Archive for the ‘seo news’ Category
Wednesday, July 10th, 2024
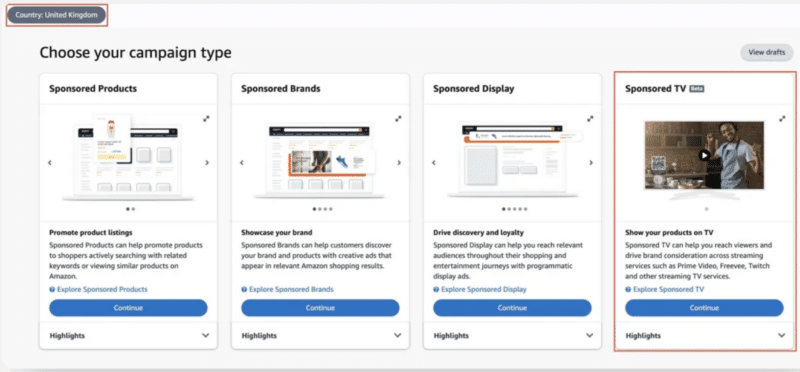
Amazon is rolling out its Sponsored TV ads in the UK, currently in beta, following a successful launch in the U.S. market.
Why we care. This move opens new advertising opportunities for brands on popular streaming platforms like Freevee and Twitch, leveraging Amazon’s extensive data for targeted ad delivery.
The details.
- Available to sellers in the Amazon Brand Registry, vendors, agencies and U.S. brands not selling on Amazon.
- Some categories, like health and personal care, are ineligible.
Between the lines. Amazon’s first-party shopping and streaming data allows for precise targeting, potentially increasing ad effectiveness.
Exceptions. Brands must review Amazon’s guidelines and acceptance policies before launching campaigns, as certain product categories are restricted.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
The big picture. This expansion reflects Amazon’s growing influence in digital advertising, challenging traditional TV ad models.
What to watch. How UK brands adapt to this new advertising avenue and whether it will impact their overall marketing strategies.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, July 10th, 2024
Internal linking is one of the most under-utilized arrows in the quiver of a site owner.
Although inbound link building gets all the press, it’s the correct use of internal linking that can really move a site algorithmically when done strategically.
Google has been vocal about the importance of Internal linking for years.
Google’s John Mueller touched on this specifically in this Office Hours Hangout from 2022, calling internal linking “super critical for SEO success.”
As a site auditor who routinely touches multiple sites daily and hundreds of sites annually, I know first-hand how important internal linking is for site recovery and improvement.
In my experience, fixing these specific internal linking mistakes results in stronger sites, easier indexing by Google and higher rankings.
How many of these mistakes are you making?
Mistake 1: Non-descriptive anchor texts
One of the simplest things to understand about internal linking is the following: we link by what we want to rank for.
Do you want to rank for “banana cream pie” and then use that anchor text or these close variations:
- “banana cream pie recipe”
- “easy banana cream pie”
- “banana cream pie with instant pudding”
- “old fashioned banana cream pie”
- “no bake banana cream pie”
- “how to make a banana cream pie”
And yet, routinely, a link scan of a client site may result in large numbers of non-descriptive anchor texts like the following:
- “Click Here”
- “See this”
- “Here”
- “Get this Recipe”
- “My pie recipe”
- “This link”
When possible, be descriptive with internal linking. Use anchor texts that accurately describe to the user and Google what exactly you’re trying to index and rank.
Not only is this good SEO, but it’s also a sound accessibility practice.
Nothing annoys someone using a screen reader more than hitting non-descriptive anchor texts that fail to communicate where the user is being sent via a click-through.
Mistake 2: Anchor text cannibalization
We know that having clear, descriptive anchor texts is important to users and Google. But what happens when you use identical anchor texts on multiple posts or pages?
Let’s say you have four different chocolate chip cookie recipes and used the anchor text “chocolate chip cookies” on all of them.
Congratulations! You have basically guaranteed none of them will rank as competitively as possible for “chocolate chip cookies” and, most probably, won’t rank at all.
This is where the concept of internal linking cannibalization comes into play.
Google routinely limits which results from a site rank for specific queries. This search diversity limit prevents any site from dominating the SERPs for the same target queries.
Fixing this, though, is not difficult.
Sticking with the “chocolate chip cookies” example, focus on differentiating the internal links by varying the anchor texts.
Maybe one of the recipes is an oatmeal chocolate chip cookie recipe, the other is a double chocolate chip cookie recipe, and still another is a chocolate chip cookie with brown sugar recipe.
By working methodically to map and differentiate internal links and corresponding anchor texts to prevent shared anchor text cannibalization, all these recipes can rank and rank competitively.
Mistake 3: Footer link spamming
It’s a known fact in SEO that all links are not created equal.
In-content links, sidebar links, footer links, etc., all count as links, but some are more important than others.
A good rule of thumb is this: a link that is clicked is always more powerful than a link that is not.
In the vast majority of cases, footer links are seldom clicked and don’t send much traffic.
Footer links are best used to publicize About and Contact pages, links to main category pages, links to copyright and accessibility policies and links to social media and location-specific information.
Unfortunately, spamming footers is a recent trend that has gained steam by publishers using blog support companies who are struggling to recover their sites from recent HCU, Core and Spam Update hits.
If you encounter a footer stuffed with anchor text-rich links to posts and pages, it’s probably because the publisher was incorrectly advised that footer links are a great way to increase authority sitewide.
The truth about footer links, though, is clear: they look spammy and do not remotely send a positive signal to Google.
Bottom line: Only place links in the footer that users will expect to see. That seldom will be anchor text rich text in multiple columns.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
Mistake 4: Linking to noindexed content
In the early Wild Wild West days of digital marketing, we had a concept called PageRank sculpting.
The concept involved controlling the amount of link equity passed through pages on a site by selectively nofollowing links on those pages.
That practice, however, has not worked in over a decade. Instead, when Google crawls a page and notices that a link on a page is nofollow, those links are ignored for algorithmic purposes.
Think of those nofollow links as a black hole on the page that just sucks up the link equity and PageRank to nothingness. You can’t get it back.
As such, it’s important for internal link building and topical discoverability that we try not to link to noindexed content on a site.
Otherwise, we are wasting that internal link authority.
Mistake 5: Not fixing 404s and 503s
Nothing is more annoying to a user than visiting a page and hitting a 404 or 503.
If a user navigates through your site and repeatedly hits a 404, one thing is guaranteed: that user will not come back.
Although Google has said for years that 404s are not a sign of low quality, if the issue is widespread and systemic, 404s can absolutely hinder the flow of PageRank and link equity through your site content.
Fixing 404s and 503s is not difficult. Your SEO guide to finding and fixing broken internal links covers the issue in detail.
If you are a blogger, I recommend using the Broken Link Checker plugin or use tools like Semrush, Moz, Ahrefs, Clarity or dozens of other options to crawl your site internally and fix these issues when they arise.
Mistake 6: Automating internal linking
The use of automation in SEO is all the rage these days.
You can’t throw a rock and not hit an article that covers how just installing the correct plugin or using one specific AI tool is all you need to take your SEO to stunning new heights.
For example, if you are a WordPress blogger, the plugin Link Whisper is a very popular internal linking option. However, you cannot use it to automate your link building, or you will spam your own blog.
The paid version can be horrible in both the sheer volume of its suggested link targets and the less-than-descriptive ways it warns you to link within those targets.
In general, I’m against all automated internal linking for the following reasons:
- You end up spamming your anchor texts. A tool that allows you to link every instance of chocolate chip cookies in a post does more harm than good. I see it daily.
- The tools ignore users. Understanding UX is very important with internal linking. We link when it makes sense to users on a page. Tools seldom understand that.
- The linking may not be strategic. You know your content best. Which posts you should send users, over a tool, is always of paramount importance.
Again, I’m all for working smarter, not harder. However, when it comes to internal linking, a slow and steady approach is always better than automation. I guarantee it.
Mistake 7: Internal permalink redirects
It’s not uncommon for sites that have existed for years to change their URLs at some point.
Sometimes, those changes are simple, like slightly changing one URL to add or remove keywords. Other times, they’re more detailed, like removing dates from your URLs and changing your entire sitewide permalink structure.
Google has been clear for years that changing URLs should be avoided, especially if all you are doing is adding or removing keywords.
But one of the biggest reasons to avoid changing URLS is that this creates internal permalink redirects. These extra server hops can reduce the flow of PageRank through the site and even impact page speed at scale.
For example, links to https://example.com/2022/02/sample-url.htm can be redirected to https://example.com/sample-url/ and links from https://example.com/sample-url can be redirected to https://example.com/sample-url/.
The problem with the above is that most site owners fail to do a “find and replace” and remove all the old internal links (with the previous URL permutation) to the new URL internal links (without the previous URL permutation).
This can result in dozens, if not hundreds, of internal redirects, which can greatly reduce a site’s bottom-line quality.
To fix this, contact your host and have it scan your site to fix it at scale. You can also install a plugin like Search and Replace and do this yourself.
