out more information.
Circulate the report to all necessary parties.
Explain plans and strategies
Perhaps you have put plans in place to mitigate negative results, or maybe you have a strategy to push great results even further. Either way, communicating these and why you plan to tackle them after an update is important for keeping invested parties in the loop.
Perhaps other departments can add value or help with certain tasks to get things back on track. Encourage collaboration to improve your resources and strategies.
Address concerns and set expectations
After thoroughly investigating the data described above, you will be well prepared for any questions about the update. Make sure you’re available, responsive and confident when responding to any concerns.
It’s also wise to manage expectations around your planned actions. Make sure stakeholders understand the long-term nature of SEO work and set realistic timescales.
Update on progress
Finally, keep other stakeholders updated on your progress, any completed tasks and any changes in performance. Continue to monitor and analyze data to track improvements over time.
Keep calm, stay methodical and communicate well
It’s easy to let Google’s algorithm updates send you into a spin. They’re always shrouded in a certain amount of mystery and potential feelings of doom!
The reality is that most professionals genuinely striving to create better websites are unlikely to drop off the face of Google at the hands of an update.
Once the update has finished, keep your cool. Spend time digging into the data and learning about what has changed.
When you’ve got a better picture of your performance, create an action plan and communicate with others. Keep working through your actions and monitoring the effects of your changes – until the next one!
Dig deeper: How to survive a Google core update and come out on top
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, April 26th, 2024
Today’s SEO landscape is fraught with uncertainty, marked by:
Keeping your website strategy tied to traditional notions like keyword research based on search volume is a recipe for a slow but certain death.
But what are your options?
One possible escape route is product-led SEO, which focuses your strategy on your customers’ needs, pains and desires.
This article will help you transition from a keyword-focused to a customer-centric SEO strategy, offering practical tips for integrating both approaches effectively.
5 steps to kickstart your product-led SEO strategy
1. Identify your customer
One fundamental mistake many SEO experts make is focusing on the website and forgetting about the customers.
Remember, keywords don’t make purchases; people do (or at least for now). This is why focusing solely on keyword research or technical audit won’t do the job. You need to know who is your ideal customer persona.
There are many ways to do this. The easiest one is to talk to your colleagues from the marketing department and see if they have this already.
If you know a colleague from another department who would likely use your product, spend a day shadowing them or conducting an in-depth interview. Discover where they go online for information and learning, what factors they consider when making decisions and their biggest daily challenges.
You can also visit the GA4 Demographics report for information about age, country and interests. Take the last with a grain of salt as your website might have attracted the wrong users.
Lastly, create a profile of your ideal customer. You can easily start with HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool.
Dig deeper: Do personas REALLY matter in content marketing?
2. Dive into your data
SEO often overlooks the valuable data gathered by customer-facing departments like sales and support.
Platforms such as Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics offer rich insights into customer needs and behaviors, making them essential tools for SEO. Access to these platforms and their reports can significantly enhance SEO strategies.
The challenge with these tools is that navigation through the data directly in them could be a real pain. So, the easiest way to start is to create a report with the important information within the tool and then export it in CSV format.
Many organizations face restrictions on exporting CRM data due to privacy concerns. Always verify that your reports exclude personal identification information, such as emails, phone numbers, names and company details. Your goal is the information put in by your sales team, like a summary of the conversation or a description of the lead’s situation.
After exporting, you have a few options depending on the size:
- Read it manually.
- Cluster it with the help of a Python script.
- Or ask ChatGPT to do the heavy lifting.
As you look for repeating patterns in how your customers speak, you can also use simple tools like TagCrowd and then search for the words that are repeated the most in your initial report.
The end result of this exercise should be a document with three columns:
- Users’ pain point/challenge.
- Customers’ voice or how your customers have described this challenge.
- Information on how many times each challenge was mentioned.
Or if we need to translate these three into a more SEO-friendly language:
- Topics.
- Keywords related to the topics.
- Search volume.
Unfortunately, the data in your CRM platforms can often be insufficient.
In these cases, you need to expand your research beyond your company. One way to do this is through review platforms.
Dig deeper: An SEO guide to audience research and content analysis
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
3. Read customer reviews
If someone spent 30 minutes of their lives writing a review of your product, they either love it or hate it a lot. In either case, these users have given you valuable information.
