Archive for the ‘seo news’ Category
Tuesday, May 14th, 2024
Google is rolling out restrictions for suspended Google Ads accounts, limiting the actions advertisers can take while their accounts are suspended. Restrictions will be implemented in June 2024.
Why we care. The restrictions could frustrate some advertisers wanting full access during suspension periods.
What’s new? The functionality of suspended accounts will be narrowed to a few key areas like billing, appeals/verification, security settings and account navigation. Other actions like editing campaigns, creating new assets or making changes to suspended entities will be disabled.
Why it matters. The change gives Google more control over suspended accounts, while still allowing advertisers limited access to make payments, download reports and dispute suspensions.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Only these actions are permitted for suspended accounts:
- Billing (make payments, download tax docs, update payment method)
- Account settings (cancel account, claim refunds)
- Appeals and verification processes
- Update security settings
- Navigate the account, read info, download reports
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, May 10th, 2024
Google is encouraging merchants to enable “conversion annotations” – social proof badges that highlight a product’s purchase popularity when displayed in Google Shopping ads.
What’s new. Conversion annotations like “best selling” or “1K shopped here recently” provide visual cues about a product’s sales performance directly in the ad unit.

Why we care. Conversion annotations incentivize advertisers to share valuable purchase data with Google for visibility boosts. But they’ll have to weigh the benefits against data privacy concerns.
The pitch. Google claims conversion annotations can:
- Enhance the shopping experience by showcasing top products.
- Build trust and social proof by highlighting customer interactions.
- Ultimately, drive more purchases by making listings stand out.
Behind the feature. The annotations rely on merchants sharing aggregated conversion data from their sales.
- Merchants must have conversion tracking enabled in Google Merchant Center to qualify.
- Google says the data allows it “to be more creative and innovative to help you stand out.”
The requirements. To display conversion annotations, merchants need:
- Conversion tracking activated in the Merchant Center.
- To opt-in to share purchase history for annotation use.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, May 10th, 2024
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, is making significant strides in discussions to acquire HubSpot, a leading marketing and CRM software provider, according to a new report.
The potential deal: “Alphabet has engaged in talks with HubSpot to discuss terms for a potential acquisition, though no agreement has been reached yet”, sources told Bloomberg (subscription required).
- HubSpot’s market value stands around $30 billion.
Why we care: This update has the potential to reshape the landscape of advertising and CRM software, offering new data integration opportunities and challenges that could impact their strategies and outcomes.
The strategic rationale. Acquiring HubSpot, which focuses on smaller business customers, could help fill a gap in Alphabet’s offerings as it aims to better compete against rivals like Microsoft, Oracle and Salesforce in the CRM software space.
What we know. While the discussions are in progress, it’s important to note that a deal is not a certainty, and other potential suitors could emerge for HubSpot.
- Representatives for both Alphabet and HubSpot declined to comment on the discussions.
Antitrust concerns. There has been no update on whether the recent talks on Google’s antitrust case with the DOJ have affected the possibility of this deal going ahead.
What’s next? With talks progressing, investors and industry watchers will closely monitor for any formal announcements or bids from Alphabet or other tech giants looking to bolster their marketing software arsenals.
Dig deeper. HubSpot’s reported $617.4 million in revenue for the first quarter of the year. HubSpot earnings stay hot amid reports of sale to Google
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, May 10th, 2024
Receiving negative reviews from former employees is never fun.
Getting this sort of detrimental feedback online can feel like a sucker punch.
But get this:
Poor online feedback is not the end of the world, regardless of whether it comes from a former employee or a current customer.
How you navigate negative reviews reveals a lot about what type of business you are.
This article covers the importance of navigating negative reviews from past employees, learning from these reviews and ensuring your company doesn’t take a reputational hit.
Indeed, Glassdoor and employer review websites
Negative reviews from customers on Google and Yelp are one thing, but employer reviews are another matter entirely.
Before diving into how one can navigate negative employer reviews, it’s important to discuss these reviews and where they circulate.
Employer review websites provide a safe space for former or current employees to review their experience at a company. These employees can discuss salaries and wages, company culture, other staff members, the onboarding experience and a whole host of other matters.
Glassdoor and Indeed are the most well-known employer websites. Aside from being the most well-known, Glassdoor and Indeed also tend to rank highly in Google’s search results.
That means if your company has poor ratings on either website, the results will likely show up early when someone on the job hunt searches for your organization on Google. (The same goes for if you have good reviews.)
A higher rating on either of these sites indicates a solid company reputation, whereas a lower rating must be navigated accordingly.
Dig deeper: How to repair your Google search results and reclaim your online reputation
Dealing with negative reviews as an employer
Let’s start with three absolute core tenets to adopt when navigating negative reviews.
1. Addressing concerns
Employees (both past and prospective) like to feel acknowledged by a company. They want to know a company is seriously addressing concerns, showing empathy toward its staff and not just letting the same issues persist.
So, take the issue head-on. Mention that you have thoughtfully considered the negative review(s) and that you are doing everything in your power to shore up company culture.
Be thoughtful and specific. Get to the root of the issue and devise strategies to fix it.
(If, on the other hand, you disagree with employee feedback or feel it is false or fake, you can take steps to remove negative employer reviews. We’ll discuss this process later on.)
2. Rebuilding trust
Make tangible changes.
Showing prospective and current employees that you’re working toward fixing the issue will lead to a renewed relationship. In turn, you’ll start to rebuild that trust you might’ve feared you were losing.
Trust is essential in the workplace. It is not something you should ever take for granted.
3. Maintaining transparency
Throughout this entire process, it’s critical to be open and honest. Inform your employees that you are working toward fixing the negative feedback you’ve received in the past.
Better yet, consult them. Your employees (both past and present) are the ones who know your company culture best. They can tell you what must be fixed.
Developing a transparent culture will help strengthen your bond with your employees. They will then be more likely to leave you positive reviews on sites like Glassdoor and Indeed.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
How does negative feedback lead to improvement and growth?
Again, negative reviews are not always bad. If you believe employer reviews are genuine and have come from wanting to help, they might represent an opportunity for you to improve company culture.
For instance, perhaps a review mentions a lack of communication, how competing companies offer better benefits or how an abundance of digital meetings reduces staff mental well-being.
Solve the issue by Implementing sturdier communication pathways, looking at alternative benefit options or cutting down on virtual meetings. No matter the complaint, you can and should use it to your benefit.