Mistake 8: Overlooking link placement
Not every link is equal.
It’s generally understood that an in-content link, higher on the page, is the most powerful form of link for SEO purposes.
Sure, you can have links on the sidebar, footer, in a links list, a breadcrumb, or as an image; all of those links have value. But the in-content link, placed higher on the page, is usually the winner.
Why is this the case?
Google crawls a page from the top to the bottom: first, the header, then the body, and everything else after that.
Google then renders the page and runs any JavaScript it finds at this time. This is also why it’s important not to have a ton of JavaScript on the page to slow things down, especially pushed-out client-side.
Further, as far back as 2016, Google has said that in-content links within the primary area of a page are always treated as more relevant than those in the header, menu, footer and sidebar.
For internal linking purposes, it’s always a good idea to link naturally from the top of the page to the bottom. But placement absolutely matters.
Mistake 9: Orphaned content pages
An orphaned content page is an internal page that has no incoming internal links.
Fixing orphaned content pages is the epitome of low-hanging fruit for any site owner looking to improve their topical discoverability with Google and their bottom-line SEO.
As a general rule, I recommend pages have a minimum of 3-5 unique incoming links from related content and in many cases, much more.
Finding and fixing orphaned content is not difficult. Orphaned content linking reports are built-in to most site auditing suites, including Semrush, Ahrefs, Sitebulb, Moz and more.
You can also use the Link Whisper plugin mentioned previously in this article. It has a simple ability to scan the entire site and then sort all your content by the number of incoming links.
Finally, you can use the Yoast plugin (premium required), the All-In-One SEO plugin or even RankMath (premium required), all of which have built-in tools to scan and surface orphaned content pages and posts.
High-quality internal linking is a confidence vote for you
My late good friend Bill Slawski used to talk a lot about link confidence.
He was a big believer that internal linking done correctly was imperative for search engines to understand the relationship between links, entities and user satisfaction.
This link confidence was necessary to rank your site and content competitively.
In the wake of relentless core, spam and HCU updates, along with the rise of AI Overviews, ranking a site effectively has never been more competitive than right now.
If you struggle to focus on where to put your SEO efforts in 2024, internal linking should be top-of-mind. Doing so helps you communicate your site more effectively to Google.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Wednesday, July 10th, 2024
TikTok’s advertising momentum is slowing as uncertainty over a potential U.S. ban looms.
By the numbers:
- Ad spend on TikTok grew 19% year-over-year in March, cooling to 11% in April and 6% in May.
- Total ad spend from January to May 2024 reached $1.5 billion, up 11% from the same period in 2023.
- Nine out of 20 advertising categories saw month-over-month increases in April.
Between the lines. Advertisers are shifting their focus on TikTok from brand awareness to more performance-driven ROI goals.
- CPMs for upper-funnel metrics were up 15% year-to-date at one agency.
- Click-through rates increased 27% in April compared to March.
Why we care. Despite the uncertainty that the potential ban brings and some slow growth, the platform still shows strong engagement metrics, which advertisers should keep considering in their media mix.
Stagnating numbers. TikTok’s user growth is stagnating, particularly among younger demographics.
- The percentage of weekly users aged 18-24 dropped from 35% in 2022 to 25% this year.
- Users aged 35-44 increased from 16% to 19% in the same period.
The big picture. Despite concerns, advertisers still find value in TikTok’s massive user base and engagement rates.
What to watch. How advertisers and users respond to ongoing discussions about TikTok’s future in the U.S. market.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, July 9th, 2024

Your opportunity to earn industry-wide recognition, boost company morale, generate new business, and showcase your company’s outstanding achievements is here: Enter the 2024 Search Engine Land Awards now!
Early Bird rates expire at the end of this week… submit your application by Friday, July 12 at 11:59pm PT to save $200 off final rates (per entry!).
Join the esteemed ranks of past winners, including Tombras & Orangetheory Fitness for Best Integration of Search into Omnichannel Marketing, Wpromote and REEF for Agency of the Year – PPC, Amsive’s Erin Rooney Doland for Search Marketer of the Year, and many more. Check out the full list of 2023 winners here – and all of the available entry categories.
And last, but certainly not least, say hello to your 2024 Search Engine Land Awards judges!

Winners will be announced on October 21 in exclusive coverage on Search Engine Land – the industry publication of record. Don’t miss this opportunity to earn international recognition, boost company morale, generate new business, and showcase your company’s outstanding achievements.
Remember to get your application in by this Friday, July 12 at 11:59pm PT to save $200 off final rates (per entry). Begin your entry now!
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, July 9th, 2024
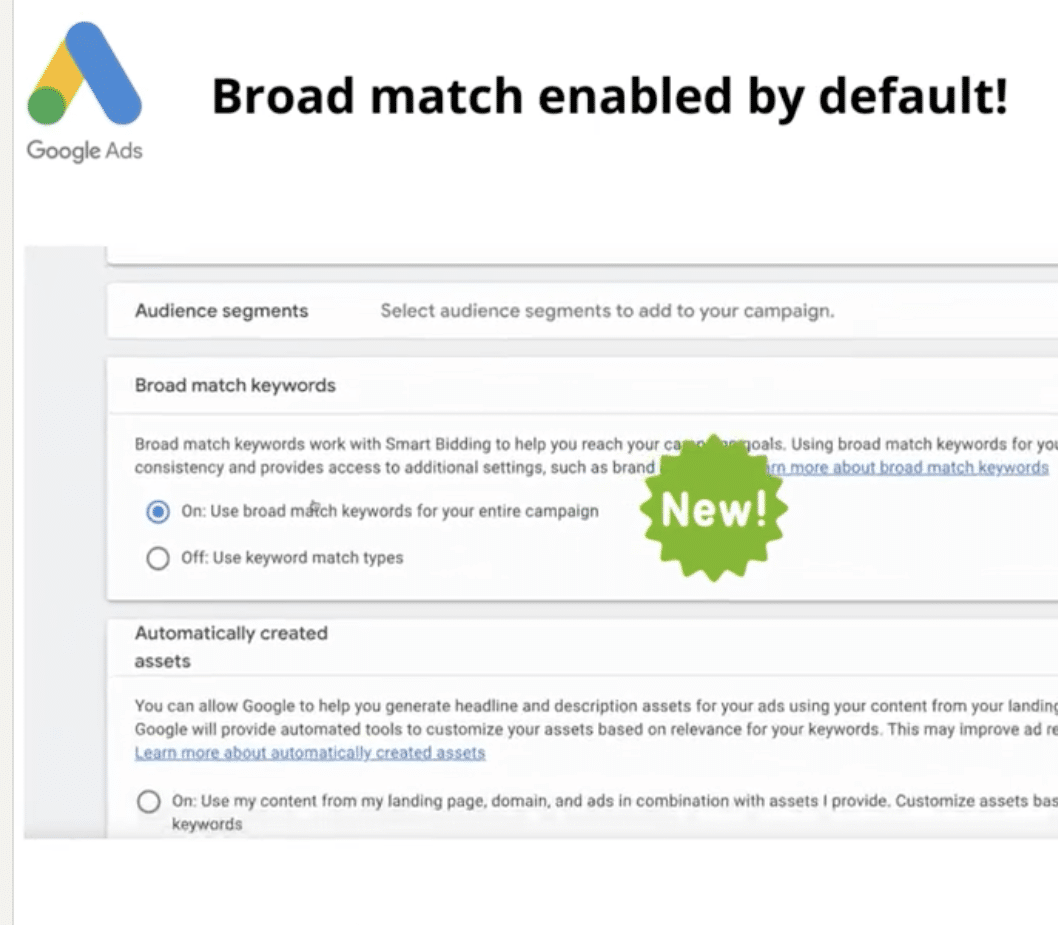
Google Ads made broad match the default setting when creating new Search campaigns, a departure from its previous default of having broad match turned off.
Why it matters. This change could significantly impact campaign performance and budget spend if advertisers aren’t vigilant.
Key details:
- Broad match is now enabled by default for new Search campaigns
- Could lead to increased costs if proper negative keywords aren’t in place
Between the lines. This move aligns with Google’s push towards more automated, AI-driven campaign management, potentially simplifying campaign setup for novice advertisers.
Yes, but. Experienced advertisers may need to be more cautious when setting up new campaigns to avoid unintended broad targeting. With broad being the most inefficient of the match types, this just adds an extra layer of check advertisers will need to take into consideration when setting up their campaigns.
First seen. We first were alerted to this update by Thomas Eccel on LinkedIn:
What to watch. How this change affects campaign performance, especially for advertisers who prefer to start with more precise targeting using phrase or exact match.
Bottom line. Advertisers should double-check their match type settings when creating new Search campaigns to ensure they align with their intended strategy.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, July 9th, 2024
Google indefinitely paused its planned Healthcare and medicines policy update that would have allowed certified advertisers to discuss opioid painkillers without promoting or selling them.
Why we care. This reversal affects advertisers in healthcare, public policy and addiction treatment sectors who were preparing for new advertising possibilities.