While you can’t do much for those who hate some of the features and functionalities, you can analyze the rest for reasons to believe in your product and the pains you have resolved in their lives.
Most platforms provide ways to export your reviews in CSV format. The analysis process afterward could be similar to the one for the data in your CRM. You can even ask ChatGPT to make a SWOT analysis for your product and identify your strengths and weaknesses.
Review platforms offer more than just access to customer feedback. They provide valuable insights and real-life examples for content creation. Additionally, they grant access to competitor reviews, enhancing competitive analysis.
Collecting initial data for your competitors might require more in-depth knowledge of Python, an extra budget for a third-party tool, a browser extension or a lot of manual work. Regardless of the method, the outcome will provide valuable insights into how customers perceive your competitors.
Extract the use cases and real-life situations from these reviews, and if your product covers them, make sure that you show them in your content. Remember to uphold ethical standards and avoid making claims without verifiable evidence.
4. Expand your knowledge with forums
SEO professionals recently expressed frustration about Google’s preference for websites such as Reddit and Quora. These platforms thrive on content generated by real users, making them valuable for Google’s algorithms. Utilize this content to benefit your SEO strategy.
One way to start analyzing them is to use traditional keyword research tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, etc. You just need to check the domain and all the keywords it ranks for, then look for keywords related to your content.
With this approach, you will end up with a list of pages ranking for relevant keywords. Some might be concrete conversations, others communities. You can then easily expand them manually.
Once you are ready with your list, you need to extract the information. You can do this with:
- A web scraping browser extension (there are many different options).
- A website crawler with the capability to extract information (like Screaming Frog).
- Or a tool like Sheetsmagic which directly puts your information in Google Sheets.
The analysis can be done again with the help of AI or Python, or you can go through it manually. This time, you will receive one extra level of information – potential titles for your future content.
Merge insights from customer conversations, your own data and reviews to discover alignments with your ideal customer persona. This integration forms the backbone of your tailored SEO strategy, and the result will be your product-led content calendar and SEO plan.
Dig deeper: Advanced tactics to maximize the SEO value of user-generated content
5. Create content that answers your customer’s questions
To make this content work, you must answer your customers’ questions and give them solutions to their challenges while showing how your product/service fits into the picture.
Your blog should not become a duplicated version of your documentation; rather, it should present the features and capabilities of your product in a more storytelling manner.
Turn the customer examples you collected into compelling stories. Ideally, include quotes from real customers. If quotes are unavailable, use supporting statistics. Companies like PWC, EY, Deloitte, Accenture and McKinsey publish tons of research that you can use for inspiration.
Dig deeper: What is helpful content, according to Google
Aligning SEO with your product’s value proposition
Starting your product-led SEO journey is not difficult, and it could be eye-opening to learn why customers choose your product.
Your strategy shouldn’t be static. Once you establish the basics, it should evolve with your audience’s changing needs.
Only by always learning and changing can you ensure that you build lasting engagement and drive growth. Your customers are leading the way, but you must be dedicated to following them.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, April 26th, 2024
The title tag is one of the most important SEO elements. It can have a great impact on your rankings. In my experience, optimizing title tags can give rankings a strong boost.
There are many different ways to approach optimizing a title tag. One is making sure they fit within the 55-60-character limit (which I think is a bit outdated today). Other SEOs suggest it’s OK to have title tags up to 70 characters long.
There are also concerns that having the title truncated in search results or rewritten by Google can negatively affect organic performance and click-through rate.
In this article, we’ll explore the basis for such concerns, Google’s official statement about title length, and my findings after manually looking at 645 title tags of Google’s SERPs.
Example of title tag cut off in SERPs
Technically speaking, the number of characters for a title tag that Google can display in SERPs is measured in pixels. When your title tag is too long, Google can cut it off like this.
The title tag update and the aftermath
In August 2021, Google released an update aimed at title tags. This update enables Google to show a different title to users in SERPs than the one available in the HTML title tag.
HTML title tags may get rewritten in SERPs when they are:
- Too long.
- Stuffed with keywords.
- Missing or containing repetitive “boilerplate” language (i.e., home pages might be called “Home”).
Once the update was released, it caused an uproar in the SEO community as many SEOs have reported incidents where the title rewrite went “horribly wrong.”