Perhaps you can even use information from negative employer reviews to poll your current staff and ask them what changes they would like to see
Always look at negative employer reviews as a place to learn and grow. Learning from your mistakes can help you foster a healthier, more attractive company culture.
The impact of negative employer reviews on recruiting
Speaking of company culture – negative reviews can impact your ability to recruit new employees.
People on the job hunt tend to research the companies they interview with. They want to know if they’re stepping into a culture that values their mental health or one that couldn’t care less.
Here’s a simple question: If you were on the job hunt, would you want to work at a company with a 3.7-star rating on Glassdoor or one with a 4.7-out-of-5 rating?
The answer is easy. You’d choose the latter company. You might even choose them if the salary at the former company is slightly higher.
For this reason, dealing with and navigating negative employer reviews is crucial. It will contribute to more fluid and healthy recruiting and interviewing processes.
What options do employers have for removing negative, false and/or fake reviews?
Not all negative reviews come from an honest place and not all reviews help your company grow.
While some former employees want to help, others merely wish to harm their old bosses and bring down the company.
It’s unfortunate to say, but some companies end up dealing with the following:
- Fake reviews from competitors.
- “Review bombing” from former employees.
- Negative, false and defamatory reviews from former employees.
If any of these are the case, knowing how to remove negative reviews is crucial.
The first step in such an instance is to contact either Glassdoor or Indeed’s employer help center. They can occasionally help you get to the bottom of the matter and remove the review.
But sometimes that simple procedure doesn’t work. In such instances, it might be beneficial to reach out to an online reputation management firm.
Online reputation management firms specialize in managing a company or individual’s reputation and ensuring that negative, unfair reviews are permanently removed. They handle the ugly matters, so you don’t have to.
Several instances in which these firms can help you remove negative employer reviews. For instance, reviews can be removed if:
- They violate guidelines.
- They are deemed bullying or harassment.
- They are defamatory or libelous.
- They are not relevant to your company.
Hiring an online reputation firm can be much easier than going about it yourself, as a team of experts will analyze everything for you.
Navigating negative reviews from former employees
It’s never pleasant receiving a negative review from a former employee. But it’s also not the end of the world.
Negative reviews can serve as an opportunity to grow and learn. Address the concerns, work toward rebuilding healthy relationships with your workers and maintain transparency throughout the process.
If you feel the online feedback is defamatory or untrue, you can always work with an online reputation firm to remove negative employer reviews.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Friday, May 10th, 2024
Experimentation is an underutilized tool in content strategy for SEO.
Traditionally, we create content based on research and theory, wait months to see how it ranks, then iterate if needed – an ongoing cycle.
However, the rise of social search platforms presents an opportunity to accelerate this process.
Social search allows users to discover content through social interactions rather than just keyword searches.
By leveraging real-time data, trends and user-generated content on these platforms, SEOs can test and refine content much faster than waiting for traditional ranking signals.
Embracing a “search everywhere” approach powered by social data can help find optimized content solutions sooner.
This article explores how integrating social search insights can enable more efficient content testing, optimization and on-site enhancements.
Understanding social search
Social search continues to be a key driving force behind the evolution of search marketing.
Within a search everywhere strategy, social platforms offer a unique avenue for users to discover content through social interactions rather than traditional keyword-based searches.
Unlike conventional search engines, which primarily rely on algorithms to rank and display results, social search platforms leverage content creators, user-generated content (UGC), brand communities and engagement metrics to surface relevant information, providing a more personalized approach to search that resonates with younger audiences.
The significance of social search lies in its ability to reflect real-time user behaviors, trends, interests and preferences. By tapping into the collective wisdom of online communities, these platforms provide invaluable insights into trending topics, user sentiments and emerging discussions.
When we partner this with our traditional search efforts, understanding and harnessing the power of social search can unlock new opportunities for content discovery, audience engagement and more efficient content optimization.
Social-led search content testing
Where algorithms continuously evolve and user preferences shift, iterative content testing emerges as a crucial strategy for achieving sustained success.
Content testing lets search marketers try various strategies, formats and messages to find what connects best with their audience. While not a new concept, social search accelerates the process of gaining insights compared to traditional methods.
By systematically testing and refining content elements such as headlines, keywords and calls to action, strategists can optimize their content for maximum impact, driving higher visibility, engagement and conversions – both on social search platforms and traditional search, essentially unifying the search universe.
Social search platforms are excellent for quick content testing due to their real-time nature, large user base, and varied engagement metrics. Unlike traditional methods, which can take weeks or months, social search gives instant feedback.
The interactive nature of social search platforms lets you engage directly with your audience to understand their preferences and concerns. Social interactions like comments and shares help gauge content effectiveness early on before Google ranks it on a SERP.
Below are practical ways to deploy iterative social search content testing:
Polls and surveys
- Social search platforms have tools for polls and surveys, helping you gather data on audience preferences and behaviors.
- Asking specific questions about content topics or formats lets you understand audience sentiment and adjust your strategy.
- This technique is essential in establishing FAQ-type queries that can surround my content on a particular topic.
Question-based posts
- Crafting question-based posts encourages audience engagement and fosters meaningful discussions around specific topics or pain points.
- Gathering feedback from the community helps you find valuable insights and improve content.
- These insights should then be mapped to keywords/clusters to assist in understanding what content solutions need to be included as H2s/H3s within content.
Analyzing engagement metrics
- Looking at likes, shares and comments gives you a better understanding of how your content is doing and what people think about it.
- Tracking these metrics allows you to spot trends and improvement areas, quickly refine strategies, learn from failures and find success faster.
- If a post doesn’t do well on social search, it’s a sign we may need to adjust it for traditional search, too.
Dig deeper: How to turn polls and surveys into great content
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Integrating social search insights into on-site optimization
In search marketing, engaging users and being relevant are crucial. Include social search insights in on-site optimization, especially if your brand targets younger audiences who use social search in their search process. Social search platforms provide lots of up-to-date data, including UGC, which gives valuable insights into what audiences like and do.
Let’s discuss the areas directly affected by this approach to testing and improving content.
Content development and keyword targeting
- Social search and forum platforms are rich sources of user-generated content that can guide content creation and keyword strategies.
- By tracking trends and popular topics, you can find relevant keywords and themes more effectively than through traditional keyword research.