Key details:
- The original update was set for June.
- It would have allowed discussion of public policy solutions for opioid abuse.
- It required a new certification for advertisers.
What they’re saying. Google stated:
- “Due to implementation challenges, Google will be indefinitely pausing this policy update. We apologize for any inconvenience.”
Between the lines. The implementation challenges hint at potential complexities in verifying and monitoring certified advertisers.
The big picture. This policy shift and subsequent pause reflect the ongoing challenges in balancing public health discussions with responsible advertising practices.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
What’s next. Advertisers should continue to follow existing policies, which prohibit ads promoting or selling prescription opioid painkillers.
Bottom line. While the pause maintains the status quo, it also delays potential opportunities for legitimate discussions about opioid issues in advertising.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Tuesday, July 9th, 2024
There’s a new search strategy in town! Generative engine optimization (GEO), the younger sibling of search engine optimization (SEO), has arrived at the station.
There’s a good chance you’re already familiar – if you head to Google and ask it a question, you’ll likely see an AI-generated blurb at the top of your search results.
If you own a business and have spent time and resources vying for that top search position with SEO, this shift might be frustrating. Do you need to start all over again to optimize your content for this new type of search?
Good news: There’s no need to reinvent the wheel, but it is time to adjust strategy slightly.
Your existing SEO best practices will handle most of the heavy lifting, but there are a few clever shifts to make to stay visible, relevant and competitive.
Understanding generative engine optimization
Acronyms abound in the digital marketing world. What does this new one mean and why is it important going forward? Here’s what you need to know.
What is generative search?
Generative search relies on artificial intelligence (AI) to pull together information from multiple sources and compile unique, coherent responses to user queries.
With generative search, users receive AI summaries with direct answers at the top of their search results page instead of a traditional list of links.
When generative search results are accurate, they can save time and increase helpfulness for the end user.
For people creating internet content, however, this signals a slight shift. To get your content featured in that top-result AI summary, your content needs to be AI-ready.
The rise of generative engine optimization
Generative engine optimization is how you get AI-ready content.
GEO combines traditional SEO practices with an understanding of how AI models process and prioritize content. If you apply GEO principles well, your content will be poised for visibility in generative search engines such as Google’s AI Overviews and Microsoft Copilot.
Fortunately, best GEO practices don’t exclude human readers. You can (and should) write for both human and AI audiences – but more on that in a moment.
First: Why is it critical to focus on this now?
GEO is a brand-new concept and an area of AI use that’s getting understood and structured right now. That means there’s a lot of uncertainty surrounding the adoption of these strategies.
And there are a lot of opportunities for those who do adopt these strategies to stand out.
The upcoming shift in SEO practices
In a nutshell, traditional SEO relies heavily on keyword and backlink placement, good content structure and back-end technical site optimization.
Although these elements are and will remain important, it’s time to shine a spotlight on creative, authoritative and relevant content to succeed with GEO.
Your mission is to write content that is clearly helpful and well-structured so that both AI and human readers instantly understand the value you’re bringing to the table. That’s a big ask, but I have some practical tips to share.
Strategies for navigating generative search
Are you interested in being an early adopter of GEO best practices and taking advantage of this paradigm shift?
Start weaving these practices into your content creation routine.
1. Focus on content fluency and structure
Here’s a term to keep in mind: Fluency optimization. This trendy phrase boils down to keeping your content easy to read for robots and humans alike.
Here’s a quick checklist for accomplishing this:
- Make sure your content flows smoothly. Get rid of jargon and long sentences. (Reading your content out loud is an easy way to identify these!)
- Use clear headings and subheadings – often. Make these headings descriptive and down to earth.
- Use bullet points and lists. These break information down into easily digestible formats to improve readability.
Keeping your content organized and skimmable makes your information accessible for all readers, AI and otherwise. A clear, strategic content structure also makes it easier for you to stay on track.
Dig deeper: Mastering content quality: The ultimate guide
2. Leverage E-E-A-T principles
As you learn more about GEO, E-E-A-T is an acronym you’ll see often.
It stands for experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness.
The more you sound like a trustworthy, authoritative, experienced expert in your content, the more humans and AI want to read, remember and rank your pieces.
To do this, consider:
- Experience: Share personal anecdotes and case studies to demonstrate hands-on knowledge.
- Expertise: Cite reliable sources and include detailed, accurate information.
- Authoritativeness: Highlight credentials, awards or recognitions related to your field.
- Trustworthiness: Use clear language, avoid clickbait and ensure your content is free of errors.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
3. Optimize for both humans and AI
The Venn diagram of content that’s written well for both machine and human writers may be a circle. Keep your language structured and clear, with personable asides to delight human readers and crisp, to-the-point headers so robots can hone in on shareable information.
Your goal is to make it very, very easy for AI to extract key points for use in generative search and keep your content fun and valuable for humans to read.
This may seem like a tall order, but with consistency, structure and clarity, you’ll be well on your way.
Dig deeper: 25 tips to optimize your content for people and search engines
4. Consider using AI tools for content creation – at first
The thought may have already crossed your mind that if you’re writing for AI, at least in part, then using AI to write may be a strategic choice.
This depends on your familiarity with AI and your comfort as a writer. Relying on AI as an assistant for initial content outlining, brainstorming and even content analysis can be valuable. (It certainly helps with the hardest part of any project – getting started!)
One word of caution: Although AI can help you generate initial drafts or iterate engaging headers, you should still plan on editing, fact-checking and refining the content before publishing. For one thing, AI can make things up (or “hallucinate” information) and you wouldn’t want to put your readers or your own reputation at risk with false content.
In addition, it will become increasingly important to differentiate what you say from the growing mass of purely AI-generated content out there. (E-E-A-T, remember?)
Dig deeper: AI content creation: A beginner’s guide
The two things you need to remember for successful GEO
As you expand your experience with generative search techniques and tweak your content with GEO, two factors will help you succeed:
Why?
- Education will help you use AI better. Investing in AI training, staying up to date about generative search and keeping an eye out for the latest AI tips and tricks will help you (and your team!) get the most out of AI tools.
- Learning more about GEO will keep you ahead of the curve. This is brand-new tech and the best practices will likely shift over the coming months. Knowing about those shifts will help you take advantage of every single one.
- Regular training will reduce fear and boost adoption. If anyone on your team is leery of AI or GEO, that makes sense! These are big concepts to take in. Educate your team on the benefits of AI in content strategy, reinforce the idea that AI is a tool to enhance human talent (not replace it) and start with small, manageable AI integrations.
- Play the long game. Applying GEO techniques requires upfront labor in exchange for a delayed payoff. Remind yourself and your team that, even if progress seems incremental, it’s a critical strategy that will benefit your company with time.
- Balance your SEO and GEO efforts. GEO is not the end of traditional SEO! Continue to invest in technical SEO, keyword research and a backlink strategy. Your efforts will build off each other if you’re consistent, so make each a part of your ongoing content strategy.
Generative search is giving savvy business owners an opportunity to rethink online visibility. By investing in both GEO and SEO techniques, you can boost the relevancy and competitiveness of your content.
The main thing to remember is that your content needs to be high-quality, authoritative and relevant.
Write to your strengths and prioritize clear content structure, and you’ll be well on your way to winning the game with generative engine optimization.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Monday, July 8th, 2024
Google Ads is automatically upgrading Shopping and Performance Max campaigns from Country of Sale to Feed Label functionality to match Merchant Centre feeds, in August.
Why we care. This change affects how advertisers manage product feeds across different markets, potentially streamlining operations for multi-country campaigns.
Key details:
- Affects all campaigns using Country of Sale.
- No action is required from advertisers.
- Campaigns will continue to run without interruption.
- New campaigns can’t use Country of Sale after the change.
What it means. Feed Labels offer more flexibility in organizing products across geographic locations and language similarities.
First seen. We were alerted to this update via Navah Hopkin on LinkedIn, when she shared an email sent by Google:
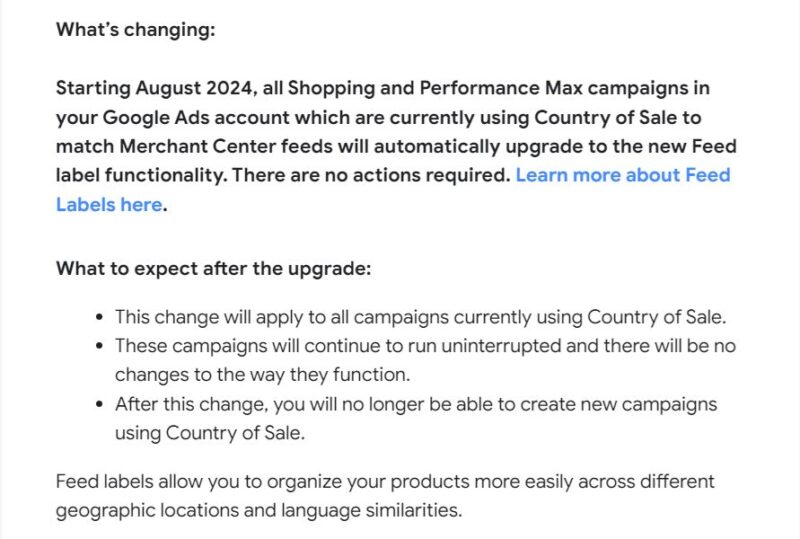
In her post, Hopkins said the update “will give you more control over how your shopping feeds and campaigns are managed in traditional shopping and PMax campaigns.”