Rob Woods reported an incident where the title tag was replaced with the URL slug:
shared this elsewhere. The query was "colored contacts" which appears in the title and H1. Instead of one of those, they are using the URL slug as the serp title. pic.twitter.com/eg9IVgCEyO
— Rob Woods 

 (@robdwoods) August 18, 2021
(@robdwoods) August 18, 2021
Chatter in the SEO community showed many examples of Google replacing <title> tags in the search results with alternative page elements like H1 tags, image alt texts, image file names, and sometimes the selected text was not even within the source code of the page. The most noticeable insight from the title tag update is that “Google wants shorter titles displayed in SERPs.”
This has caused some panic in the SEO community. Many SEOs started to double down on the importance of avoiding title rewrites by making sure their titles are short and within the character limit.
The confusion
It is clear to everyone that Google wants shorter titles in SERPs.
But does that mean they will use the titles displayed in SERPs (which may be potentially cut off or rewritten) for rankings instead of the HTML title?
This has led many SEOs to assume that longer titles will either get cut off or rewritten, and Google will not consider them for rankings but will consider the new title displayed in SERPs for rankings instead.
What is Google’s official statement about title length?
In a Search Off the Record episode, Google’s John Mueller asked Gary Illyes about title tag length:
“I have a question that is, maybe, just a yes or no thing, Gary. Is there a value in having title tags that are longer than the displayable space and the sections of it?”
To which Illyes gave a very clear and precise answer, “Yes.”
He added, “The title length, that’s an externally made-up metrics… Technically, there’s a limit, like how long can it be anything in the page, but it’s not a small number. It’s not 160 characters or whatever– 100, 200, 20, or whatever.”
And recommended to “Try to keep it precise to the page, but I would not think too much about how long it is and whether it’s long enough or way too long. If it fills up your screen, then probably it’s too long, but if it just one sentence that fits on one line or two lines, you’re not going to get a manual action for it.”
If we refer to Google’s documentation on SERPs titles (a.k.a., title links), there’s no recommended length or character limit specified for the title tag.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Would having longer titles impact rankings?
If longer title tags can get cut off or rewritten in SERPs, wouldn’t that impact rankings? Luckily, Lily Ray popped this question on X and got this reply from Glenn Gabe.
Google has always explained that what you provide in the title tag is what's used (no matter what their systems dynamically change the title to in the SERPs). I've been checking and haven't seen a ton of changes yet. Def. some (esp. brand tags at the end), but nothing crazy.
— Glenn Gabe (@glenngabe) August 18, 2021
This is aligned with what Mueller said in Google’s SEO Office Hours from Dec. 11, 2020.
So whether your titles get cut off or rewritten in SERPs, Google still uses the HTML title tag for ranking considerations, not the titles shown in SERPs.
I personally think we should not write shorter titles for the sake of it. The title tag is one of very few elements that impact rankings over which we have control. I always try to utilize them to the maximum, avoiding spammy practices like keyword stuffing.
My analysis
I want to put this argument to rest. Hopefully, as an industry, we stop recommending to clients to “shorten” their title tags for the sake of it. There’s been a title length metric circulating in almost all online resources and tools with nothing but “we don’t want our titles to get cut off or replaced” as evidence to support this recommendation.
I put together a set of 100 URLs and analyzed the HTML and SERP titles for each of those URLs. For those selected URLs, I also had historical data of their SERP titles from 2022, which means we can also see how Google changed how they displayed titles in SERPs (interesting, right?)!
Here are my findings:
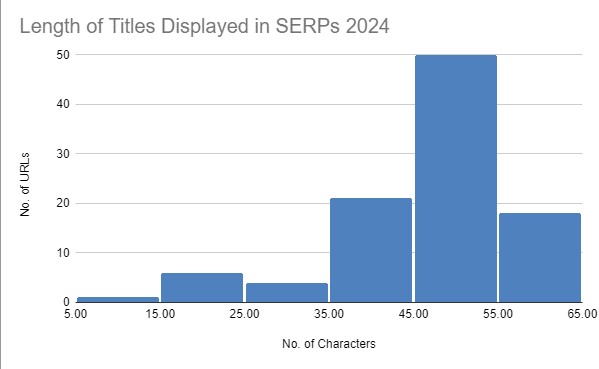
- Google seems to prefer displaying shorter titles. The longest title displayed in SERPs in my sample of 100 URLs is 61 characters long.