- Analyzing social engagement helps refine content creation by showing what resonates with the audience. If something doesn’t work, it can be adjusted and tested again easily.
User experience enhancements
- Insights from social search can help improve user experience on websites, like navigation and design.
- By knowing how users interact with content on social platforms, you can adjust on-site elements to match their preferences.
- For instance, if social search suggests people like visuals or shorter content, you can update how and where you present content on the website.
Dig deeper: The SEO-UX paradox: Achieving visibility without sacrificing user delight
Link building and internal linking strategies
- Social search platforms can affect how you build links and connect content internally by helping you find authoritative sources, influencers and relevant content online.
- By engaging with these connections, you can get valuable backlinks and boost the visibility of your content.
- Also, using social search insights in your internal linking strategy improves how easily users find content on your site.
- For instance, if users often go to page X after reading content piece A on social search, we can link to page X within content piece A on our site.
Practical techniques for a more seamless social search integration
Using social listening tools helps track brand mentions, trends, and audience sentiment on social platforms. This information guides on-site optimization and content creation.
Sharing on-site content on social media and vice versa boosts visibility and promotes a holistic search marketing approach. Creating shareable content for social platforms and engaging with communities drives traffic to our site, building authority and trust.
Analyzing on-site and social engagement metrics shows how content is performing and guides optimization efforts for ongoing success in a search-focused strategy.
How we can maximize the search optimization process
Search marketing is an ongoing process of improvement, adapting to changes in search engines, user behavior and market trends. We must continually refine our strategies to stay ahead and make the most impact.
This means regularly adjusting keyword targeting, content, technical setup, and links. By tracking metrics, analyzing data and adjusting tactics, we can improve website visibility, traffic and conversions.
The feedback loop
Silos must go. This collaborative process between search and social marketers could assist brands in aligning teams.
Continuous optimization relies on a feedback loop between social search insights and on-site efforts. This involves collaboration between social and search teams.
Social platforms provide valuable data for on-site strategies. SEOs can learn about user preferences by listening to feedback, monitoring trends, and analyzing metrics.
This helps inform content, keywords, user experience and links on-site. Integrating social insights into optimization keeps websites relevant and competitive in social-first search marketing.
Dig deeper: Search universe analysis: A deep dive
Accelerating SEO success with social search insights
In today’s democratized search landscape, integrating social search insights is vital for maximizing on-site optimization and SEO success.
Embracing social search unlocks new avenues for content discovery, engagement and conversions.
As we enter the “search everywhere” era, harnessing the power of social data will separate optimization leaders from laggards. Those who effectively leverage these insights will accelerate SEO wins and shape the future of search marketing success.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, May 9th, 2024
Some Meta advertisers received an alert yesterday when they opened their accounts. A source from Meta confirmed this alert was sent in error.
What was announced? The message said setting new detailed targeting exclusions would no longer be possible when creating campaigns after June 28.
- Existing exclusions would remain unless ad set targeting is modified.
- Exclusions based on brand suitability and employment will still be allowed at the account level across all campaigns.
However, this alert was an error, Meta confirmed to Search Engine Land.
Why we care. Getting alerts about functionalities that advertisers rely on can be destabilizing. If false alerts like these keep showing – how should advertisers trust the alerts we see?
Concerns from advertisers. Dario Zannoni, who got this alert, shared the information with his followers:
- “By using targeting exclusions in combination with the other targeting options, it was possible to not only exclude interests for brand protection but also to create well-curated Audiences that are aligned with the specific product or service.”
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Search Engine Land contributor Navah Hopkins was also not happy to hear that is was coming:
- “I’m pretty devastated by the news that Meta is removing audience exclusions for all campaigns in June 28, 2024.
- One of the reasons audience exclusions were really impactful is they enabled us to be very specific about who we were going after. Beyond the flexibility of “or” and “and” audience statements, they ensured we could really fine-tune our messaging.”
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, May 9th, 2024
The new buzzword in SEO is information gain. And like all new buzzwords, SEOs are throwing it around like we’ve just discovered fire.
But there’s a massive problem.
Information gain means different things to different people.
In this article, you’ll learn about information gain and how to use it to your advantage.
The 3 schools of information gain: Humans, machines and search engines
Information gain can be used in three topics:
- Machine learning.
- Google Patent.
- Information foraging theory.
Information gain is used to train decision trees in machine learning. And unless you are a computer programmer, we can largely leave that can of worms unopened (for now).
When SEOs talk about information gain, they mainly refer to the Google patent.
Google was granted a patent in 2022 regarding an information gain score that applied to documents.
This patent showed that Google had developed a way to measure the “sameness” of content and either promote or demote it accordingly.
This is a great way for Google to deal with content that is essentially unoriginal or simply copied from another source and reworded.
But what about information gain in relation to the information foraging theory?
Information foraging theory was documented in the book of the same name, written by Peter Pirolli.
It applies the models of how animals search for food (optimal foraging theory) to how humans search for information (which we’ll talk about later).
As you can see, we have three different meanings for the same term.
With regards to SEO, the Google patent is mainly easy to understand – just make your content unique.
However, information foraging is more complex, so we need to examine it more thoroughly.
Why information foraging matters for SEO
Recently, Google started discussing information foraging theory in their decoding decisions report (the messy middle).
Indeed, information foraging theory seems to be the direction Google is heading, and to quote their report directly:
“An explosion in product choice and information has made it harder to feel confident about making the right decision.”
Or, to put it another way, there’s just too much information out there.
If we have too much information, the time to make a purchase decision is increased, and this isn’t good for anyone.
You can see why Google SGE might help things if you think about this.
By providing a generative AI response to a search query, a search user immediately grasps the subject without needing to click a website.
This initial information should help a user to make their next search decision.