The big picture. This shift reflects Google’s efforts to simplify campaign management for global advertisers.
What to watch. How this change impacts campaign performance and management efficiency for international ecommerce advertisers.
What’s next? Advertisers should familiarize themselves with Feed Labels functionality before the August rollout.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Monday, July 8th, 2024
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free gift from Google to SEO professionals that tells you how your website is performing.
With data-packed amenities, SEOs can scavenge through GSC to locate stashes of hidden nuggets like clicks and impressions from search queries, Core Web Vitals and whatever other surprises lay within your website.
Custom regex filters take you around your million-page website.
And while all SEO professionals hope to avoid any catastrophic SEO-related events with Google’s AI Overviews, all we can really do is be prepared.
For starters, keep reading this guide below to Google Search Console. It’s engineered to withstand zombie pages, panda claws and even penguin attacks, so it’s exactly what you need when the SEO industry gets dicey.
What does Google Search Console do? And how does it help SEO?
Google Search Console is a free website analytics tool Google provides. Google Search Console tracks your website’s performance in search results on Google.
As an SEO director, I use Google Search Console daily. I check website performance for content updates and troubleshoot any technical changes. It helps me make informed business decisions about where to dedicate my team.
How do I set up Google Search Console?
Getting set up on Google Search Console is quick and easy but may require technical support.
First, you need to have a Google account.
Next, go to Google Search Console: https://search.google.com/search-console.
If you don’t see any profiles listed, you’ll need to choose a domain or prefix URL and verify your website ownership.

How do you choose between domain vs. prefix URL? Let me walk you through the differences.
Domain property paints the full picture of your website
A domain property includes all subdomains but no protocols (HTTP:// or HTTPS://) and no path strings (/sub/folder/).
A domain property provides a holistic view of how your website is performing Google search results.
I recommend setting up domain properties first.
To set up a domain property in Google Search Console, remove the HTTPS and trailing slashes.

GSC website domain
After you hit continue, you can verify your ownership via DNS record through TXT files.
I recommend going this route as it is the easiest.
You’ll need to log into your hosting provider to submit the TXT file.
Another option is to verify through the CNAME. If you have technical support, this could be an easy alternative.
URL prefix property allows you to dissect sections of a site
A URL prefix property includes the HTTPS or HTTP protocol and path string. This means that if you want to really dive into a section of your website like /blog/ subfolder or a blog.website.com subdomain, you can do this.
After I set up my domain property, I set up individual URL prefix properties for each subdomain, HTTP versions and /blog/ subfolders.
By having multiple URL prefix properties, I can dig deeper into sections of the website to help troubleshoot.
I can also create reporting specific to the website’s sections that may be more relevant to my co-workers.
For example, I work with customer support team members looking for data on how their Help Center content is performing.
Key moments in history for Google Search Console
Some really crazy stuff has happened with Google Search Console over time. Google Search Console is notorious as a delicacy for many SEO professionals, an incessant phantom of manual actions and the culprit behind better understanding our website health.
I’ve compiled a short history of my SEO bromance with Google Search Console over the years to give you a glimmer of how we got here.
- June 2005: Google Webmaster Tools (now called Google Search Console) was launched.
- May 20, 2015: Google changed the name to Google Search Console from Google Webmaster Tools.
- June 21, 2016: Google Search Console tests new mobility usability report.
- Sept. 6, 2016: Google Search Console improves Security Issues report.
- Sept. 8, 2018: Google Search Console released Manual Actions report, “Test Live,” and request indexing features added for the URL inspection tool and upgraded to 16 months of historical data.
- Nov. 8, 2018: Google experiments with domain properties.
- June 26, 2019: Google Search Console adds mobile-first indexing features.
- May 27, 2020: Google Search Console adds Core Web Vitals report.
- Nov. 22, 2021: Google Search Console rolls out new design.
- Sept. 14, 2022: Google Search Console launches new HTTPS report.
- Nov. 16, 2022: Google Search Console adds Shopping tab listings feature.
- Sept. 11, 2023: Google Search Console rolls out new Merchant Center integrated reports.
- Nov.r 15, 2023: Google released a new robots.txt report.
- The future: New Google AIO reports will be coming soon!
Breakdown of Google Search Console for SEOs
While some SEO professionals may be waiting in the tunnels for Skynet and AIO to take over, there’s one thing we can all still depend on: Google Search Console.
So before you join your freelance mission with SEAL Team 6, walk through the anatomy of Google Search Console.
Overview
The Overview section in Google Search Console provides a bird’s eye view of all data sets users can uncover in Google Search Console.
Search Console Insights
If you click the top section under “Search Console Insights,” you’ll see a snapshot of the past 28 days.
It gives you a high-level overview of achievements you can share with your client or team.
Performance
The performance section is also called the “search results” section.
On my end, I only see this called “Performance” under some of my international sites, specifically in China.
Similar to the “search results” section found below, the “Performance” section showcases metrics like search traffic over time, search queries, search queries based on mobile devices and page performance.
URL inspection
The URL inspection tool lets you see what Google sees per URL.
The URL inspection tool is one of my favorite SEO tools.
Unfortunately, today, you can only inspect one URL at a time. However, if you use the Search Console URL inspection API, you can test up to 2000 URLs per day.
The test will show if the URL is indexable and explain why it may or may not be indexed.
You can also request a URL be indexed.
Search results
Search results are every content marketer’s favorite report in Google Search Console. It shows search traffic over the past 16 months (with comparisons) and search queries, devices, counties and search appearances.
It will also show you which pages are ranking for certain queries.
I leverage this report to show which pages are performing best vs. worst. It also helps troubleshoot if there are any major drops or spikes in traffic.
You can segment this report based on clicks, impressions and CTR.
Discover
The Discover report in Google Search Console showcases your content’s performance in Google’s Discover feed.
You can filter by pages, countries, search appearances and devices like the search results report.
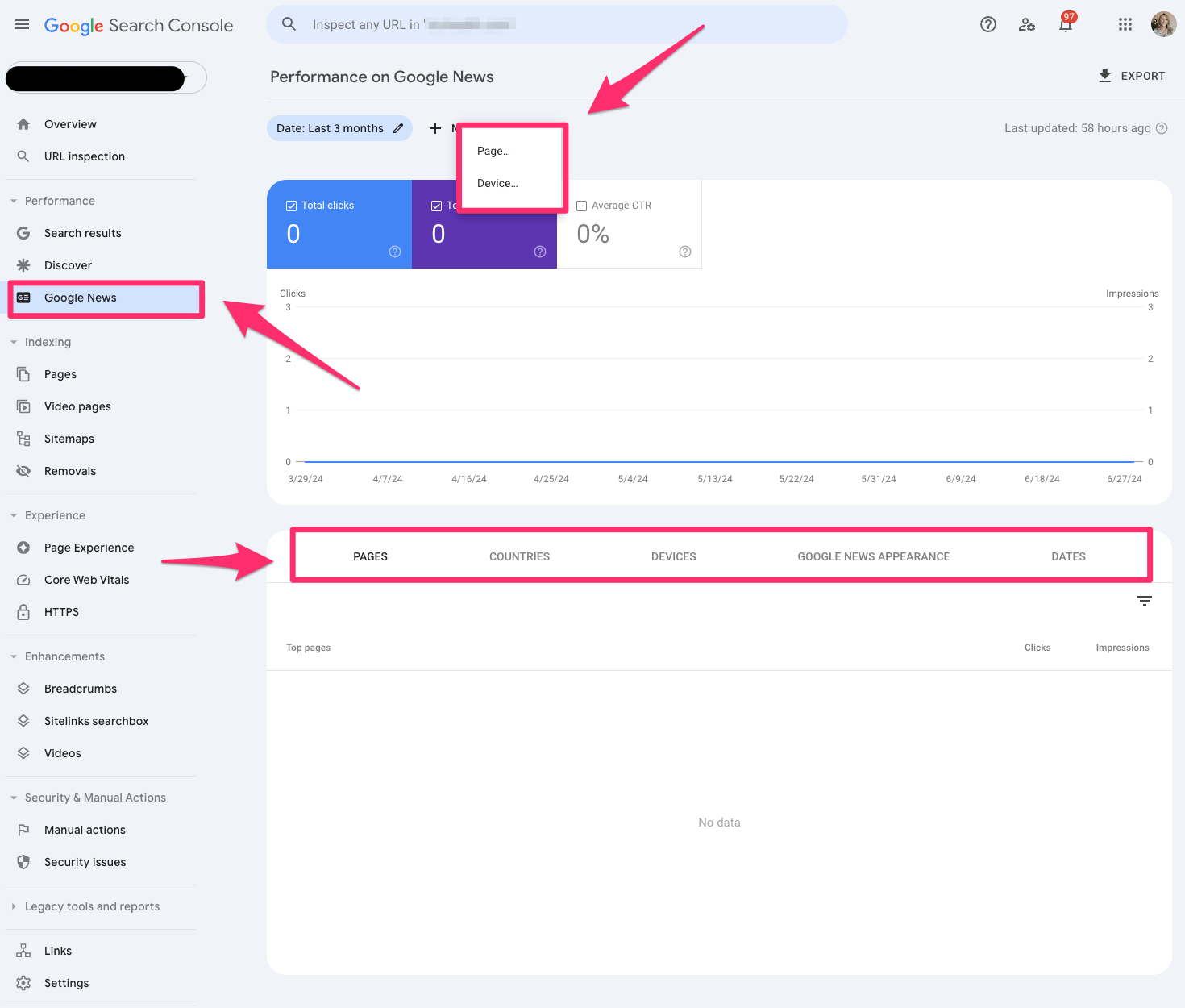
Google News
The Google News report in Google Search Console tells you how your content performs under Google News in Google search results.