- 27 URLs had their titles cut off. The HTML titles in those situations ranged from 59 to 117 characters. So, does creating shorter titles guarantee that you will not get cut off in SERPs? No!
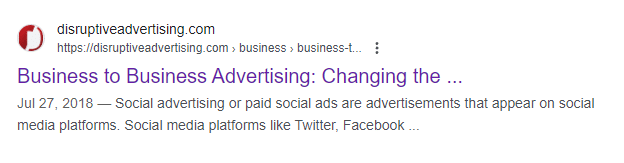
- Here’s an example of a URL with an HTML title of 59 characters “Business to Business Advertising: Changing the Conversation” and this is how it looks like in SERPs – still cutoff:
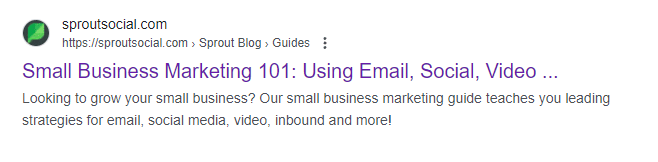
- Another interesting observation is an instance where Google re-wrote the title and decided to cut it off. Yes, Google cut off the title it created! The URL has an HTML title of “Small Business Marketing Guide: Everything You Need to Know to Grow” with 67 characters, and here’s how it looks like in SERPs:
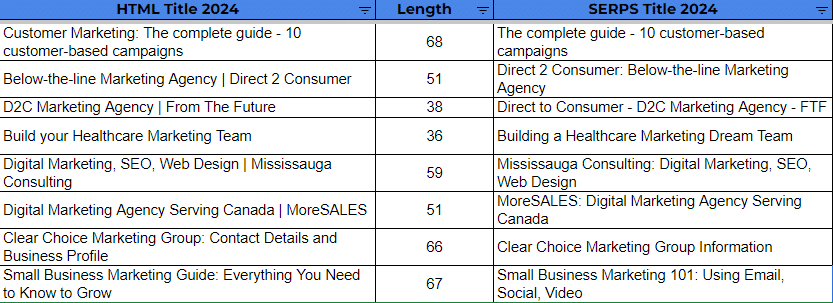
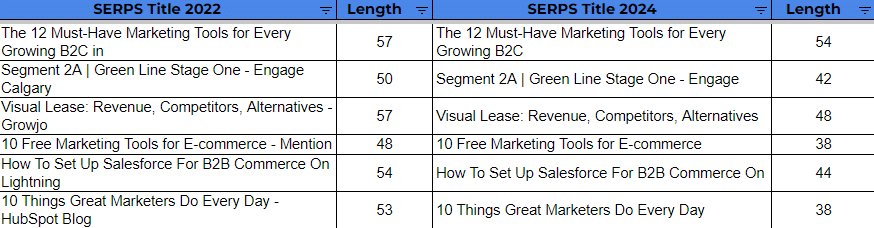
- When comparing SERP titles in 2022 with SERP titles in 2024 for the same set of URLs (making sure that their HTML title didn’t change), we see that out of the 100 URLs, 33 had their titles SERP titles changed differently than their 2022 version. This means that Google can and will change SERP titles over time if needed. The main difference noted is:
- Google removed the branding text appended at the end of the title tag. This means that even if you add branding text at the end of your HTML title tag, Google can decide against showing it. The recommendation is not to count the branding text as part of your character limit, regardless if you want to have a shorter title.
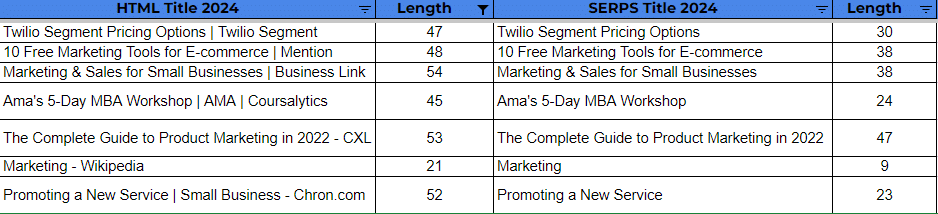
- Google generally shortened the titles in SERPs even more in 2024 vs. 2022. Here’s a sample of the changes noted:
- On the other hand, in the 100 URLs sample, there’s one example where Google decided to add the brand name to the title in SERPs, even though the brand name was not part of the HTML title tag.