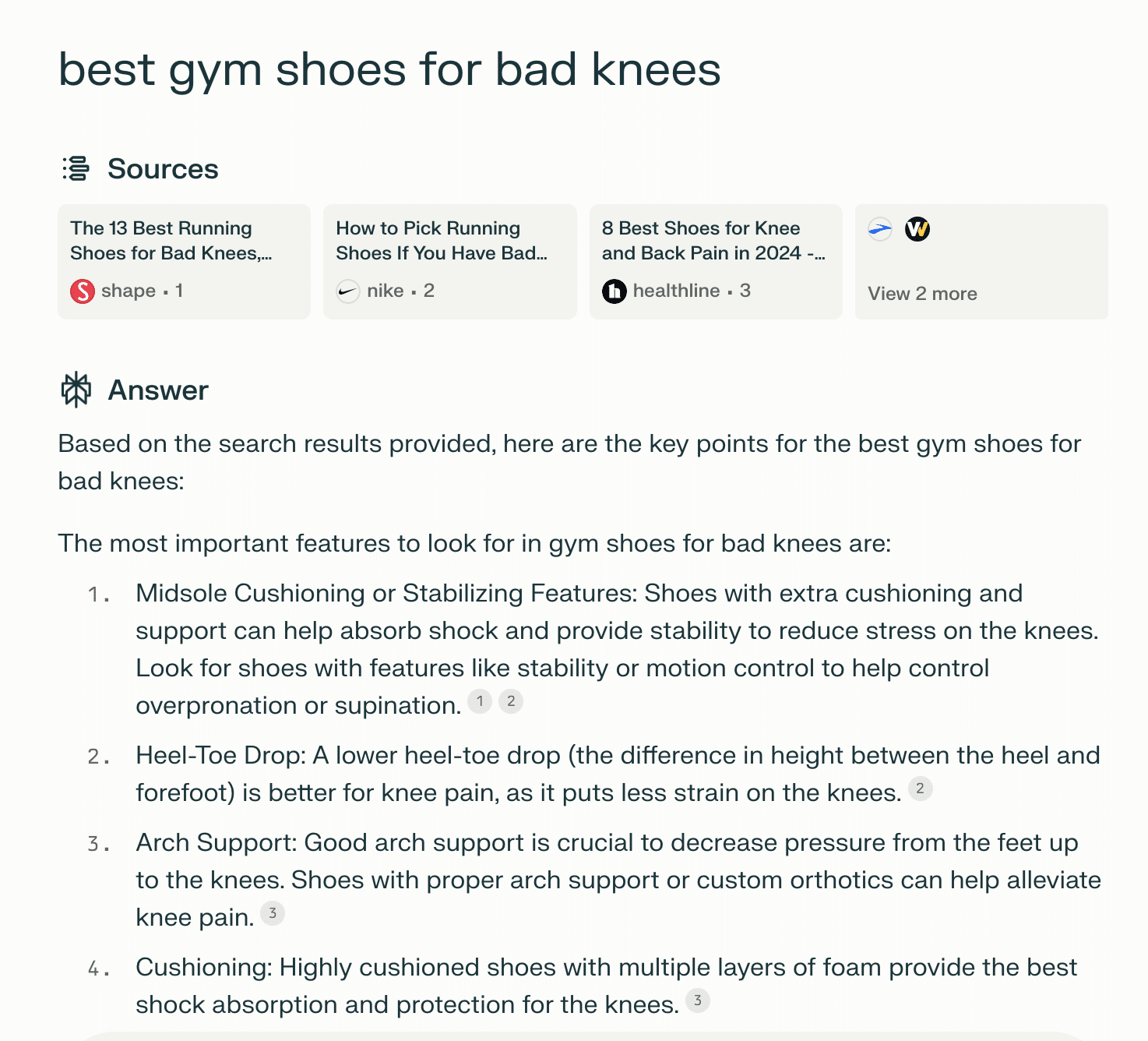
Take this result from a search in Perplexity.
Within seconds, my knowledge of the best gym shoes for bad knees has increased, and there are many links and suggestions.
My next click will be to look at the suggested shoes, not to read another five blog articles.
If SGE works similarly, you can see how it will radically change commerce.
We’re no longer optimizing for Google. We’re optimizing for AI.
Dig deeper: LLM optimization: Can you influence generative AI outputs?
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
From SEO to information gain optimization
Google has been involved in AI for a long time, and AI is part of many of its systems.
They used BERT to improve their understanding of language, and I’m sure many more systems are in use.
The point is that Google is trying to understand content to serve search engine users better. Therefore, Google itself is reading your content.
Sure, not like a human does, but they are reading it.
So, it makes sense to apply a similar approach to increase Google’s information gain from content, just like humans.
In essence, we become information optimizers.
Our job as SEOs is to continually increase the rate of information gain.
The rate of gain, explained
Information gain rate, when it comes to information foraging theory, is described as:
- Rate of gain = Information value / Cost associated with obtaining that information
You see, while search engines carry a cost for indexing and retrieving documents, so do humans.
When we use our brains, we consume calories, and the body is highly efficient at not wasting them.
We use heuristics (mental shortcuts) to filter the world and make decisions.
Information foraging theory suggests that we seek to do the same. We attempt to gain as much information as possible from a source in as little time as possible.
To do this, we go through a five-stage process.
Goal
- What information do we need?
Patch
- We decide on what source of information would best deliver our goal. This could mean that we go to Tripadvisor, TikTok, YouTube or any website/ search engine that comes to mind.
Forage
- Here, we search for the information we need on the platform of choice. For this example, we’ll stick with Google. You type into the search engine keywords to try and find the information you need.
Scent
- When we head to search engines, we’re looking for the scent of good information sources; signals such as reviews, higher rankings and page titles that encourage clicks.
- We click on sites, scan information and decide whether to invest time reading the resource.
Diet
- We consume information from multiple sources before making decisions. This is what Google refers to as the messy middle of search.
- For brands/ sites, being part of your consumers’ information diet increases the propensity that they will come to depend on you for information and trust you.
As we know, that trust leads to purchases or increased clicks (which can lead to advertising/ affiliate revenue). So this means that SEO should include optimizing around information scent.
But if you’ve read the above, you can see that Google search works similarly, just a machine version.
Information optimization: The new science
If we’re going to optimize around information gain, we need to understand that it requires a greater understanding of two factors:
- Machine learning.
- Human learning.
We already know that Google wants original, experience-based information from the best sources.
They also want to reduce the cost of extracting that information.
Yes, Google wants an easy life. So, how do we do this on a practical level?
Simply put, we make extracting information easier for both machines and humans (at the same time), and here’s how.
The optimal website maximizes the value gained per interaction
Contrary to what many think, fast websites might matter, but if the information gain rate from a website is low or has a high perceived cost, then the person will leave.
Here’s an example.
I’ve asked ChatGPT for some information about a hotel in Paris. It gives me the information the best way it can.