You can filter the report by page and device.
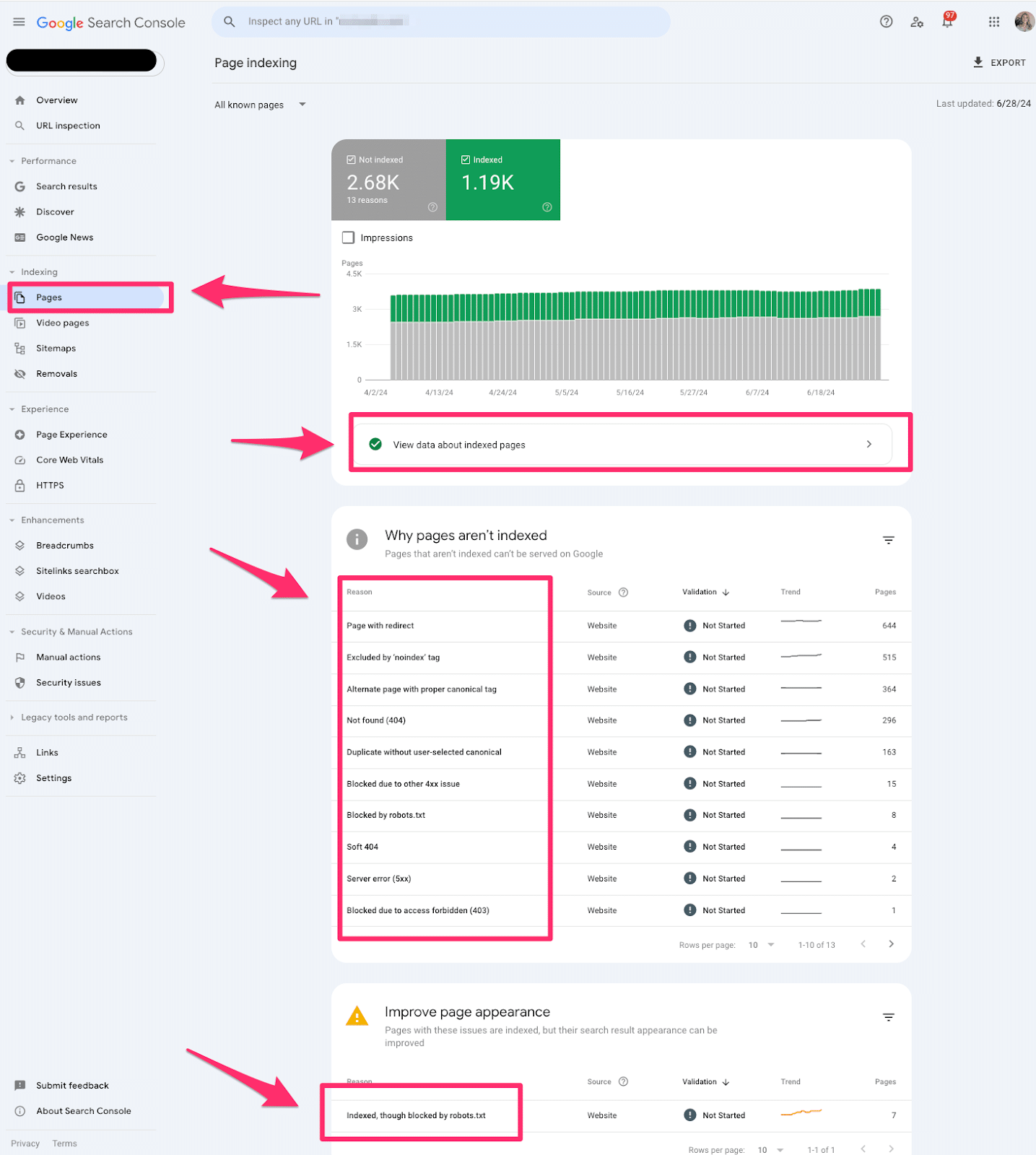
Pages
Pages indexing report in Google Search Console shares which pages in Google can find (or not find) on your website.
The Pages report is valuable for every technical SEO. This report offers tons of quick wins for technical SEO. I always like to start with this section when I’m auditing a website.
If you see an increase in pages indexed or not indexed, you’ll want to investigate why it’s happening.
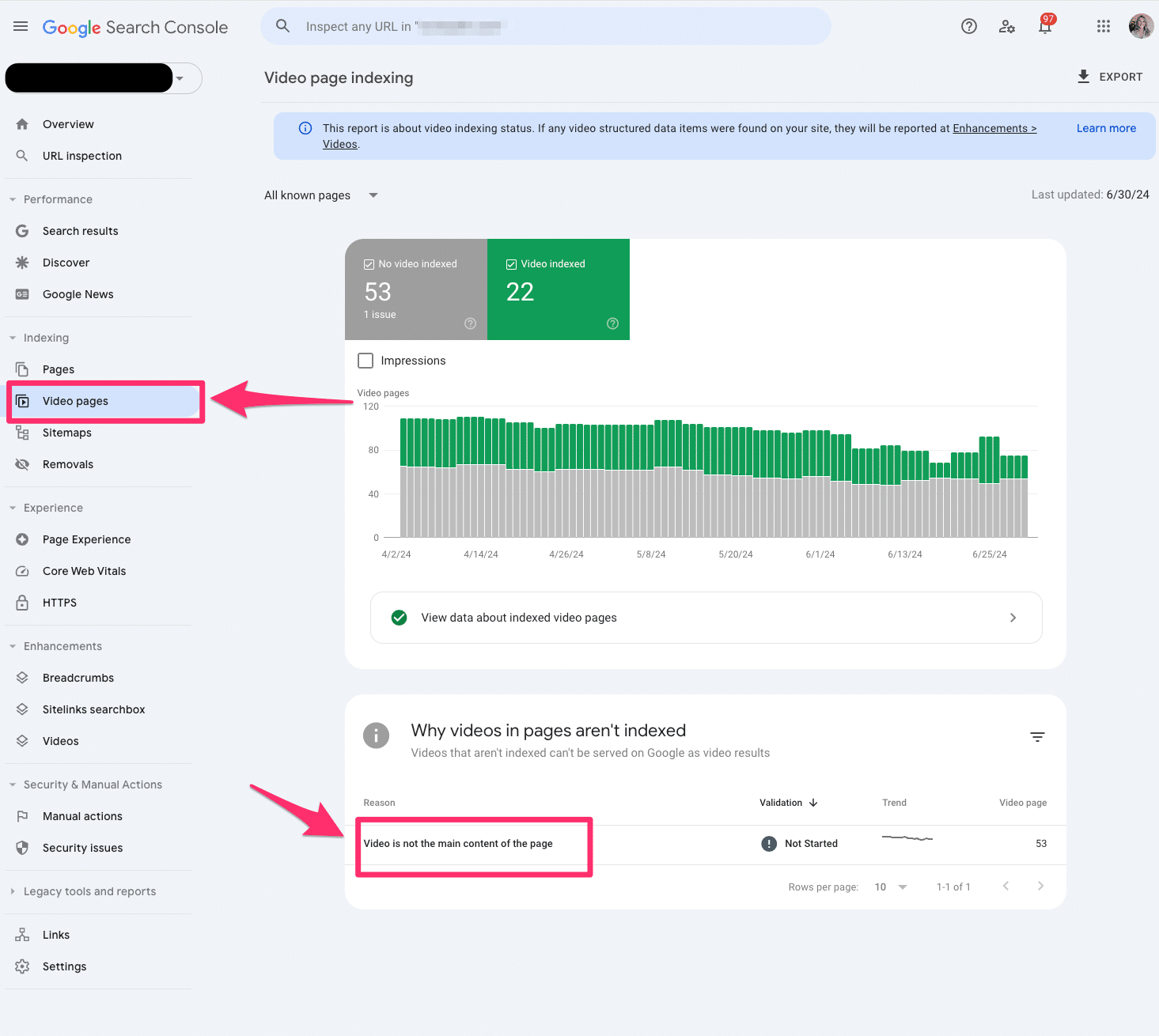
Video pages
The video indexing report displays how many pages on your website are indexed with video content somewhere on the page.