- Out of the 100 URLs sample, 29 are the same as the HTML title.
- Google seems consistent with removing the branding from title tags, even if the title tags are short. Here’s are examples of titles that are below 55 characters that had their brand name removed from SERP titles:
- Will writing shorter titles help you avoid title rewrites? No! Here’s a list of example titles that were short and still got re-written by Google in SERPs:
- The most common length of titles displayed in SERPs in this sample is between 45-55 characters (see histogram below):
- Here’s also what the title length looked like in 2022 so you get an idea of the changes that occurred. You can see that the titles are getting shorter. (Note that the sample here was much bigger for 600+ URLs)
Title tag length in 2024
You do not need to stick to a 55-60-character limit for your title tags. Your titles can be – and should be – as long as needed within reason. Shorter titles guarantee you no additional benefit in terms of SEO:
- Shorter titles can get re-writes.
- Shorter titles can still get cut off.
- Shorter titles can still get their brand name removed.
Shortening your title tags does not have any real value. Optimize them well and leverage the whole real estate. Title tags are among the few assets that highly impact rankings that we still have some control over. Let’s make the best of them.
The best advice I can give is to optimize your titles to rank first even if you go above the 60-70 character limit. Then, experiment to adjust how your titles look in SERPs.
Additionally, if you decide to use a character limit, do not count your brand text that’s appended at the end of the title as part of your character limit since, chances are, Google may ignore that part anyway.
If you don’t rank, it doesn’t matter how long your titles are. So focus on optimizing the titles first to rank, then evaluate how they look in SERPs and fine-tune accordingly.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, April 26th, 2024
Meta’s ad revenue increased 27% in Q1 2024, a significant improvement over the 4% growth it saw in the same quarter a year ago.
Advertising revenue was $35.6 billion in Q1 2024 compared to $28.1 billion in Q1 2023. This success helped drive total Meta revenue to grow 27% year-on-year from $28.6 billion in Q1 2023 to $46.4.1 billion in Q1 2024.
- “If you look at our two end-to-end AI-powered tools, Advantage+ Shopping and Advantage+ App Campaigns, revenue flowing through those has more than doubled since last year,” said Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg.
By the numbers. Across Meta’s “family of apps” (Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, WhatsApp), year-over-year:
- The average price per ad increased 6%
- Ad impressions increased 20%.
- Daily active users increased 7% to 3.24 billion.
Meta search advertising. Could Meta AI bring in search advertising dollars at some point in the future? Zuckerberg was asked this question during the earnings call, given Meta AI assistant now includes search results from Google and Microsoft Bing:
- “We’re not working on search ads or anything like that. I think this will end up being a pretty different business.”
- “I do think that there will be an ability to have ads and paid content in Meta AI interactions over time as well as people being able to pay for, whether it’s bigger models or more compute or some of the premium features and things like that. But that’s all very early in fleshing out.”
AI investments. Meta is accelerating AI investments, with plans to spend between $35 million and $40 billion this year. Also:
- “Tens of millions of people” have tried the Meta AI assistant since being pushed into Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger apps last week.
Threads. With 150 million monthly active users, Threads now has more users than X. This is likely why Meta is reportedly looking to launch ads in Threads later this year.
Why we care. Meta had strong advertising growth, perhaps a good sign for the industry. We’ll know more as Google and Microsoft are set to report earnings today.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, April 26th, 2024
Google will stop allowing publishers to add publications to the Google Publisher Center manually. Instead, Google will automatically add eligible publications pages later this year.
This change will likely lead to even more confusion around Google News inclusion, which we have had for years since Google changed the inclusion process back in 2019.
What Google said. Google wrote:
Starting today, publishers can no longer add publications to the Publisher Center. We are making this change as part of a transition to roll out automatically created publication pages later this year.
Google added that previously this feature allowed publishers to manually create a source page for users to follow. But going forward, “publishers with manually created publication pages will continue to have access to customization features until later this year, when pages will shift to being automatically created. Users will continue to be able to follow their favorite publications.”
“Content from publishers that adheres to our content policies is automatically eligible for consideration in Google News and across News surfaces,” Google added.