It gives a lot of information I can easily extract at a low cognitive cost. But how should a website deal with this?
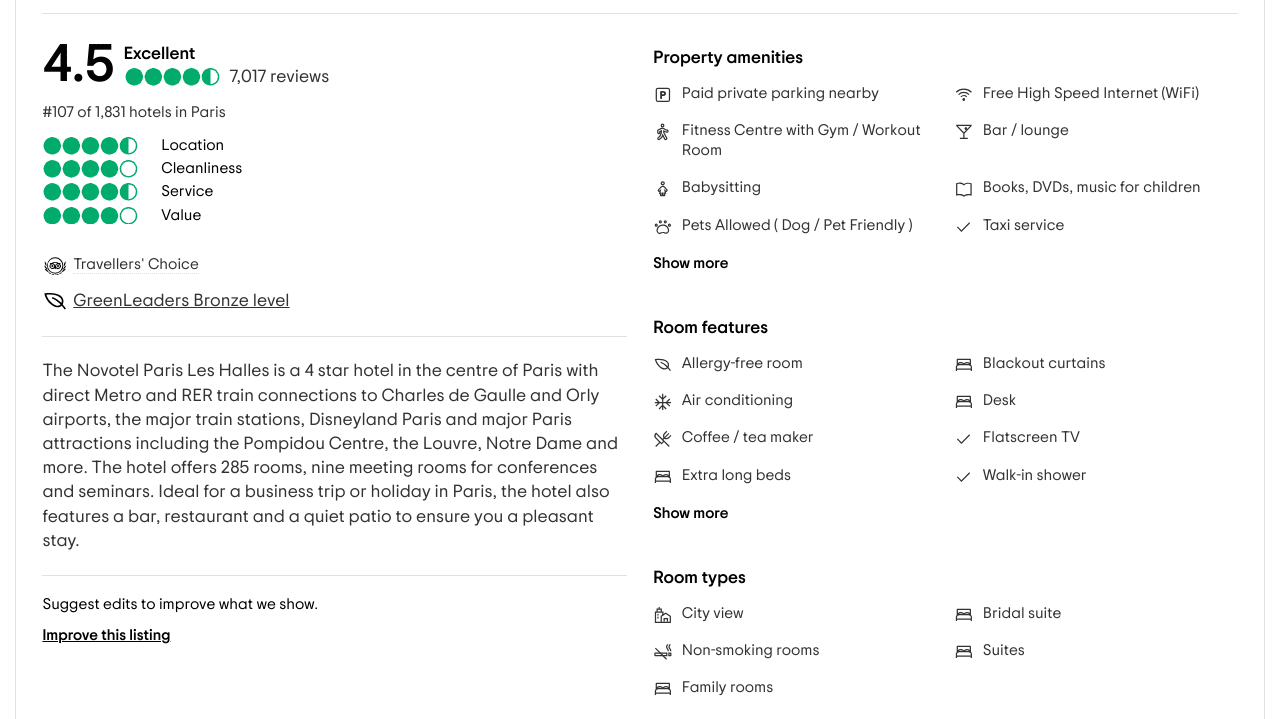
Tripadvisor has a whole page dedicated to the hotel. Look at how they’ve optimized one section for information gain rate.
The content – which uses symbols, scorecards and lists room types – is designed for humans (and machines) to gain the most information in the least time/cost.
And it’s this that we have to get our heads around to help search users.
But we need to destroy some myths around content.
Good content is context-based
I read a lot of good content, but most of it’s in my inbox in the form of blogs people have written that are not designed to gain traction from search.
Good content for SEO is wildly different.
When we search online, we have an emotional need state that requires solving.
Kantar and Google did some research a while ago.
In this study, the above need states were used by searchers, who came to search engines looking for them to be resolved.
Some words that stand out across from each need state are:
- Quick.
- Laser focused.
- Specific phrases.
- To the point.
- Simplicity.
- Uncomplicated.
- Trust.
- Ratings.
- Reviews.
- Competence.
- Location.
It’s these attributes in information that search users look for in content online.
Strikingly, we can see how Tripadvisor’s content displays these attributes, and we can also see how applying them to content would increase the information gain rate for humans and machines.
But how can we start to take the approach of information optimization to content?
Well, here’s a four-part process to get you started.
Part 1: Content structure
Look at how your page should be structured for search to increase the information gain rate.
A good example is the Tui website:
They’ve used faceted search “buttons” to help users find what they are looking for.
Consider how best to design your page for humans and search engines to increase the information gain.
UX matters, as does the information on the page.
Part 2: Information architecture
Consider how you want your information to be structured for maximum information gain.
You might consider giving information early and quickly, for example:
“When is the best time to travel to Jamaica?”
“March is the best time to travel to Jamaica.”
Look at your content and aim to add some, if not all, of the following attributes.
- Quick adventure.
- Laser focused.
- Specific phrases.
- To the point.
- Simplicity.
- Uncomplicated.
- Trust.
- Ratings.
- Reviews.
- Competence.
Part 3: Content design
The last impact is the design of the content.
Consider how best to add value, such as using unique images to your posts to help explain information or data.
Backlinko uses images like the above to convey data in an interesting format.
This leads us to the final part.
Part 4: Content difference
If you do all of the above, you should have content that is very different from what already exists.
But if you don’t, ensure that you do.
There are 1,000 different ways to say the same thing, but it requires creativity and consideration about how best to display your unique angles and viewpoints around this.
But here’s a little challenge.
Head to a site like Backlinko or HubSpot and look at their content.
Find an article and apply the above four-part system, and think about how you would improve it based on your unique views or experience.
This could serve as a suitable workshop for agencies and in-house staff to consider the information gain and how best to apply it.
Because in the era of generative content, information gain is king.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, May 9th, 2024
The number of Google Search queries without SGE increased last month from 25% to 65%. This is a surprisingly big drop, especially considering rumors that SGE could launch ahead of, or during, Google I/O next week.
Search results without SGE increase. Why did this happen, starting in mid-April? The reduction of SGE can be traced to Google’s Opt-in results type (when users must request an AI-generated answer).