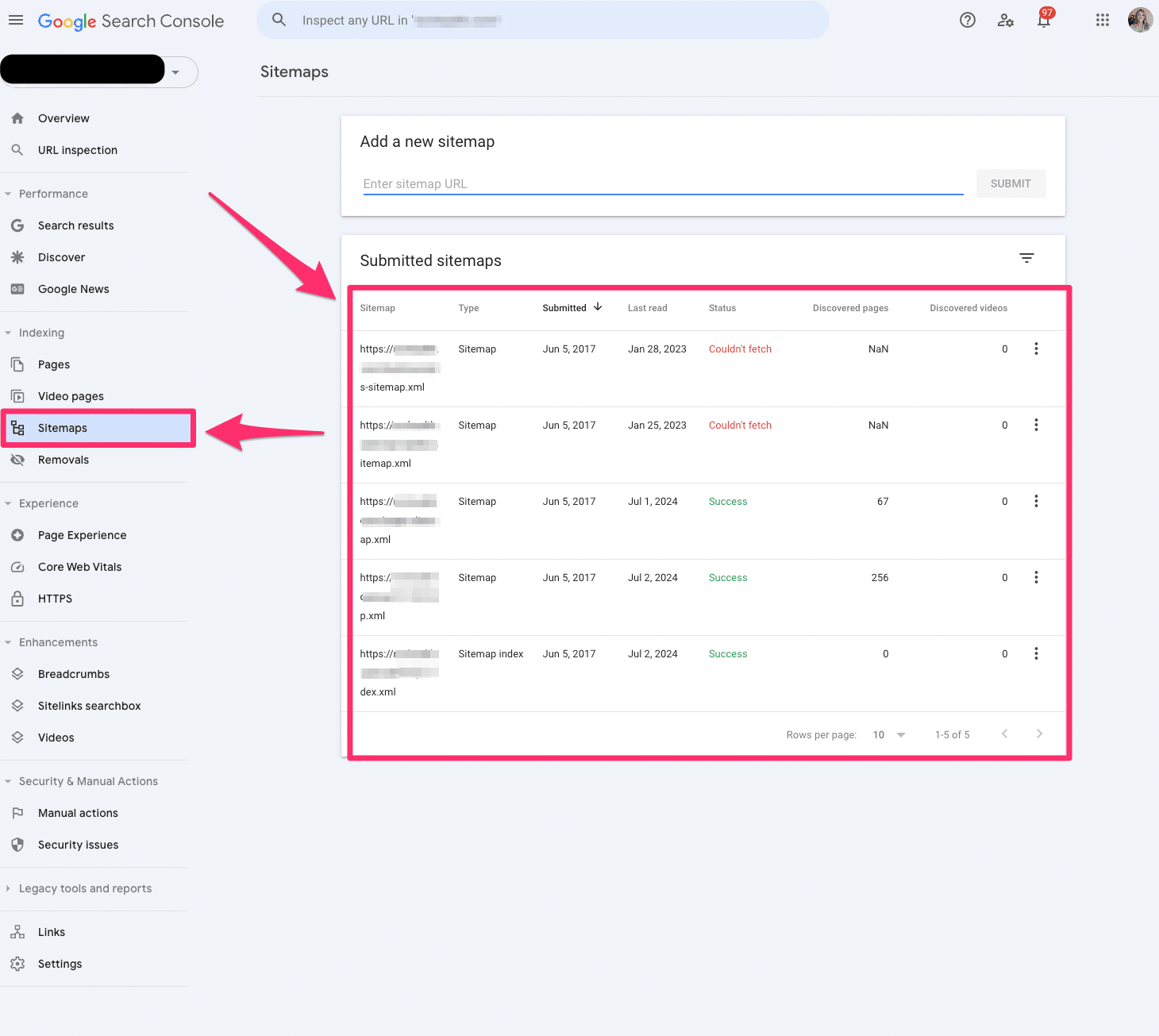
Sitemaps
The sitemap report allows you to submit all your XML sitemaps to Google Search Console. Ideally, you have at least one XML sitemap to submit.
You’ll have to submit all your XML sitemaps if you have video, image, or language-specific XML sitemaps.
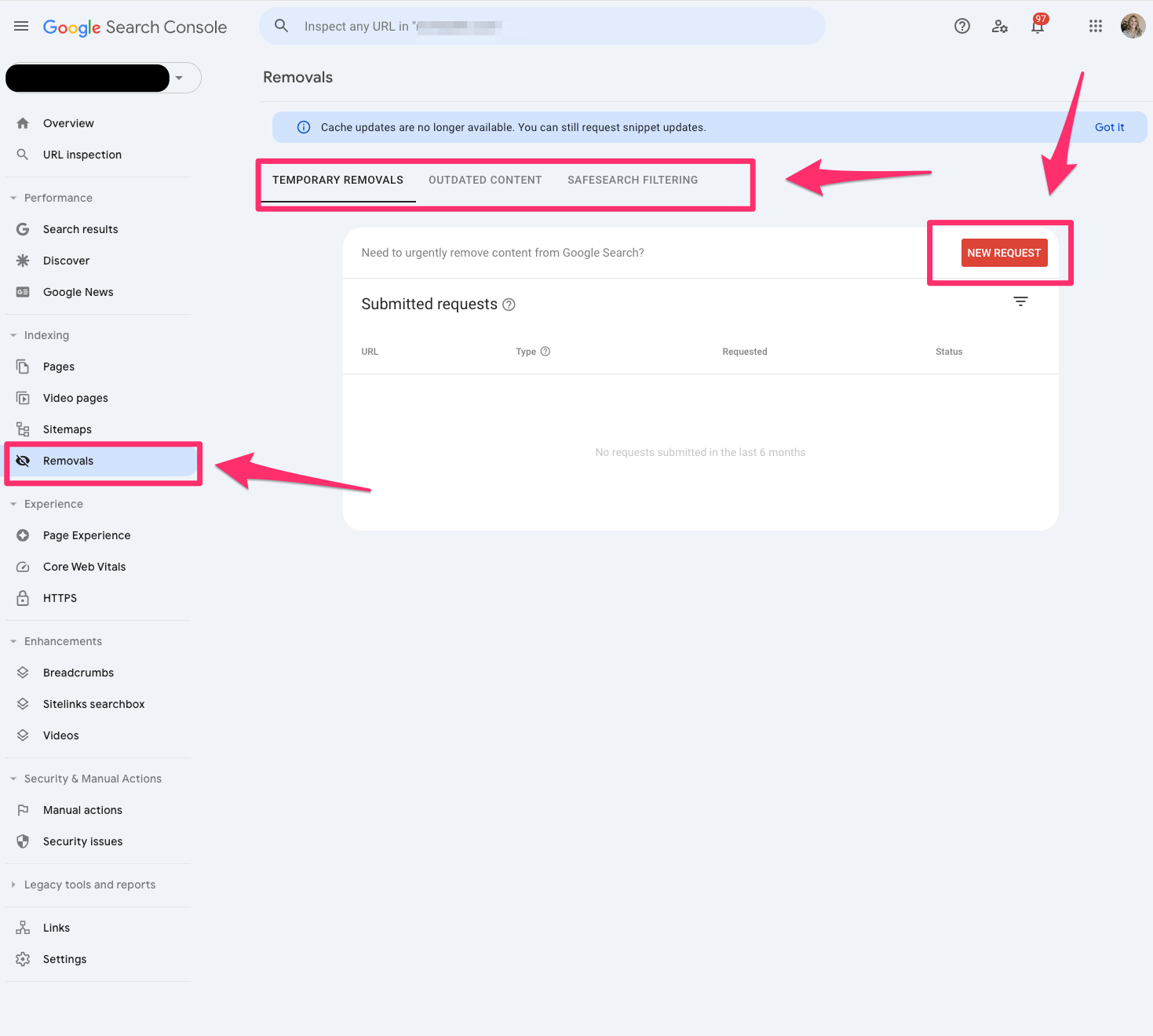
Removals
The removals tool in Google Search Console allows you to block pages from Google temporarily.
Remember, these must be pages that you own on your website. You cannot submit pages you do not own.
This is the fastest way to remove a page from your website. However, I recommend working on a long-term solution if you want this web page permanently removed.
Page Experience
The Page Experience report in Google Search Console provides a glimpse of how user experience is on your website.
It’s important to remember this is based on URL level.
The page experience report includes Core Web Vitals and HTTPS usage.