What it looked like. Here is a screenshot within Google Publisher Center of how to add a publication – note this is going away:
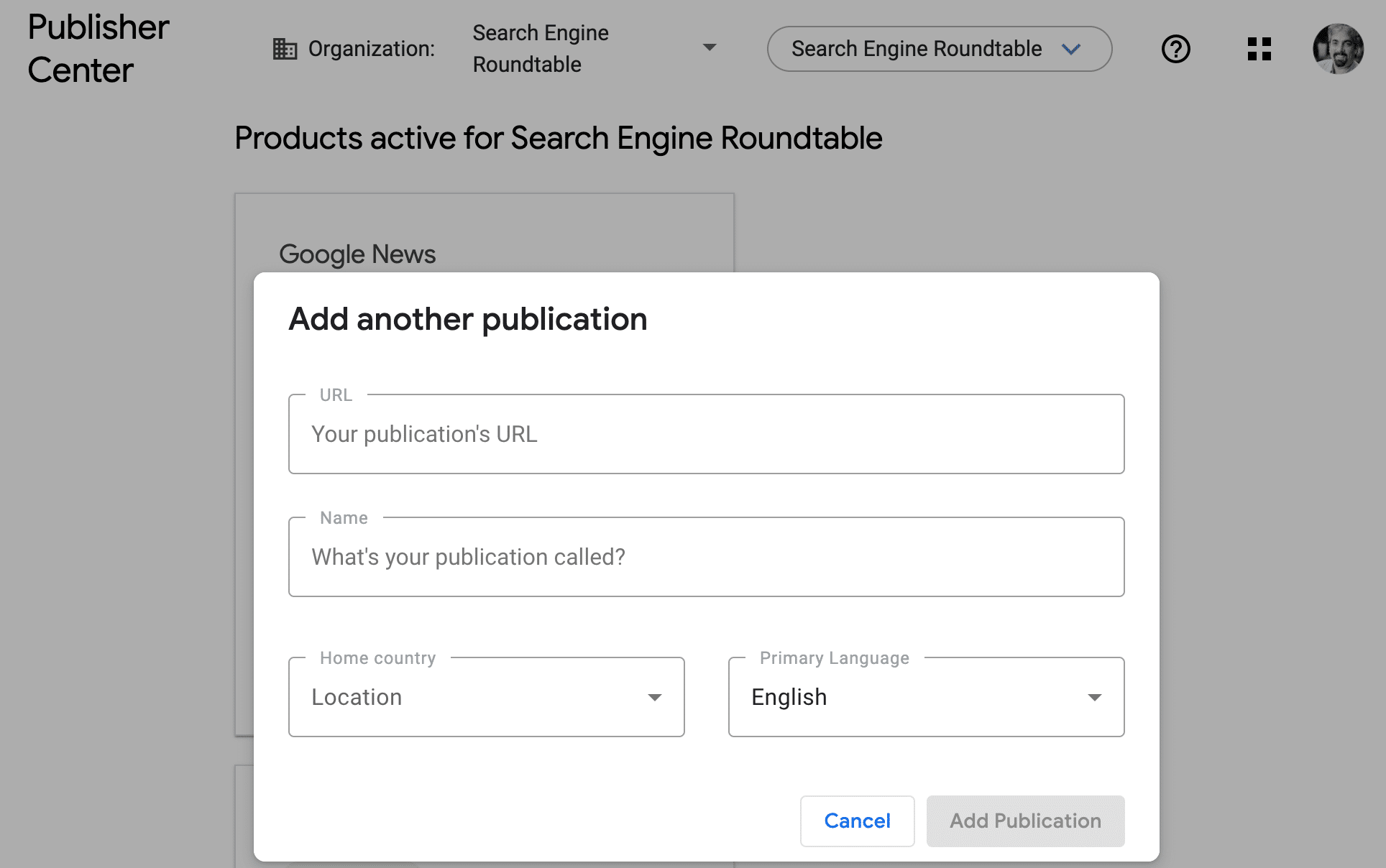
Why we care. I expect this change to cause more frustration and confusion amongst publishers. As you know, the whole Google News inclusion process, which was once a clear and straight forward process, is now automated and very unclear and completely not transparent.
This will only make things even more confusing for publishers.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, April 25th, 2024
President Joe Biden today signed a bill into law that forces TikTok to either divest from Chinese parent company ByteDance or face a full ban in the U.S.
What it means. ByteDance must sell TikTok in nine months. That deadline can be extended by 90 days if needed to complete a sale.
- If ByteDance doesn’t divest, app stores will no longer legally be allowed to distribute TikTok.
- Interestingly, 270 days from today is Jan. 19, 2025, which is one day before the scheduled inauguration of the next U.S. President.
What TikTok is saying. CEO Chew Shou Zi posted a video response, promising to challenge this ban (which he said is unconstitutional) in court, adding, “We aren’t going anywhere.”
Why we care. TikTok said it has 170 million U.S. users. Brands and businesses will be impacted because they will be unable to reach those people anymore should this TikTok ban go through in 2025. Any TikTok marketing investments would likely need to be redirected to YouTube or Meta properties.
Search and advertising impact. TikTok has increasingly become the starting point for search and discovery among younger users, like Gen Z. TikTok introduced Search Ads in August and added Search Insights in March.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, April 25th, 2024

As search marketers, we’re constantly striving to stay in lockstep with the latest changes and algorithm updates from Google – while embracing cutting-edge technology to keep us ahead of the competition.
At SMX Advanced, online June 11-12, two exclusive keynotes will deliver first-hand advice and actionable insights that will help you achieve these critical objectives.
Keep reading for more details… and if you’re ready, grab your free pass now: events.searchengineland.com/smx-advanced-2024

Last month, Google released one of its largest search algorithm updates – a core and spam update – that brought in elements of the helpful content update, core ranking systems, and more. With these ranking changes, Google has made it clear that they want search marketers to build content that users find helpful.
Every SEO under the sun has their own advice on how to create content that Google will rank well AND that users will want to read. But why not get your answers straight from the source?
Join Search Engine Land’s own Barry Schwartz for a candid interview with the Google executive who announced these updates in March, Elizabeth Tucker, Director of Product Management. Don’t miss this unique opportunity to uncover actionable insights from Google itself.
Pro-tip: Register now to submit a question you’d like Barry to ask Elizabeth during their interview.
 For decades, paid search had been one of the more precise forms of marketing. But the era of AI has thrust us into full-funnel advertising.
For decades, paid search had been one of the more precise forms of marketing. But the era of AI has thrust us into full-funnel advertising.
Match types act more like programmatic suggestions. Ads read like mad libs, picking and choosing which headlines and descriptions present the best message for each searcher. Search assets are now leveraged to create upper and lower-funnel display ads alike.
At this point, every search campaign type has some form of prospecting and branding involved. What is a search marketer to do?
Join Aaron Levy, former VP of Paid Search at Tinuiti, as he reveals how to put the “marketing” back in “search engine marketing,” and prepares for the future of paid search, whatever it may hold.
These keynotes are just the start. See what else is in store for SMX Advanced 2024 – and stay tuned for the full agenda launch May 6: searchengineland.com/smx/advanced/agenda
If you can’t attend June 11-12, register anyway – the entire program will be immediately available on-demand.
P.S. Have you heard? The 2024 Search Engine Land Awards is open for entry. Learn more and begin your application today: awards.searchengineland.com/2024/
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, April 25th, 2024
Dynamic Product Ads, the newest addition to the Reddit shopping suite, is being released into public beta.
This solution allows you to reach potential customers while they’re actively researching, discussing and deciding what to buy.
Why we care. Reddit is already benefiting from additional Google Search visibility, which means Reddit is likely getting more organic traffic than ever, including product searches. Reddit is saying Dynamic Product Ads drove 1.9x greater Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) when compared to conversion objective campaigns, based on the results of testing in Q1.
How it works: Dynamic Product Ads combine shopping signals with machine learning and advertiser product catalogs.
This combination will then work to serve the most relevant products to convert high user intent into action by connecting people with the products they’re looking for when they’re looking for them, Reddit said.
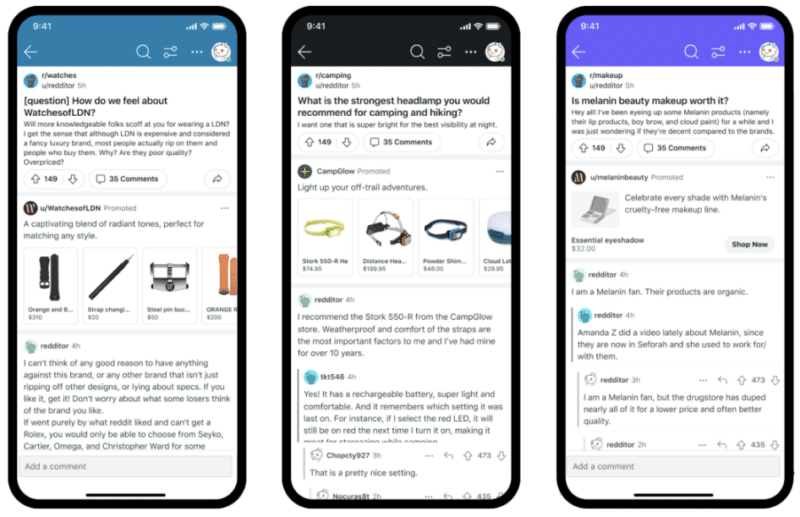
Key features. Here’s what Reddit advertisers can expect:
- Instant campaign creation as the ads auto-populate in real-time with the latest images, pricing and product images from an advertiser’s catalog.
- Two new targeting options:
- Retargeting: Ads are served to people based on products they’ve previously engaged with on the advertiser’s site.
- Prospecting: Ads are served for the most relevant products based on what people engage with on Reddit or advertiser sites.
- Support across the purchase journey with feed and conversation placement and single image or carousel format ads to reach Reddit users in the discovery, consideration, or decision-making mindset.
Available now in public beta: Dynamic Product Ads are available to all Reddit advertisers globally. English, German, Spanish, French, Italian and Portuguese languages are supported via the Reddit Ads Manager.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, April 25th, 2024
Prabhakar Raghavan, the head of Google Search, expects his team to move more quickly and in different directions as part of a new “cost” and “operating reality.”
That’s according to audio of Raghavan speaking during a Google all-hands meeting, obtained and reported on first by CNBC.
A new reality. Google has been cutting costs and staff over the past year. Raghavan painted a fairly bleak outlook of Google – essentially saying that the “good old days” are long gone:
- “I think we can agree that things are not like they were 15-20 years ago, things have changed.”
- “It’s not like life is going to be hunky-dory, forever.”
- “What that means is our growth in this new operating reality has to be hard earned.”
Challenges. Google is under attack on many fronts. Some of those Raghavan highlighted:
- More competition: Raghavan didn’t name any specific competitors, but OpenAI, Microsoft, Meta and many other companies are all competing hard with Google to win the AI arms race.
- Costs: Google is “spending a ton more on machines” due to generative AI.
- Slowing growth: The number of new devices coming into the world “is not what it used to be.”
- Regulation: Google is “navigating a regulatory environment unlike anything we’ve seen before,” such as the European Union’s Digital Markets Act.
- Internal bureaucracy: “The number of agreements and approvals it takes to bring a good idea to market — that’s not the Google way. That’s not the way we should be functioning.”
Go faster. Raghavan told his team to “meet this moment” and “act with urgency,” adding:
- “It won’t be easy. But these are the moments and the history of industries that will define us.”
- “If there’s a clear and present market reality, we need to twitch faster, like the athletes twitch faster.”
- “There is something to be learned from that faster-twitch, shorter wavelength execution.”
Twitch, or twitchiness, refers to an athlete’s ability to quickly or explosively move their body in different directions during high-intensity or physical sports.
Why we care. Google Search has received much criticism in recent years – with a great deal of it coming under Raghavan’s leadership. Many believe we are seeing the inevitable enshittification of Google, where Google puts profit above everything, including its users. Fittingly, Raghavan referred to Google’s advertising business as “the envy of the world.”
Velocity and focus. In response to the leaked audio of the all-hands meeting, a Google spokesperson told CNBC:
About Raghavan. He is a senior vice president at Google, responsible for Google Search, Ads and many other Google products. Raghavan was promoted to his position in June 2020. Prior to joining Google, he was at Yahoo from 2005 to 2012, a period during which Google ascended and Yahoo declined rapidly.
- There is an article making the rounds today, mainly about Raghavan, The Man Who Killed Google Search. The article makes several fair points but also tries to paint Raghavan as the sole villain responsible for the downfall of Yahoo Search and now Google Search. It also discusses the code yellow we reported on last fall.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing










 (@robdwoods)
(@robdwoods)