This screenshot shows the data from enterprise SEO platform BrightEdge and the company’s BrightEdge Generative Parser:
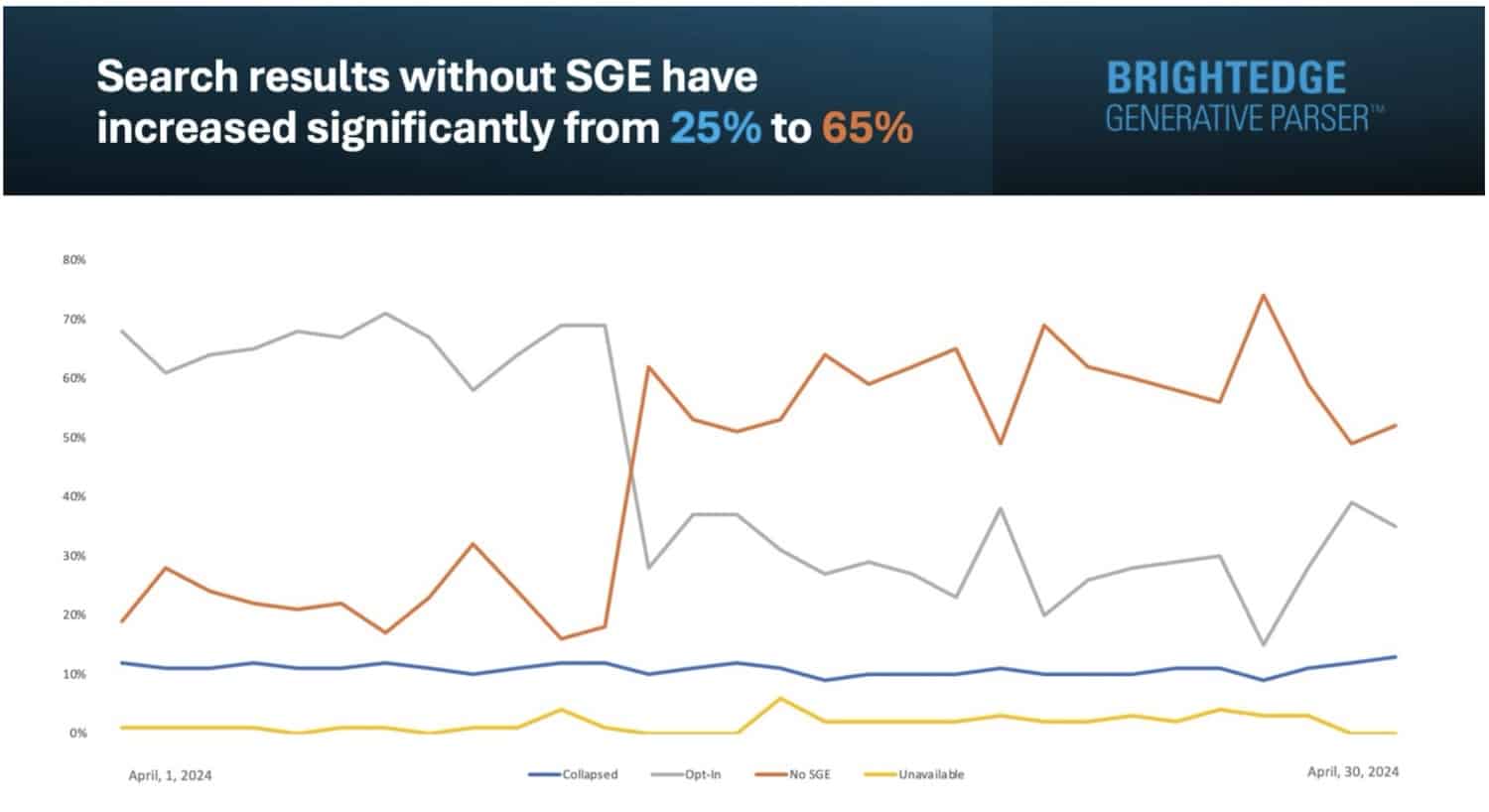
Why we care. Many SEOs have been worried about the day Google SGE moves from being an opt-in experiment to the default experience because of the potentially devastating impact it could have on how much organic traffic Google sends to websites. But it seems like Google has been cautiously and patiently testing a variety of factors over the past year, all with the goal of improving it for a wider launch.
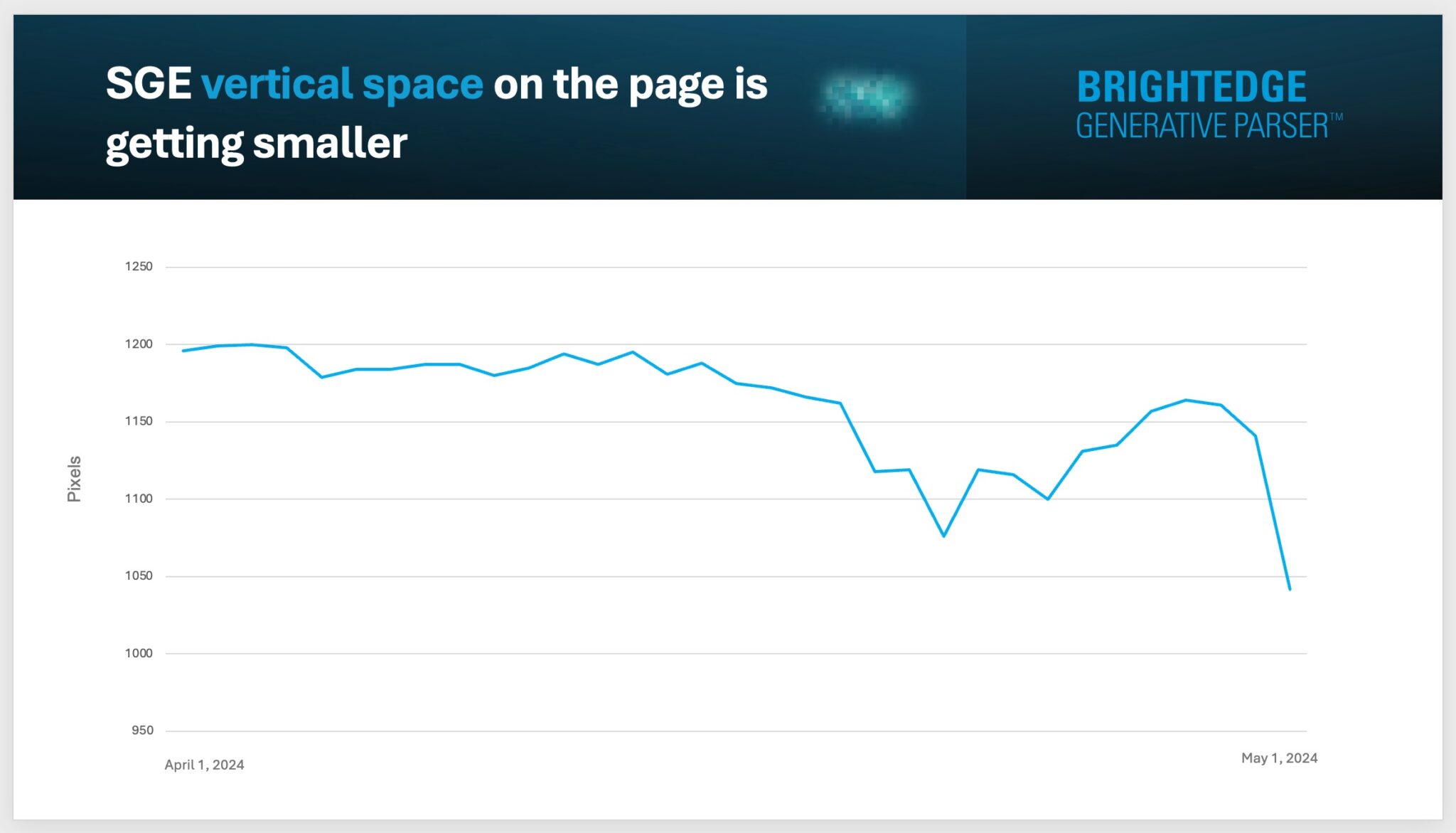
SGE vertical space shrinking. In addition to SGE showing on less queries, the amount of space SGE occupies has been getting smaller over the past month. Here’s a screenshot showing SGE dropping from around 1200 pixels to under 1050 pixels:
Product viewers decrease. There was a significant drop of this SGE format at the end of April:
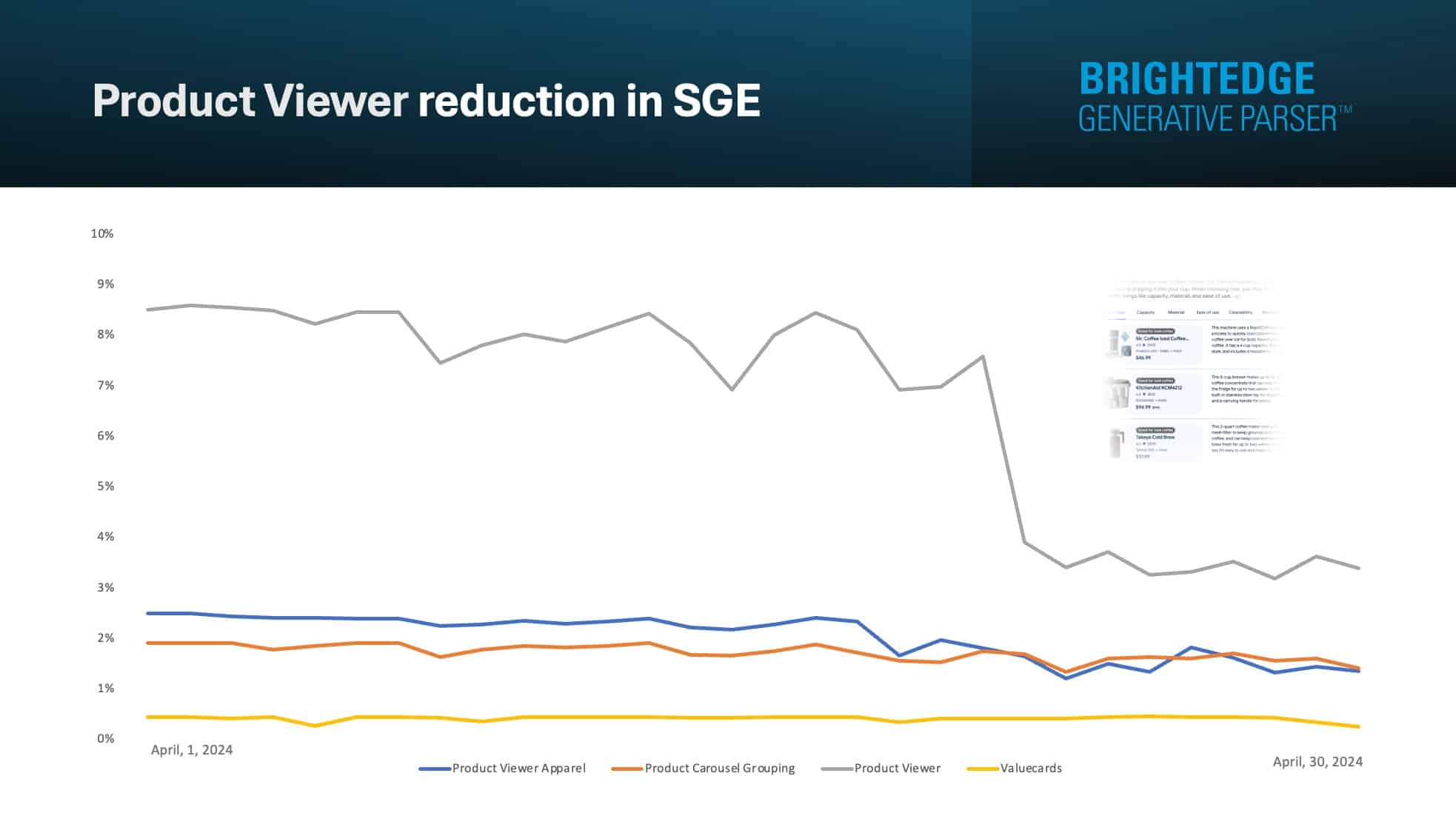
Apparel carousel results increase. This format type gained visibility in SGE for queries specific to apparel.

More warnings. A new, universally-applied warning appeared in April: Generative AI is experimental. This warning now appears across industries and query types.
AIO. SEO for Classic Search will remain important for the foreseeable future, but it’s become clear that AIO (Artificial Intelligence Optimization) may become equally or more important in coming years for AI Search, according to BrightEdge founder and executive chair Jim Yu:
- “Google search has undergone massive changes in the past few months to test and perfect SGE, with the goal of providing the best possible search experience. For marketers, it is essential to stay in lockstep with these changes to adapt to the new ways of optimizing for generative AI search.”