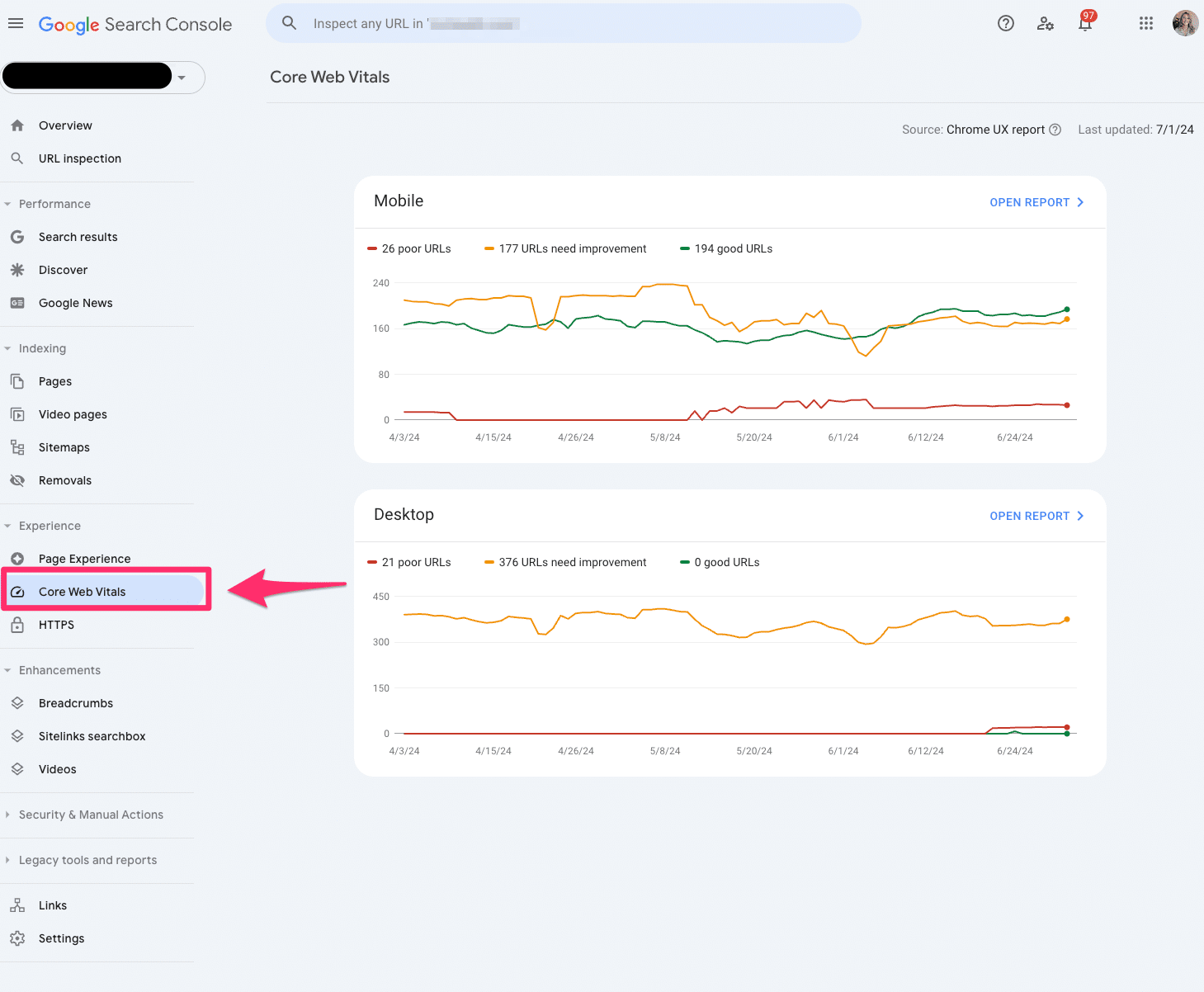
Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals report uses real-world data to tell you how your pages perform.
Again, this is based on a URL level.
The report is grouped into mobile and desktop with segments of poor, needs improvement and good.
The report is based on LCP, INP and CLS user data.
Only indexed pages will be included in the Core Web Vitals report.
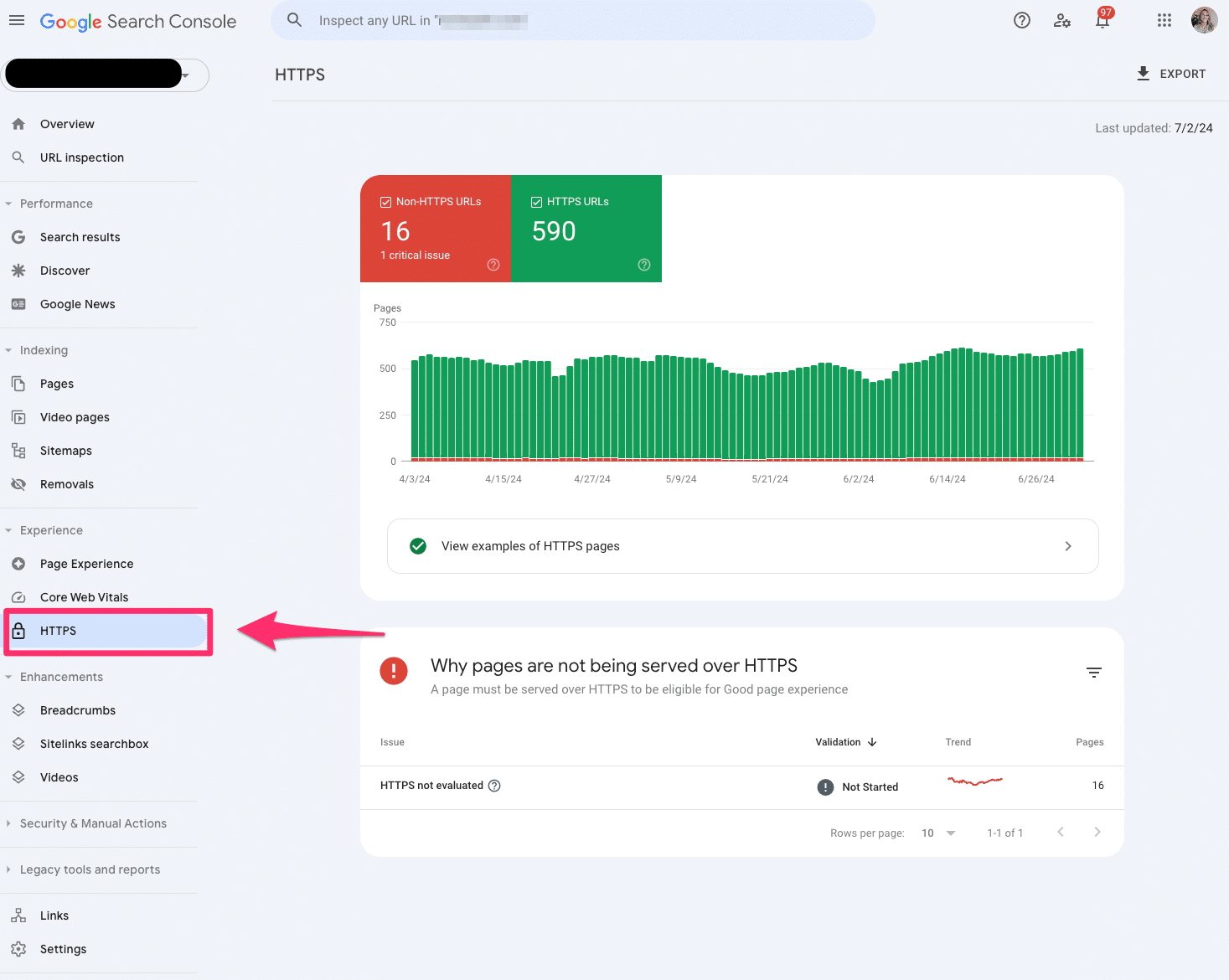
HTTPS
The HTTPS report tells you how many indexed pages on your website are HTTP or HTTPS.
If you notice any HTTP pages on your website, you should convert them to HTTPS. Google indexes the HTTPS version to protect searchers’ security and privacy.
Product snippets
Product snippets are part of the structured data reporting in Google Search Console that showcases which products have product markup on the page.
Currently, Google only supports product snippets for pages with one product.
Be aware of Google’s algorithm updates; there can be changes in impressions and clicks for product snippets.
Merchant snippets
Merchant snippets are also part of the rich result report in Google Search Console and serve as extensions of your Product snippet.
Merchant snippets are like getting a golden ticket. It provides more enhanced features in the SERPs like carousels or knowledge panels.
Shopping tab listings
Shopping tab listings are also part of the rish result reports in Google Search Console and showcase the pages listed in the Shopping tab in Google search results.
If you’re an ecommerce marketer, you’ll want to live inside this report.
Pro tip: If you don’t see this information in Google Search Console, make sure your website’s structured data fits within the Merchant listing structured data requests.
AMP
The AMP report in Google Search Console shows all the AMP pages on your website and potential issues you may need to troubleshoot.
If AMP is a big part of your SEO strategy, you’ll want to ensure you reach zero in the critical errors section of the report so Google can detect your AMP pages.
Breadcrumbs
The breadcrumbs report is also part of the rich result report in Google Search Console, which tells you if your breadcrumb structured data is correct and readable by Google.
Breadcrumbs are essential to maintain a healthy site architecture and user experience. If you see any errors in the breadcrumbs, I recommend prioritizing this quickly.
FAQ
The FAQ report is also part of Google Search Console’s rich results report, which shares insights into which pages received the FAQ snippet.
However, with Google’s changes to visibility of HowTo and FAQ rich results, you may see this fluctuate quite a bit.
Profile page
The Profile page report reflects which pages are getting the profile page markup. You’ll want to validate and clean up any makeup you may be missing because these offer interesting SERP features.
It’s almost like a card functionality similar to the recipes.
Review snippets
Review snippets showcase your validation of review markup on pages.
You should check that all your markup is valid. If you notice any errors, work on updating those specific pages.
With Google’s algorithm updates, I’ve seen significant fluctuations in review snippets. Always double-check if it’s a bug, algorithm update or a true markup error.
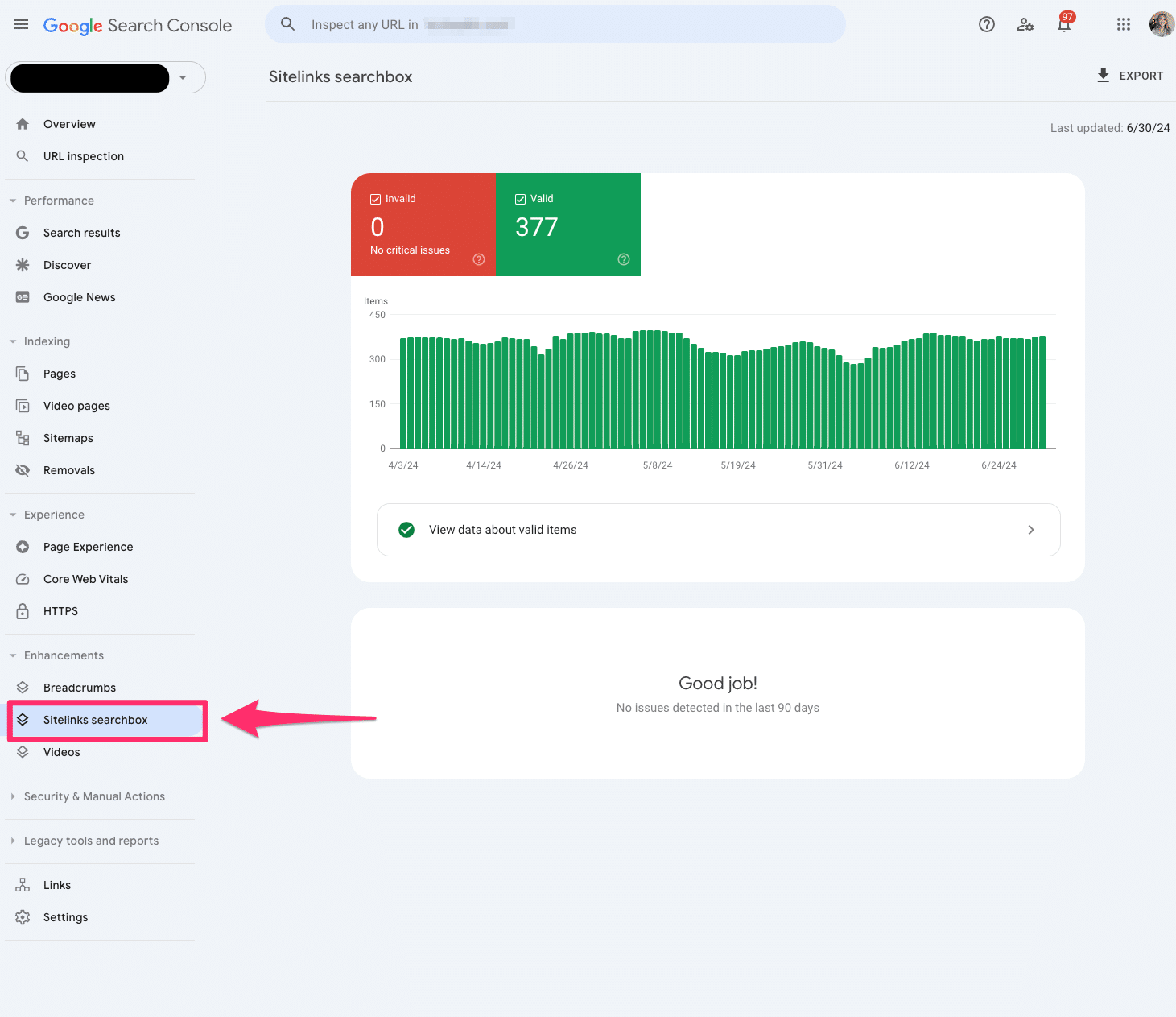
Sitelinks searchbox
The sitelinks searchbox is a feature of the rich result report in Google Search Console that tells us in more detail any errors you may have to your Sitelinks Searchbox markup.
Unparsable structured data
The unparsable structured data report in Google Search Console aggregates structured data syntax errors that prevent Google from identifying the specific structured data type.
Videos
The video indexing report in Google Search Console has expanded dramatically over the last few years, giving us more detailed information on how your videos perform in search results.
You can dissect whether the video is outside the viewport, too small or too tall. If you’re building a video content strategy, it really helps to elevate your game with your UX team.
Manual actions
If you’re running your SEO strategy properly, you’ll hopefully never have to worry about the manual action report.
But if you’re one of the unlucky ones who gets hit with a manual action, Google will tell you in this report in Google Search Console.
A manual action occurs when a human reviewer at Google determines that a specific page or pages are not compliant with Google’s spam policy.
Security issues
The Security issues report in Google Search Console will tell you if your site was hacked or harmful.
Google now emails you to notify you when you receive a security issue.
Check out this beauty I received within the first week of starting to work on a new site.
Links
The Links report in Google Search Console allows you to view all your site’s internal and external links. You can view the top link pages, top linking sites and top linking text.
This is a legacy report, so I’d be cautious about relying on it in case Google decides to depreciate it.
Settings
If you need to verify ownership or add a new user, you should check the settings in Google Search Console.
Two cool reports under Settings in Google Search Console go undiscovered, but these are two of my favorite reports.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt report tells us which pages Google can crawl or any potential issues preventing Google from crawling your site.
One of the challenges I run into when working with developers is that they often choose to disallow it in the robots.txt file instead of adding a noindex, nofollow tag.
This report will help audit any technical updates with your dev team.
The robots.txt report is only available if you set up a domain property.
Crawl stats
The crawl stats report shows Google’s crawling history on your website. It can be sorted by how many requests were made and when, server response and availability issues.
It tells SEO professionals if Google is encountering problems when crawling your website.
This report is only available if you have a domain property or a URL prefix at a root level.
Unlocking the power of Google Search Console for better SEO
That’s a lot to unpack. But the gist is that Google Search Console is a place that helps you better understand how your website is performing.
All of the above is just part of the early phases of Google Search Console’s transformation. Google also hopes to add Google’s AI Overviews data in the future. That seems like a worthwhile endeavor, seeing as no tool supports AIO data today.
And I know you all must be hoping Google’s AI Overviews don’t overtake your jobs.
But in the insane event it does, at least you’re covered on how Google Search Console got here today.
Until then, you’ll have to make do with luxe URL inspections, regex filters and manual action surprises.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing
Monday, July 8th, 2024
The EU sent Amazon a new request for information (RFI) on Friday, focusing on the ecommerce giant’s recommender systems, advertising transparency and risk assessment measures.
- This is Amazon’s third RFI since being designated a very large online platform (VLOP) under the DSA.
- The company must respond by July 26.
Why it matters. The European Commission’s latest request for information (RFI) to Amazon signals intensifying oversight of big tech under the Digital Services Act (DSA), potentially leading to hefty fines for non-compliance.
Details. The EU is seeking information on:
- Transparency of Amazon’s recommender systems.
- Design and implementation of its ad repository.
- Risk assessment reporting.
Why we care. The EU’s focus on recommender systems could lead to more transparency in how ads are displayed and targeted on Amazon’s platform. This may provide advertisers with:
- Better insights into ad performance.
- More clarity on how their ads are being served to consumers.
- Potentially fairer competition in ad placement.
The big picture. The DSA aims to regulate digital services and protect users from online harms, with stricter rules for larger platforms like Amazon.
Between the lines. The Commission’s focus on these areas suggests concerns about the potential societal impact of AI-driven systems and the need for greater transparency in digital advertising.
What they’re saying. Amazon stated it’s “working closely with the European Commission” and shares the goal of creating a “safe, predictable and trusted shopping environment.”
What to watch. The EU’s response to Amazon’s information could lead to a formal investigation, with potential fines up to 6% of global annual turnover for DSA violations.
Courtesy of Search Engine Land: News & Info About SEO, PPC, SEM, Search Engines & Search Marketing