The report. BrightEdge continues to do live SGE update monitoring as part of its resource, The Ultimate Guide to Google SGE.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Thursday, May 9th, 2024
As Google Search continues to incorporate AI-generated answers into Search, links will live on, Alphabet/Google CEO Sundar Pichai told Bloomberg in a new interview. Here’s what you need to know from Pichai’s interview.
Future of links. Unlike in previous statements, where Pichai indicated that the Search experience would evolve substantively in the next 10 years, in the Bloomberg interview he seemed to indicate that links to websites will continue to be an important part of Google Search results:
- “I think part of what makes Google Search differentiator is while there are times we give answers, it’ll always link to a wide variety of sources. We’ve had answers in Search now for many, many years. We are just now using generative AI to do that.”
- “I think [links will] always be an important part of Search.”
- “There will be times when they want quick answers. My son is celiac, so we did a quick question to see whether something is gluten-free. We just want to know. But often it leads to more things, and then you want to explore more. I think understanding that, meeting all that needs, is part of what makes Search unique.”
Google Search getting worse. Pichai was also asked about search getting worse and “more SEO spam.” Pichai didn’t directly answer it (a typical Pichai non-answer answer), but my interpretation is Pichai acknowledged the issue without confirming it. Here’s what Pichai said, you can decide what it means:
- “Anytime there’s a transition, you get an explosion of new content, and AI is going to do that. So for us, we view this as the challenge, and I actually think there’ll be people who will struggle to do that, right? So doing that well is what will define a high-quality product, and I think it’s gonna be the heart of what makes Search successful.”
He was later asked how concerned he was about AI-generated content ruining Search. His response:
- “The challenge for everyone, and the opportunity, is how do you have a notion of what’s objective and real in a world where there’s gonna be a lot of synthetic content? I think it’s part of what will define Search in the next decade ahead, right?”
- “People often come to Google right away to see whether something they saw somewhere else actually happened. It’s a common pattern we see. We are making progress, but it’s gonna be an ongoing journey, right?”
Google’s business model. Google made more than $192 billion just from search ads in 2023. Pichai was also asked whether a chatbot giving AI-generated answers, rather than links, is “an assault on Google’s business model.”
- “So we’ve always found people want choices, including in commercial areas, and that’s a fundamental need. And I think we’ve always been able to balance it. As we are rolling out AI Overviews in Search, we’ve been experimenting with ads, and the data we see shows that those fundamental principles will hold true during this phase as well.”
Other quotes of note. Pichai was asked about the perception that Google is behind other companies (e.g., OpenAI, Microsoft) in AI, (even though Google became an AI-first company in 2016):
- “I take a long-term perspective and say, when the internet just first came about, Google didn’t even exist then, right? So we weren’t the first company to do search, we weren’t the first company to do email, we weren’t the first company to build a browser. So I view this AI as, you know, we are in the earliest possible stages.”
Meanwhile, in what I consider a fairly shocking moment, Pichai – the leader of a company that while not perfect is doing and has done many amazing things – couldn’t articulate a coherent reason when asked a simple question: why anyone we trust Google:
- “Well, I share the notion that no one, you shouldn’t blind lead, you know? That’s why it’s important to have systems in place. Regulation has a part to play, you know, test balance innovation. But as these AI systems get more capable, it shouldn’t just be based on a system of trust people or trust companies.”
What’s the biggest threat to Google’s future, according to Pichai:
Pichai was also asked whether we’ll look back on this “LLM era” and laugh because it will someday look basic and rudimentary:
- “I hope we do … my kids aren’t impressed by touchscreens or the fact that they have this extraordinary amount of computing in their hands. So similarly … there’s no reason we wouldn’t scale up our computing a hundred thousand times in a few years. … I hope some of this looks like a toy in the future. I hope it is that way, otherwise, we didn’t do our job well.”
Why we care. Just the other day, former Google CEO Eric Schmidt said “Google is not about blue links. It’s about organizing the world’s information,” which seemed to echo Pichai’s recent statement about Google evolving toward Search Generative Experience, where links to websites will eventually become less central to Search. AI answers are the present and future of Search – they’re not going away, especially if ChatGPT delivers on its rumored search product.
The interview. Google CEO Sundar Pichai and the Future of AI | The Circuit
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, May 8th, 2024
All signs point to ChatGPT launching a search feature soon. When? That remains the big question.
Rumor has it. OpenAI is developing a ChatGPT feature that searches the web and cites sources in its results, Bloomberg reported (subscription required):
- “The feature would allow users to ask ChatGPT a question and receive answers that use details from the web with citations to sources such as Wikipedia entries and blog posts … One version of the product also uses images alongside written responses to questions, when they’re relevant. If a user asked ChatGPT how to change a doorknob, for instance, the results might include a diagram to illustrate the task…”
And. “OpenAI has been aggressively trying to poach Google employees for a team that is working hard to ship the product soon,” according to the Verge.
Why we care. Search has quickly evolving in a new direction since the emergence of generative AI – with OpenAI seemingly perceived to be ahead of Google in many ways (not yet including Search), even though ChatGPT’s user base is still much smaller than Google. However, there is clearly growing frustration with all aspects of Google – from the quality of Search results to its abundance of advertising. Not to mention Google’s alleged monopolistic practices that have hurt advertisers, users and competitors.
X things we know about ChatGPT search. ChatGPT doesn’t want to copy Google’s model or layout (he hates ads). OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said as much earlier this year:
- “I don’t think the world needs another copy of Google,” Altman said.
ChatGPT’s version of Search wouldn’t be traditional, or classic, general web search. Altman’s vision is integrating ChatGPT with Search:
- “…We are interested in how to do that well. That would be an example of a cool thing. I don’t think anyone has cracked the code on yet. I would love to go do that. I think that would be cool,” Altman said.
Dig deeper. Is ChatGPT the Google Search killer we’ve been expecting?
Other ChatGPT search developments. We first heard rumors about OpenAI’s search product in February. Other stories Search Engine Land has covered:
More evidence. search.chatgpt.com appeared in the log files for some servers, as reported In Report: OpenAI To Launch Search Engine on Search Engine Roundtable by Barry Schwartz. There were rumors that ChatGPT’s search product would launch as early as tomorrow (May 9), but that seems unlikely at this point.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing